Search Results
Results for: 'blood glucose levels'
By: HWC, Views: 7807
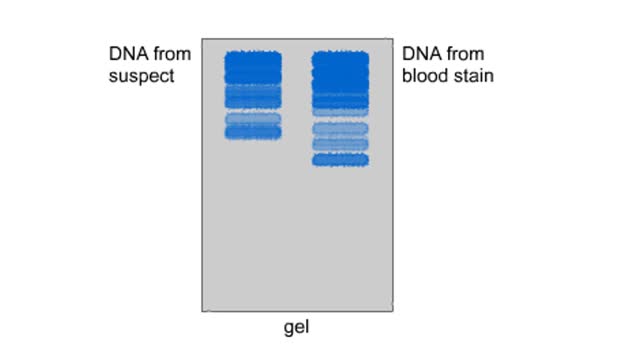
DNA fingerprinting enables a scientist to compare the DNA from two biological samples, such as a blood stain and a suspect's blood. A restriction enzyme is added to the samples to be compared. The enzyme cuts the DNA into smaller fragments. The DNA fragments are placed on an electrophor...
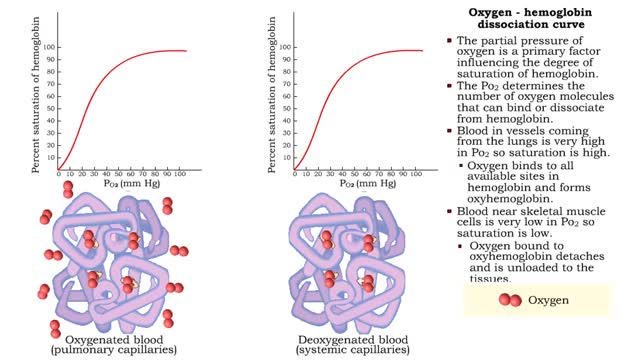
Oxygen - hemoglobin dissociation curve & Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen - acidity
By: HWC, Views: 11539
• The partial pressure of oxygen is a primary factor influencing the degree of saturation of hemoglobin. • The Po2 determines the number of oxygen molecules that can bind or dissociate from hemoglobin. • Blood in vessels coming from the lungs is very high in Po2 so saturation is high. ...
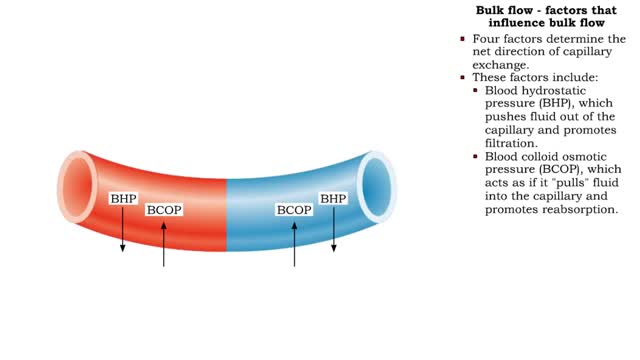
Bulk flow - factors that influence bulk flow
By: HWC, Views: 10542
• Bulk flow helps regulate the relative volumes of blood and interstitial fluid. • Flow from blood to interstitium is called filtration. • Flow from interstitium to blood is called reabsorption. • Four factors determine the net direction of capillary exchange. • These factors in...
By: Administrator, Views: 14075
How blood is taken from a patient. Phlebotomy is the process of making an incision in a vein with a needle. The procedure itself is known as a venipuncture.
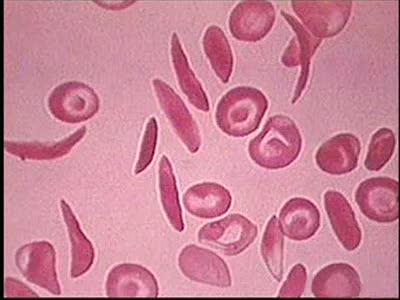
Introduction to Sickle Cell Anemia
By: Administrator, Views: 14464
Sickle cell anemia (sickle cell disease) is a disorder of the blood caused by an inherited abnormal hemoglobin (the oxygen-carrying protein within the red blood cells). The abnormal hemoglobin causes distorted (sickled appearing under a microscope) red blood cells.
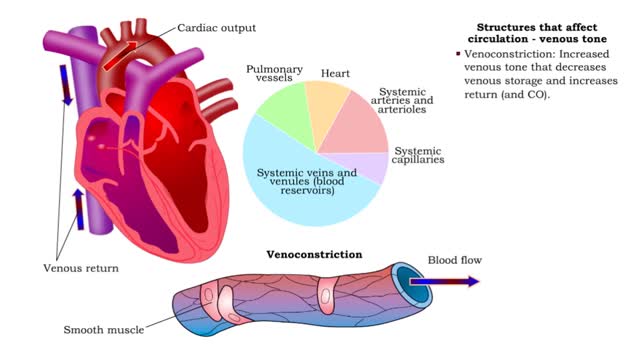
Structures that affect circulation - kidneys and blood volume and skeletal muscle pumping
By: HWC, Views: 11606
• Kidneys regulate blood volume and blood osmolarity via salt and water reabsorption. • Increased reabsorption increases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Decreased reabsorption Increases urine production, which decreases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Systemi...
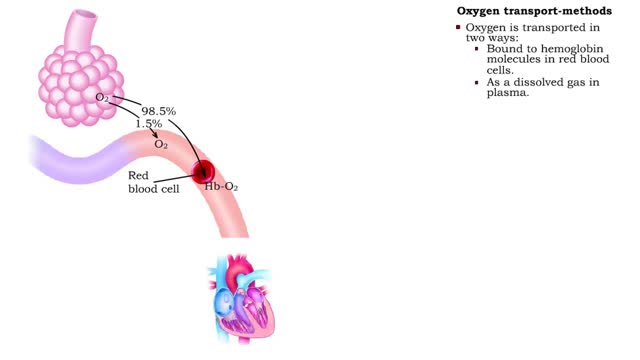
Oxygen transport - methods and oxyhemoglobin
By: HWC, Views: 10808
• The blood is the medium used for gas transport throughout the body. • Oxygen is only available in the lungs. Because the partial pressure of oxygen is higher in the alveoli than in the blood, oxygen diffuses into the blood and is transported to systemic cells. • At the tissues the par...
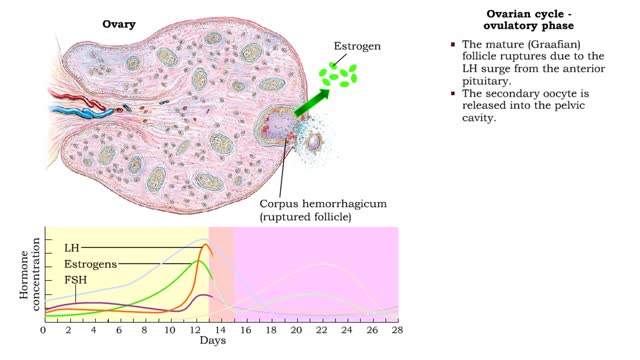
By: HWC, Views: 11291
• The ovarian cycle is a monthly sequence of events, consisting of three phases: • Preovulatory • Ovulatory • Post ovulatory Preovulatory phase • prior to ovulation: Primary follicles develop into secondary follicles. • Follicular cells surrounding the primary oocyte In...
Structures that affect circulation - arterioles and vasomotor responses
By: HWC, Views: 10585
■ Small arteries and arterioles determine SVR. ■ Blood pressure drops significantly as blood passes through arterioles. ■ Decreasing arteriole radius and decreased wall elasticity are the main reasons for increased SVR. ■ Small changes in arteriole radius can cause large changes in ...
Advertisement