Search Results
Results for: 'sheath cells'
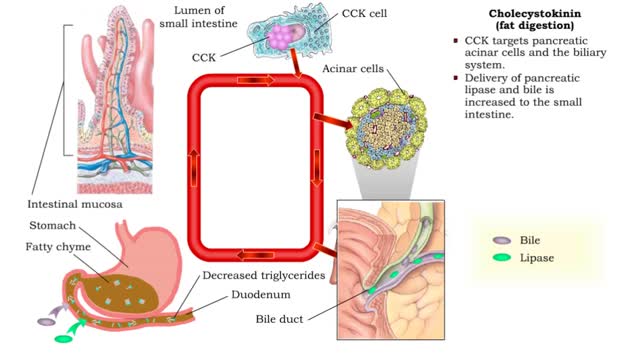
Secretin (inhibiting gastric acid secretion), Cholecystokinin (fat digestion) & Cholecystokinin
By: HWC, Views: 10421
• As chyme approaches the small intestine, secretin also targets acid-producing parietal cells in the gastric mucosa. • Increased secretin inhibits gastric add secretion. • With less gastric acid produced, the chyme going into the intestine is less acidic. • The hormone CCK also reg...
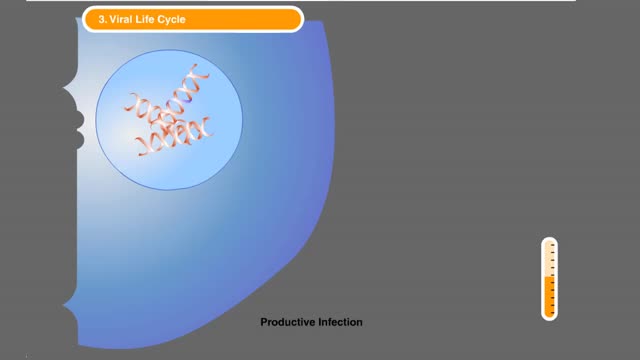
HIV Infection: Viral life cycle
By: HWC, Views: 9960
The series of steps that HIV follows to multiply in the body. The process begins when HIV encounters a CD4 cell. The seven steps in the HIV life cycle are: 1) binding; 2) fusion; 3) reverse transcription; 4) integration; 5) replication; 6) assembly; and 7) budding. Many viruses f...
Natural Selection, Species Isolation and Real World Example
By: HWC, Views: 9994
`Natural selection' is the process in which organisms with adaptive traits survive and breed in greater number than organisms without such traits. Eventually, almost all of the individuals in the population will have the same adaptive trait. This was the concept presented by Charles Darwin in ...
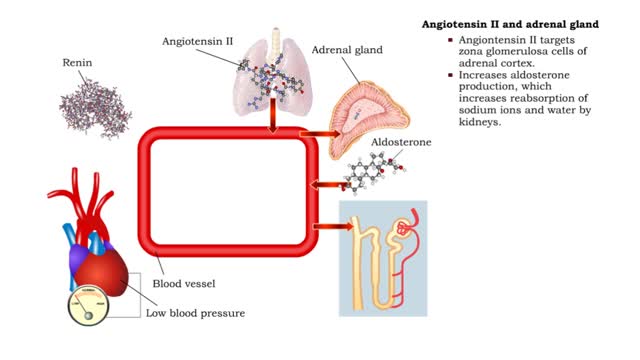
Angiotensin II - kidneys, adrenal glands and dehydration
By: HWC, Views: 10604
• Angiontensin II targets cells in the proximal convoluted tubule of the nephron. ■ The reabsorption of Na+ and Cl- ions sets up an osmotic gradient favoring the retention of water. • Decreases urine production and increases blood volume and pressure. • Angiontensin II targets zon...
By: Administrator, Views: 13871
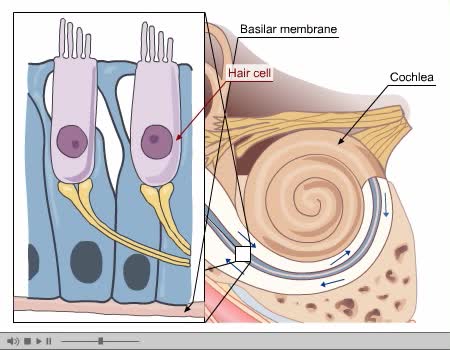
Process of Hearing Sound waves are directed to the eardrum, causing it to vibrate. These vibrations move the three small bones of the middle ear (malleus, incus, and stapes). Movement of stapes at oval window sets up pressure waves in the perilymph and endolymph. Process of Hearing The wav...
Role of the urinary system - acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 10701
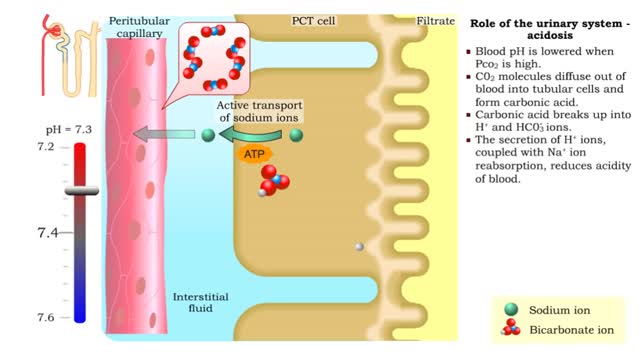
• Tubular cells of the proximal convoluted tubule and collecting tubules can alter filtrate pH and therefore blood pH. • These cells can affect blood pH with two coupled mechanisms: • Reabsorption of bicarbonate ions. • Secretion of hydrogen ions. • The reabsorption of bicarbonate...
Endocytosis -Types and Phagocytosis
By: HWC, Views: 10605
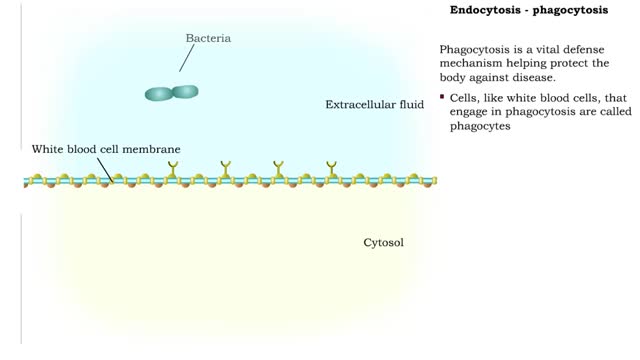
Endocytosis is the process by which a substance is brought inside a cell without having to pass through the cell membrane. It is the opposite of endocytosis, the process by which substances exit the cell without having to pass through the cell membrane. Exocytosis – membrane-enclosed secret...
Regulation of GFR: three methods, autoregulation & autoregulation via myogenic mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 11058
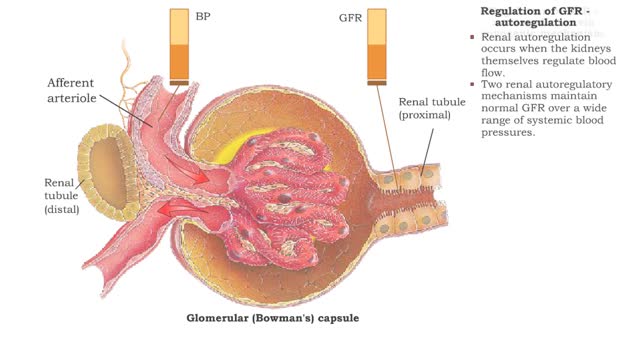
• GFR can be regulated by adjusting: • Blood flow in and out of the glomerular capillaries. • Surface area of glomerular capillaries. • There are three main ways to make these adjustments: • Renal autoregulation. • Nervous regulation. • Hormonal regulation. • Ren...
Neuron structure and function - sensory neurons, association neurons & motor neurons
By: HWC, Views: 10495
• The primary function of the nervous system is to provide rapid communication within the body to maintain homeostasis. • This function underlies behaviors, thinking and control of organ functions. • The basic functions of the nervous system are provided by: • Sensory neurons • ...
Advertisement