Search Results
Results for: 'protein structure animation'
By: HWC, Views: 5418
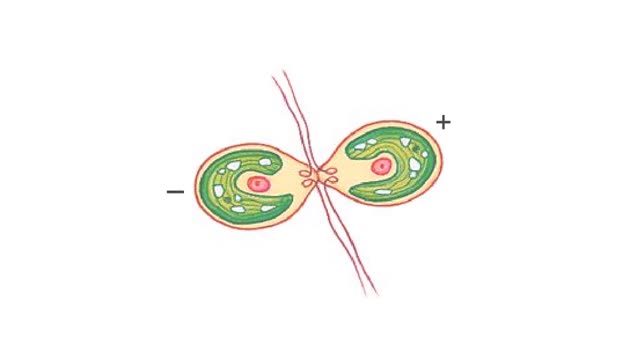
Protozoan conjugation is an unusual form of sexual reproduction Prospective partners join together, usually at the surface of their oral depressions. The cells undergo cytoplasmic fusion. Meiosis II produces four haploid micronuclei. Now the macronucleus of each cell begins to bre...
By: Administrator, Views: 1664
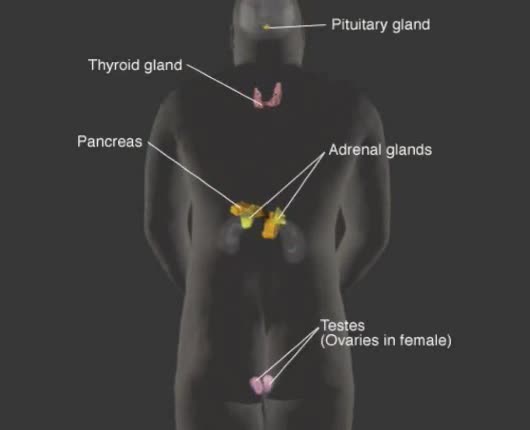
Vital function of endocrine system: Production and regulation of chemical substances called hormones. Hormones Chemical transmitters released in small amounts and transported via bloodstream to a target organ or other cells. Transfer information and instructions from one set of cells to anot...
By: Administrator, Views: 13864
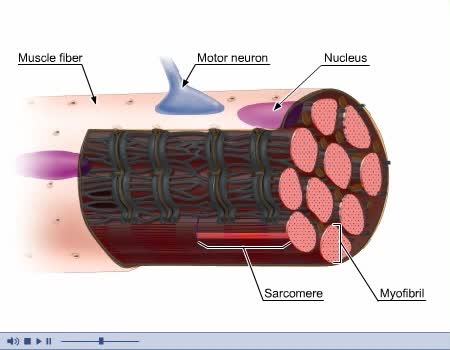
Three basic types of muscles: - Skeletal - Smooth - Cardiac Composed of striated or smooth muscle tissue and classified according to their functions and appearance. Skeletal Muscle: - Also known as voluntary or striated muscle. - Controlled by the conscious part of the brain and attach...
Cellular Respiration & Glucose Mobilization (Glucose transport & Phosphorylation of Glucose)
By: HWC, Views: 10748
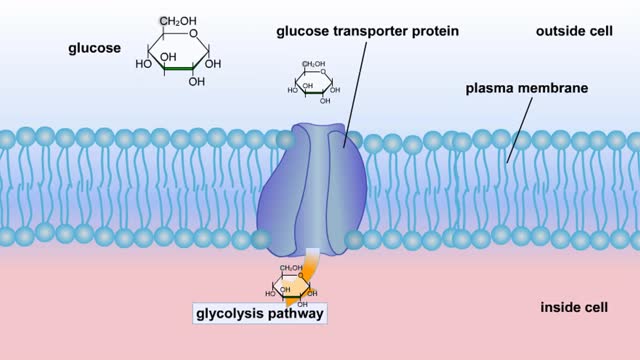
Glucose is completely broken down into CO2 and H2O during the process of cellular respiration, which includes 3 stages: 1) glycolysis; 2) the Krebs Cycle; and 3) the electron transport chain. Glucose enters this energy yielding pathway of cellular respiration in the first stage known as...
Homologous chromosomes during prophase I - Animation
By: HWC, Views: 8957
The chromosomes were duplicated during interphase and the sister chromatids are now in thin threadlike form. Each chromosome becomes zippered to its homologue, so that all four chromatids are closely aligned. The chromosomes are tightly aligned, but we will show them as separate so that y...
By: Administrator, Views: 14255
The most common cause of spinal cord injury is trauma. Spinal cord injury is most common in young, white men. Spinal cord injury can be either complete or incomplete. In complete injuries there is no function below the level of injury. In incomplete injuries there is some function remaining...
By: HWC, Views: 10758
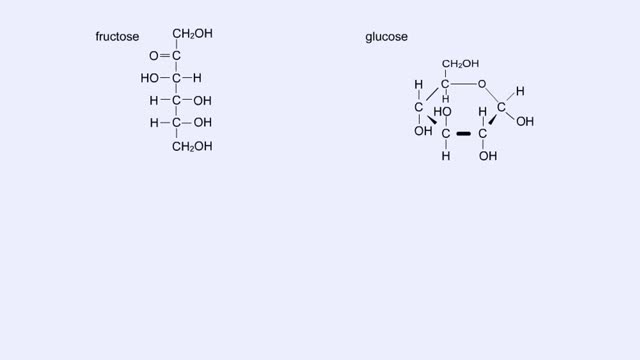
Here are the molecular structures of three simple sugars: glucose, ribose, and fructose. Look at these simple sugars and identify what characteristics they all share. As you can see, all of the carbohydrates have carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of 1:2:1 and there is always a double bo...
By: HWC, Views: 7854
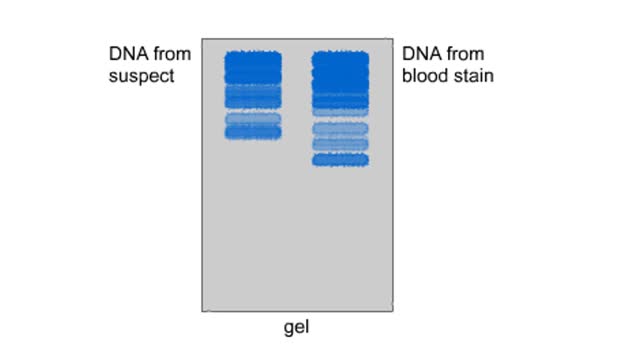
DNA fingerprinting enables a scientist to compare the DNA from two biological samples, such as a blood stain and a suspect's blood. A restriction enzyme is added to the samples to be compared. The enzyme cuts the DNA into smaller fragments. The DNA fragments are placed on an electrophor...
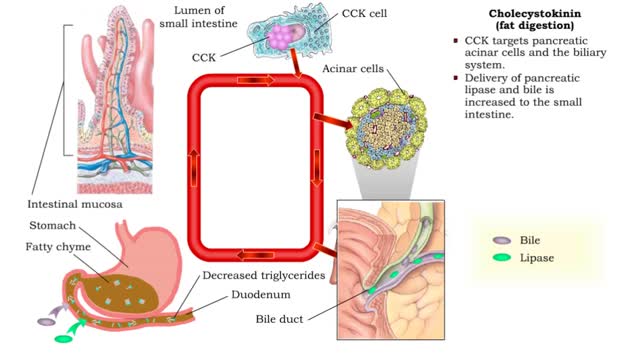
Secretin (inhibiting gastric acid secretion), Cholecystokinin (fat digestion) & Cholecystokinin
By: HWC, Views: 10863
• As chyme approaches the small intestine, secretin also targets acid-producing parietal cells in the gastric mucosa. • Increased secretin inhibits gastric add secretion. • With less gastric acid produced, the chyme going into the intestine is less acidic. • The hormone CCK also reg...
Advertisement