Search Results
Results for: 'Glucose anabolism reaction types'
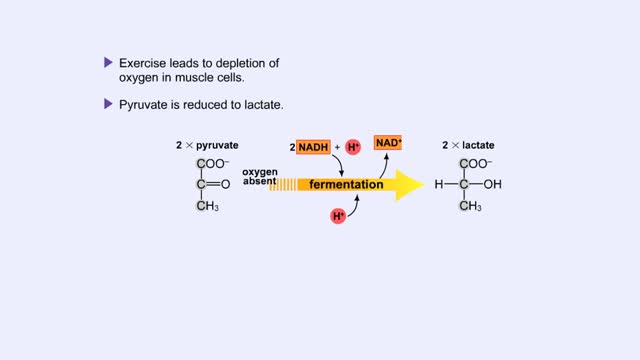
Fermentation - When Oxygen Is Absent, Pyruvate to Lactate & Pyruvate to Ethanol
By: HWC, Views: 10372
Pyruvate is the end product of glycolysis. If oxygen is present, pyruvate enters the mitochondrion where further energy yielding reactions of the Krebs cycle will take place. However, if oxygen is not present, pyruvate will enter a pathway called fermentation. This pathway regenerates NAD+ fro...
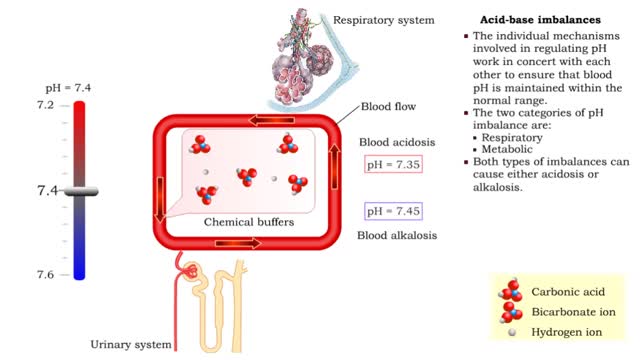
Acid-base imbalances - respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11230
• The individual mechanisms involved in regulating pH work in concert with each other to ensure that blood pH is maintained within the normal range. • The two categories of pH imbalance are: • Respiratory • Metabolic • Both types of imbalances can cause either acidosis or alka...
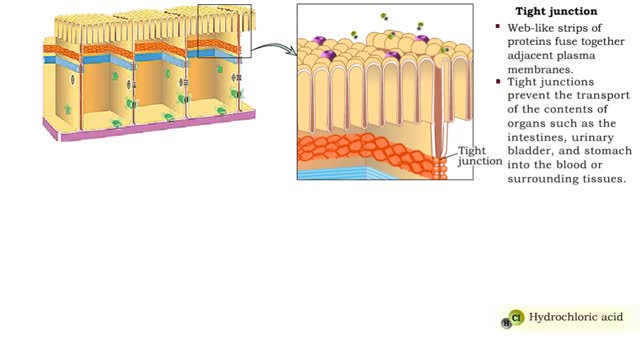
Junction Types - Tight and Adherens Junctions
By: HWC, Views: 11326
Many tissues contain in tercellular junctions between cells. 1. Tight junction 2. Adherens junction 3. Desmosome 4. Hemidesrnosome 5. Gap junction 1. Tight junction • Web-like strips of proteins fuse together adjacent plasma membranes. • Tight junctions prevent the transport...
By: HWC, Views: 10910
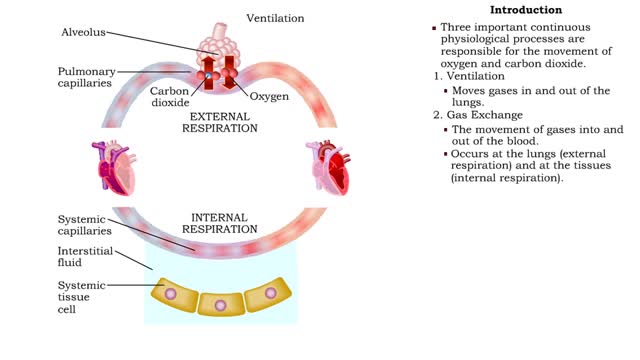
• The respiratory system is responsible for the movement of gases involved in cellular metabolism. • Oxygen is used up and carbon dioxide is generated during the aerobic breakdown of glucose and other fuel molecules in order to produce ATP. • Three important continuous physiological pro...
By: HWC, Views: 10698
An ecosystem is a community of organisms and their environment. The community forms the living component of the ecosystem. These are called the 'biotic' factors, which means all of the living things in the ecosystem. The environment forms the nonliving component of the ecosystem, such as ...
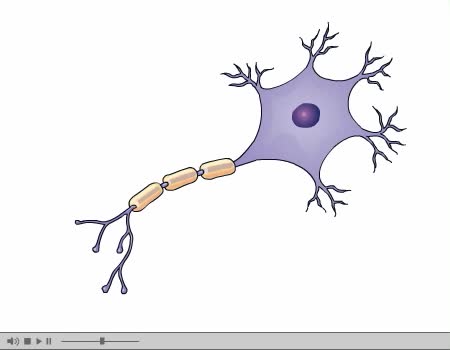
Nerve Impulse Transmission Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14331
How nerves transmit impulses. Stimulation of a nerve occurs at a receptor. Sensory receptors Specialized to specific types of stimulation such as heat, cold, light, pressure, or pain. React by initiating a chemical change or impulse. All-or-none principle Means that no transmission occ...
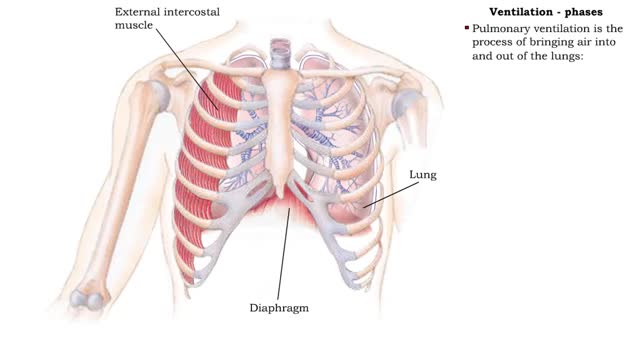
Ventilation - phases and driving forces
By: HWC, Views: 11044
Respiration is the exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells The combination of 3 processes is required for respiration to occur Ventilation (breathing) External (pulmonary) respiration Internal (tissue) respiration The cardiovascular system assists the respiratory system b...
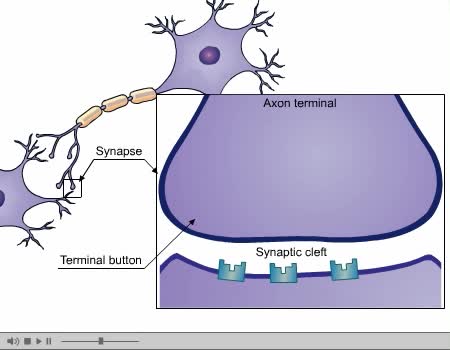
By: Administrator, Views: 14524
Dendrites (from Greek δένδρον déndron, "tree"), also dendrons, are branched protoplasmic extensions of a nerve cell that propagate the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body, or soma, of the neuron from which the dendrites project. Electrical stimula...
How does asthma work?And How do you treat asthma?
By: HWC, Views: 9895
These are the parts of the respiratory system. Sinuses and Nasal Passages Mouth Windpipe (Trachea) Lungs Airways (Bronchial Tubes) Airsacs (Alveoli) When we breathe, air moves easily in and out of the lungs. The small airways are also called bronchial tubes. The side of the tube is...
Advertisement