Search Results
Results for: 'Blood colloid osmotic pressure (BCOP)'
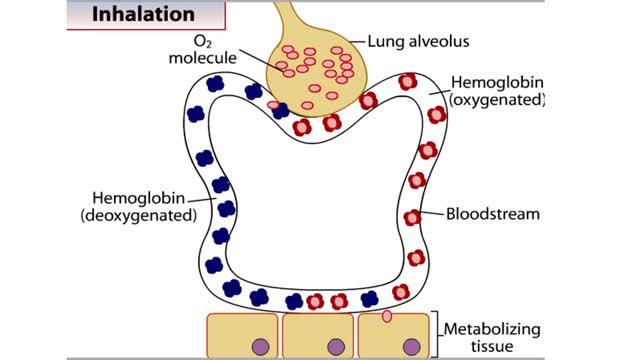
How Hemoglobin Picks Up and Delivers Oxygen
By: HWC, Views: 10373
All of the cells in our bodies require oxygen (02) for survival and must release carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste product. The respiratory and circulatory systems work together as delivery systems for these gases. The lungs exchange these gases between the environment and the bloodstream. The bloo...
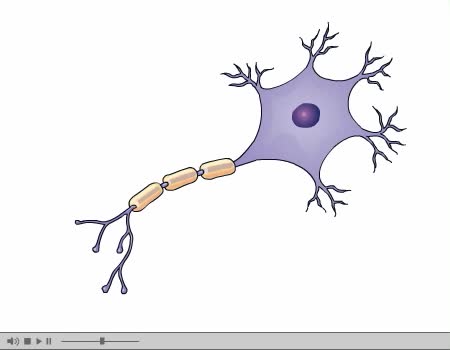
Nerve Impulse Transmission Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14441
How nerves transmit impulses. Stimulation of a nerve occurs at a receptor. Sensory receptors Specialized to specific types of stimulation such as heat, cold, light, pressure, or pain. React by initiating a chemical change or impulse. All-or-none principle Means that no transmission occ...
By: Administrator, Views: 14022
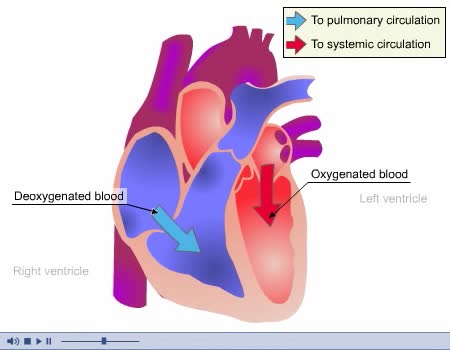
Prior to atrial systole, blood has been flowing passively from the atrium into the ventricle through the open AV valve. During atrial systole the atrium contracts and tops off the volume in the ventricle with only a small amount of blood. Atrial contraction is complete before the ventricle begins...
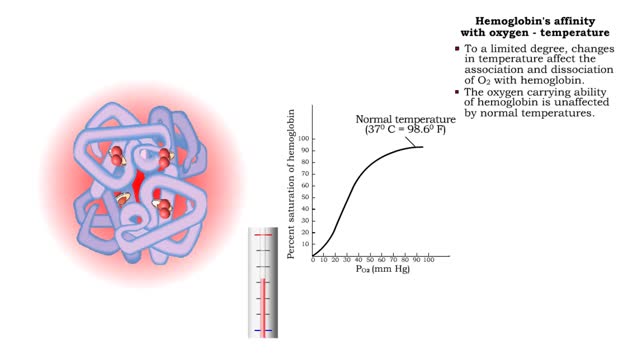
Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen - carbon dioxide, temperature and bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
By: HWC, Views: 10970
• The carbon dioxide gas is temporarily converted to carbonic acid in red blood cells by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, and then further converted to hydrogen and bicarbonate ions. • The result of increased carbon dioxide is decreased pH causing the Bohr effect. • Elevated carbon dioxid...
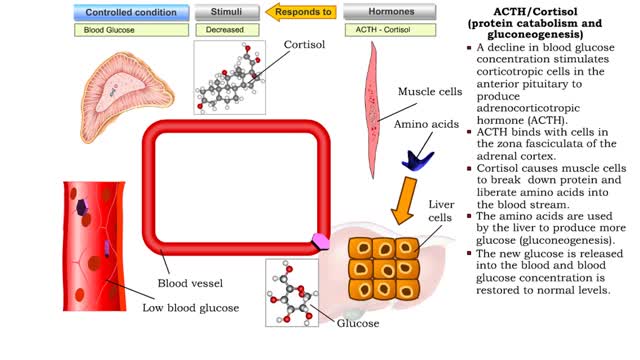
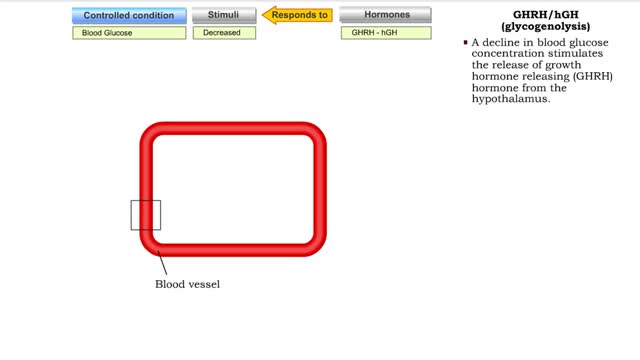
ACTH/Cortisol (glycogenolysis, protein catabolism, lipolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 10871
• A decline in blood glucose concentration stimulates corticotropic cells in the anterior pituitary to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). • ACTH binds with cells in the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex. • Increased ACTH promotes the production of cortisol, the major gluco...
By: Administrator, Views: 797
Arteries A branching system of vessels that transports blood away from the heart to all body parts. All arteries have a pulse, reflecting the rhythmical beating of the heart. Arteries Certain points are commonly used to check rate, rhythm, and condition of the arterial wall. Most commonly ...
By: Administrator, Views: 14191
Arteries A branching system of vessels that transports blood away from the heart to all body parts. All arteries have a pulse, reflecting the rhythmical beating of the heart. Arteries Certain points are commonly used to check rate, rhythm, and condition of the arterial wall. Most commonly ...
By: Administrator, Views: 577
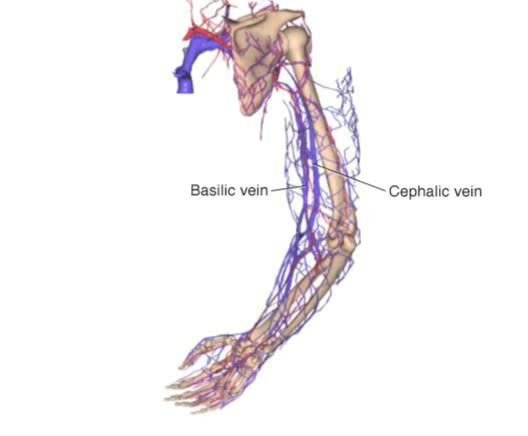
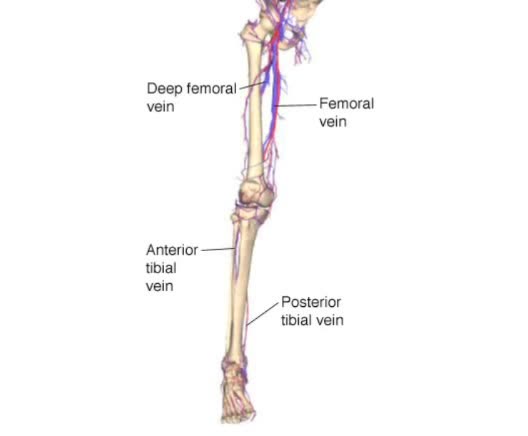
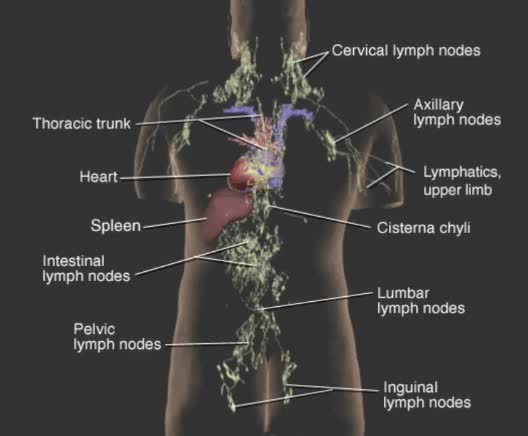
Blood and lymph are two of the body's main fluids and are circulated through two separate but interconnected vessel systems. Blood is circulated by the action of the heart, through the circulatory system consisting largely of arteries, veins, and capillaries. Lymph does not actually circulate. ...
Hormonal feedback loop components & Glucagon (glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 10802
The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: • Stimulus - a change in a body condition. • Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone after ...
Advertisement