Search Results
Results for: 'How atoms bond? Bond in biological molecules'
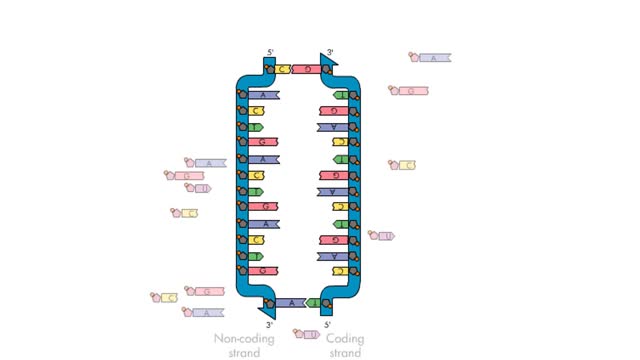
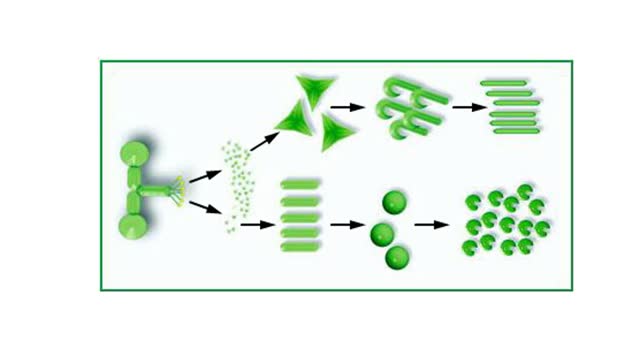
Transcription—A molecular view
By: HWC, Views: 3316
Transcription, as related to genomics, is the process of making an RNA copy of a gene's DNA sequence. This copy, called messenger RNA (mRNA), carries the gene's protein information encoded in DNA. During transcription, a DNA molecule is copied into RNA molecules that are then used to translate...
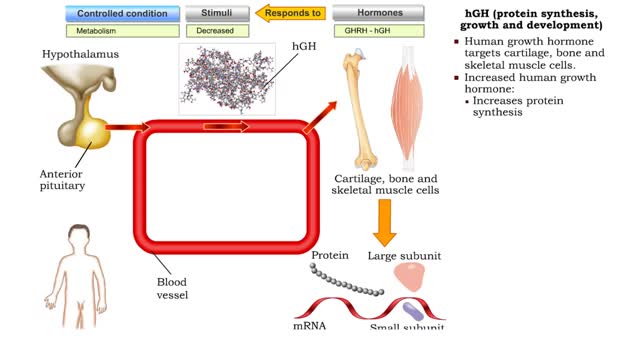
hGH (protein synthesis, growth and development)
By: HWC, Views: 8108
• Increased GHRH, a hypothalamic releasing hormone stimulated by low blood glucose, physical exertion, and increased sympathetic stimulation, stimulates the production of human growth hormone (hGH) from the somatotrophic cells of the anterior pituitary. • Human growth hormone targets cartil...
By: HWC, Views: 1669
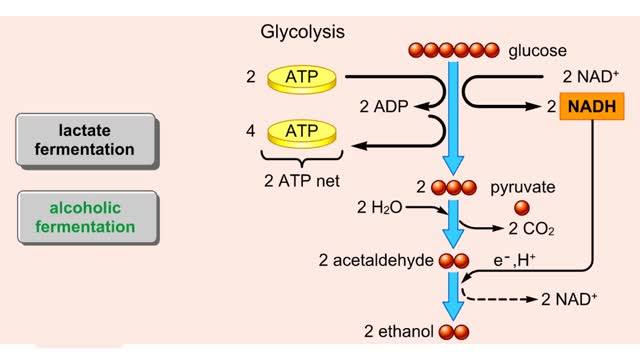
Both lactate fermentation and alcoholic fermentation begin with pyruvate formed by glycolysis. During lactate fermentation, pyruvate molecules accept electrons and hydrogen from NADH. This transfer regenerates NAD± and converts pyruvate to lactate. The net energy yield is the two ATP...
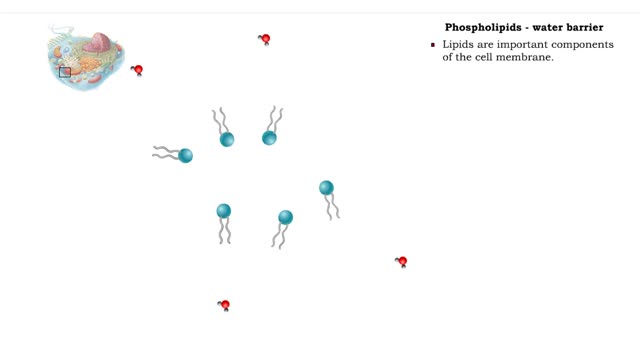
Non-polar compounds - insolubility
By: HWC, Views: 7848
• A non-polar molecule has uniform distribution of electrons. • Non-polar compounds like fatty acids in lipids have a high proportion of carbon and hydrogen. • Lipids possess no charge or partial charge. • Lipids are not attracted to water molecules. • Lipids are not soluble in...
By: HWC, Views: 4488
Formation of membrane attack complexes. Complement proteins can activate when they bind to antibodies that are bound to a pathogen. Complement proteins also activate when they bind directly to bacterial surfaces. Cascading reactions yield huge numbers of different types of complement protei...
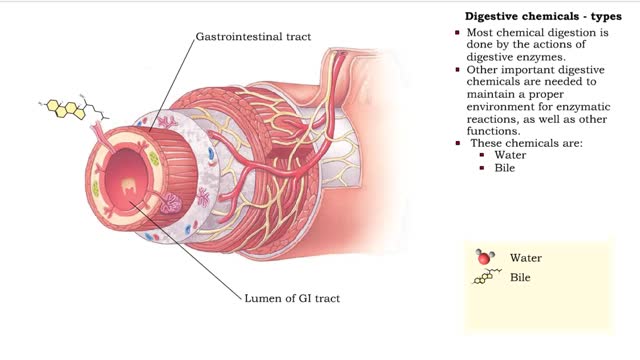
Digestive chemicals - types & enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 7708
• Chemical digestion breaks down food as it moves through the digestive tract. • Using enzymes and other digestive chemicals, the process reduces food particles into nutrient molecules that can be absorbed. • Most chemical digestion is done by the actions of digestive enzymes. • O...
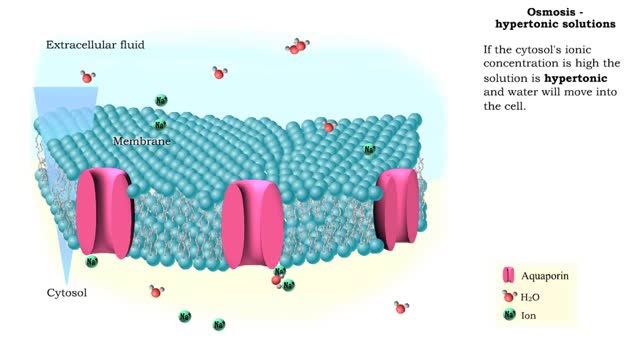
Osmosis - Isotonic, Hypotonic, and Hypertonic Solutions
By: HWC, Views: 7828
Isotonic: Equal Water moves in and out of the cell at an equal rate. The cell remains unchanged. Hypotonic: "hypo" hippo Water moves into the cell, making it swell and get fat (like a hippo). Eventually the cell can rupture and burst (aka lyse). Hypertonic: "like a raisin" Water leaves...
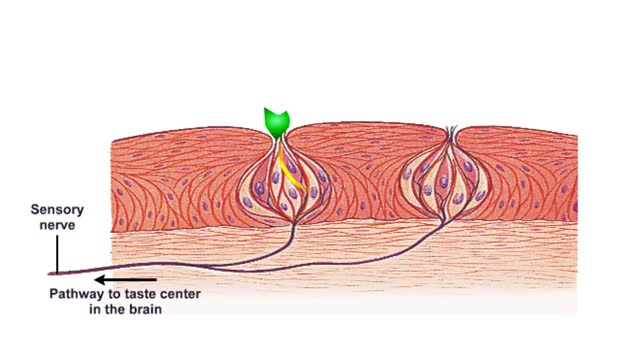
What are Taste Receptors? How Does it Work? Animation
By: HWC, Views: 4602
Do you ever wonder how you can taste the foods you eat? It all starts with taste receptors in your muscular tongue. Taste receptor neurons are found in your taste buds but you are not looking at the taste buds. The raised bumps on the surface of the tongue that you see are specialized epith...
By: Administrator, Views: 10690
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell. Synapses are essential to neuronal function: neurons are cells that are specialized to pass signals to individual tar...
Advertisement