Ventilation - phases and driving forces
By: HWC
Date Uploaded: 10/28/2019
Tags: homeworkclinic.com Homework Clinic HWC Ventilation respiratory system cellular metabolism ATP Gas Exchange Gas Transport pulmonary circulation systemic circulation Inspiration Expiration
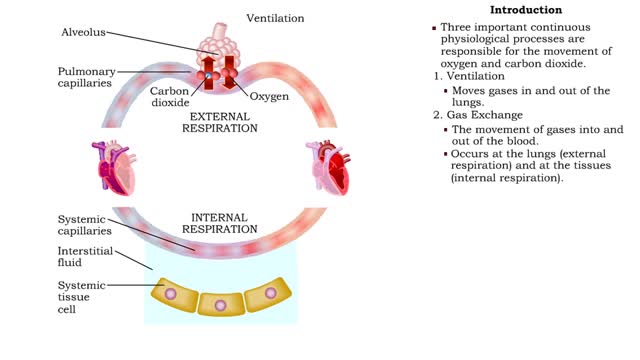
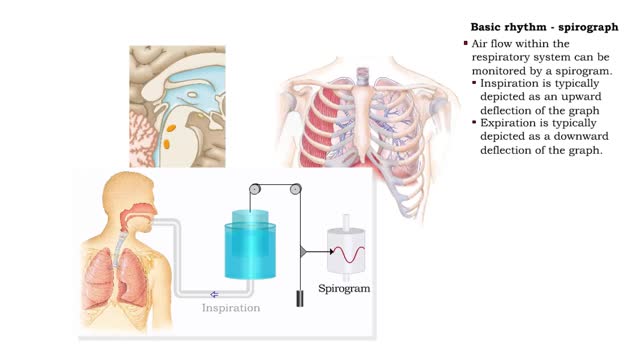
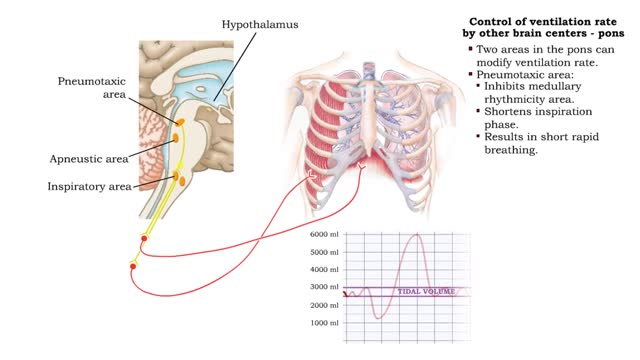
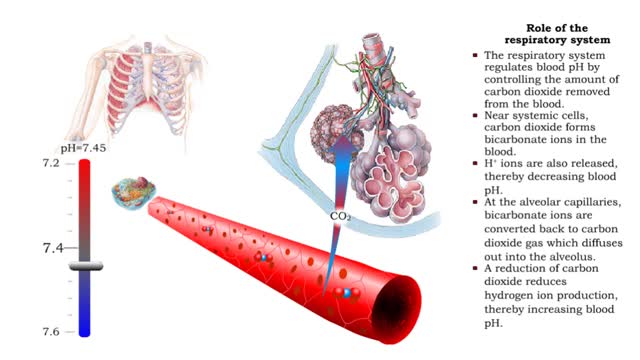
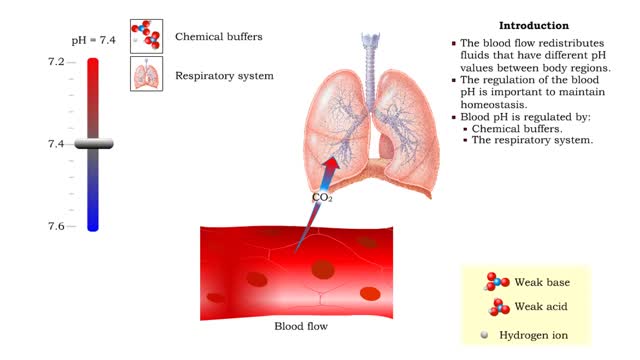
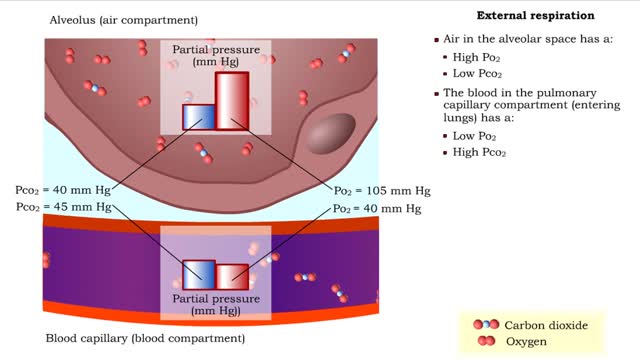
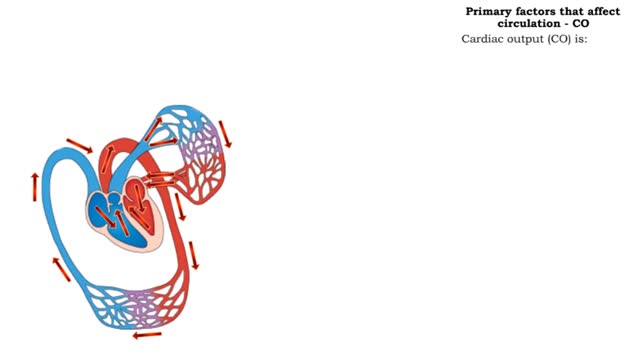
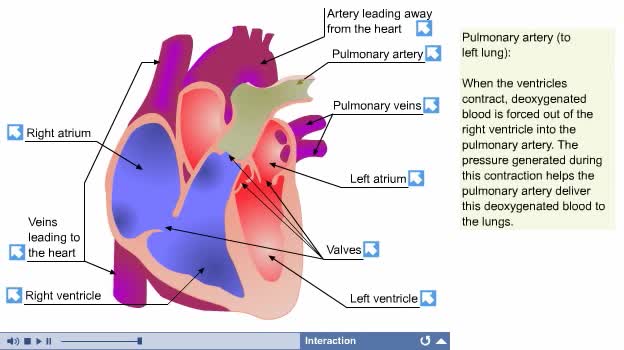
Respiration is the exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells The combination of 3 processes is required for respiration to occur Ventilation (breathing) External (pulmonary) respiration Internal (tissue) respiration The cardiovascular system assists the respiratory system by transporting gases • The respiratory system is responsible for the movement of gases involved in cellular metabolism. • Oxygen is used up and carbon dioxide is generated during the aerobic breakdown of glucose and other fuel molecules in order to produce ATP. • Three important continuous physiological processes are responsible for the movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide. 1. Ventilation • Moves gases in and out of the lungs. 2. Gas Exchange • The movement of gases into and out of the blood. • Occurs at the lungs (external respiration) and at the tissues (internal respiration). 3. Gas Transport • Blood gases are transported to the lungs (pulmonary circulation). • Blood gases are transported to the organs and tissues throughout the body (systemic circulation). • Pulmonary ventilation is the process of bringing air into and out of the lungs: • Inspiration: air moves into the lungs. • Expiration: air moves out of the lungs. • Proper ventilation is important to promote airflow, which enhances gas exchange. • Direction of airflow is determined by changing pressures. • Air flows from high to low pressure. • Pressure can be altered by changing the volume.
Add To
You must login to add videos to your playlists.
Advertisement



Comments
0 Comments total
Sign In to post comments.
No comments have been posted for this video yet.