Search Results
Results for: 'How atoms bond? Bond in biological molecules'
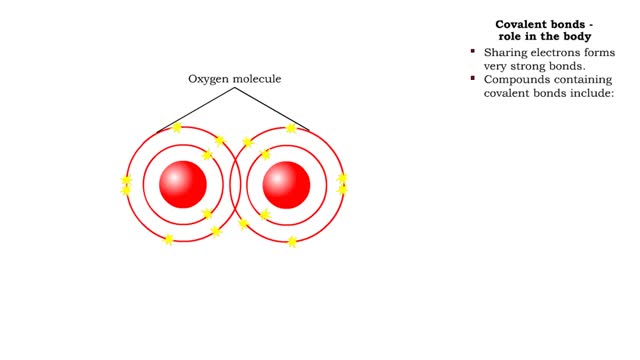
Covalent bonds - role in the body
By: HWC, Views: 7703
A covalent bond is formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. This is opposed to an ionic bond, where electrons are actually transferred from one atom to another. Formation • Atoms fill up the outer orbital by sharing electrons. • Two oxygen atoms sharing electrons form on...
By: HWC, Views: 7598
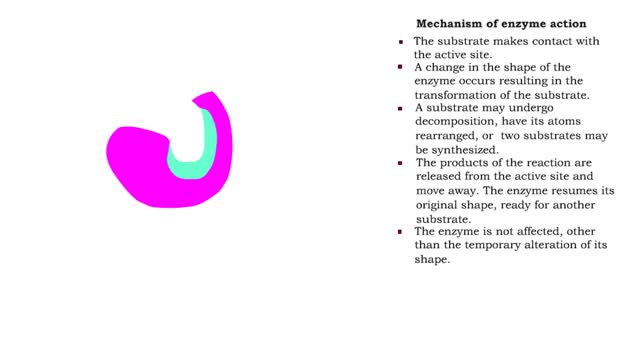
■ The substrate makes contact with the active site. ■ A change in the shape of the enzyme occurs resulting in the transformation of the substrate. ■ A substrate may undergo decomposition, have its atoms rearranged, or two substrates may be synthesized. ■ The products of the reaction...
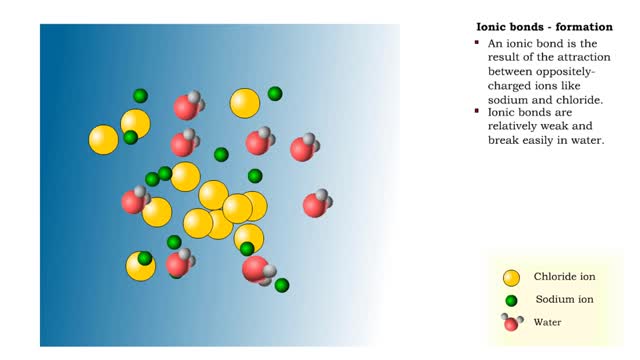
Ionic bonds - role of ions in the body
By: HWC, Views: 7915
Ions • Atoms fill up the outer orbital by transferring electrons from one atom to another. • Atoms now bear a charge and are called ions. • Sodium ion, losing an electron, has a +1 charge. • Chlorine ion, gaining an electron, has a -1 charge. Formation • An ionic bond is t...
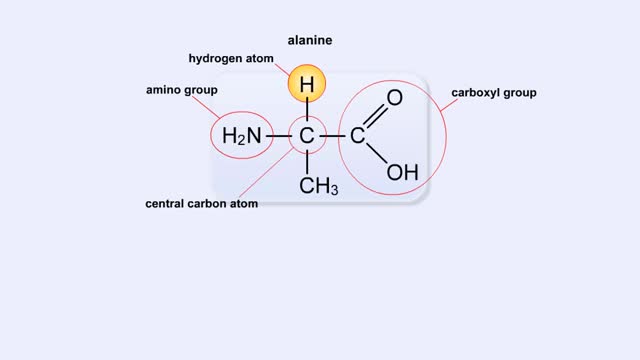
Structure of Amino Acid, Peptide Bonds & Polypeptides
By: HWC, Views: 7205
Here are the molecular formulas of three different amino acids. All amino acids share this backbone. The main difference between every amino acid is the side groups seen here, and these side groups give each of the amino acids their different characteristics. But before we get into that, let's ...
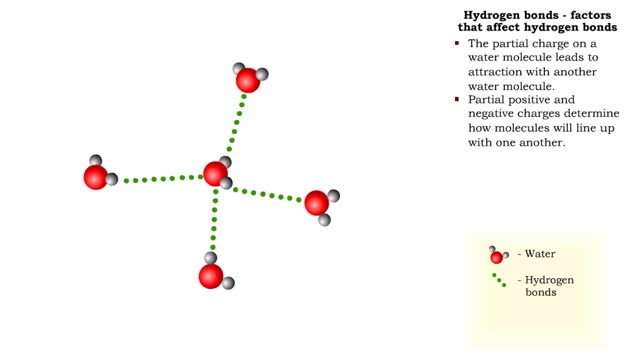
Hydrogen bonds - role in the body
By: HWC, Views: 8017
A hydrogen bond is the electromagnetic attraction between polar molecules in which hydrogen is bound to a larger atom, such as oxygen or nitrogen. This is not a sharing of electrons, as in a covalent bond. Instead, this is an attraction between the positive and negative poles of charged atoms. ...
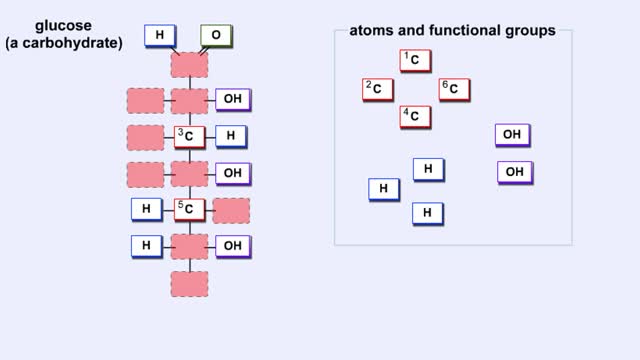
What Are Carbohydrates? Importance of Carbs & High Carb Food
By: HWC, Views: 7816
We hear a lot about carbohydrates in the news. Everybody seems to be on a low-carb diet. The news media often has stories on this diet fad, and companies are busy producing products with reduced carbohydrates. What's this fascination with carbohydrates? In a word: "Diet." The fact is that carb...
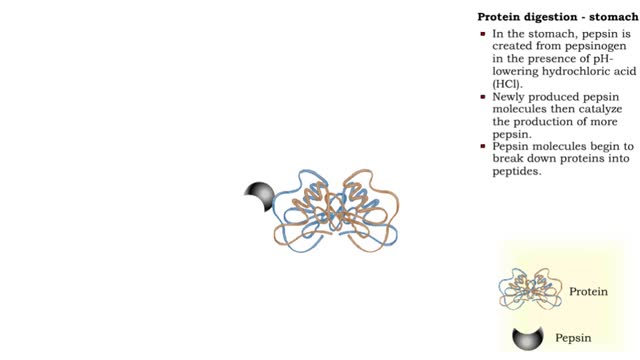
Protein digestion - stomach & small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 7193
• Protein digestion occurs in the stomach and small intestine. • The stomach enzyme pepsin initiates the process. • Pancreatic and intestinal brush border enzymes complete the digestive process. • In the stomach, pepsin is created from pepsinogen in the presence of pH-lowering hyd...
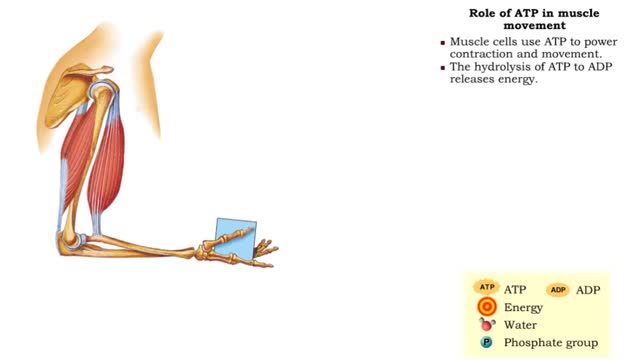
Role of ATP in muscle movement
By: HWC, Views: 7819
• Muscle cells use ATP to power contraction and movement. • The hydrolysis of ATP to ADP releases • ATP can be regenerated by adding to ADP. • During muscular contraction, ATP molecules: • Energize the myosin head • Detach myosin from actin • ATP must be then regenerat...
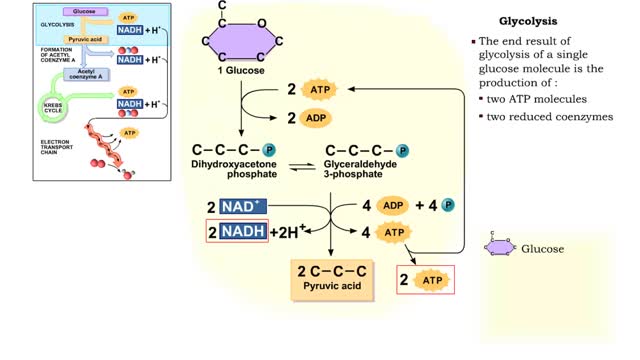
By: HWC, Views: 7984
The first reactions involve a single 6-carbon glucose sugar undergoing phosphorylation using two ATP molecules and resulting in two 3-carbon compounds. • The rest of this pathway involves an oxidation reduction reaction, forming two reduced coenzymes, and generation of four ATP molecules. ...
Advertisement