Search Results
Results for: 'Molecules and Membrane'
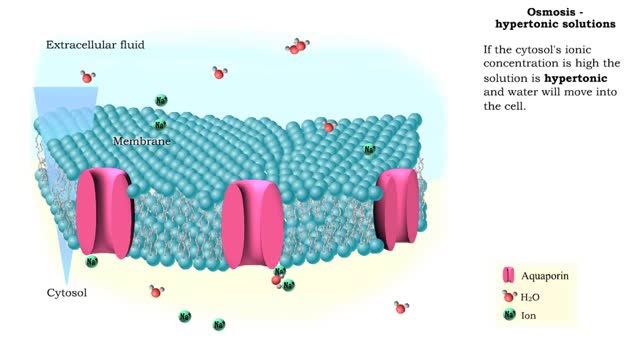
Osmosis - Isotonic, Hypotonic, and Hypertonic Solutions
By: HWC, Views: 11024
Isotonic: Equal Water moves in and out of the cell at an equal rate. The cell remains unchanged. Hypotonic: "hypo" hippo Water moves into the cell, making it swell and get fat (like a hippo). Eventually the cell can rupture and burst (aka lyse). Hypertonic: "like a raisin" Water leaves...
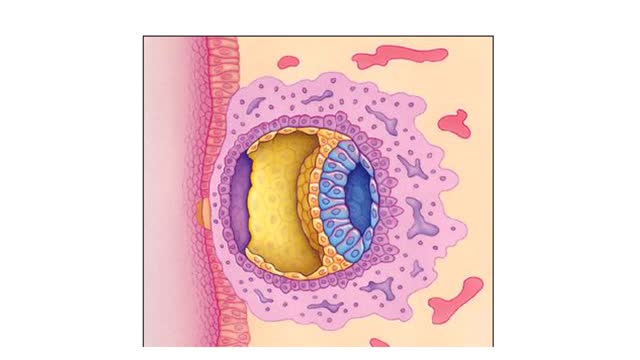
Cleavage and Implantation Animation
By: HWC, Views: 8508
✔ https://HomeworkClinic.com ✔ https://Videos.HomeworkClinic.com ✔ Ask questions here: https://HomeworkClinic.com/Ask Follow us: ▶ Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/HomeworkClinic ▶ Review Us: https://trustpilot.com/review/homeworkclinic.com Fertilization typically takes pl...
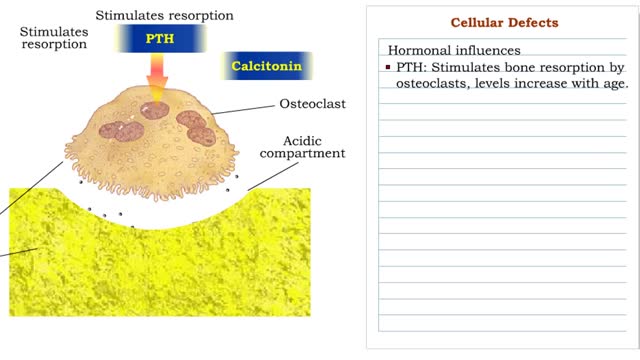
Cellular Defects - Osteoblasts, Osteoclasts and Osteocytes
By: HWC, Views: 10608
■ Metabolically active bone-building cells that secrete astroid. ■ Cover surfaces of newly formed bone and respond to growth stimuli ■ Less responsive to growth factors as the body ages. ■ Contribute to hone loss once their reproductive and biosynthetic potential lessens....
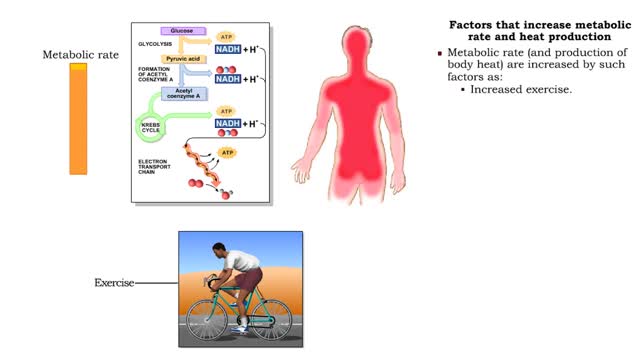
Factors that increase metabolic rate and heat production
By: HWC, Views: 11095
• All vital biochemical reactions are temperature dependent. • The overall rate at which metabolic reactions use energy is known as the metabolic rate. • Metabolic rate greatly determines body temperatures. • Temperature is maintained by balancing the loss of heat to the environment...
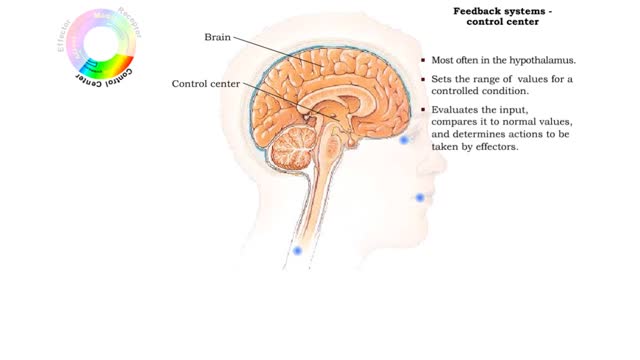
Component of feedback systems & Communication and regulation of body systems
By: HWC, Views: 11127
• Primary responsibility for communication and regulation in the body is shared by the nervous and endocrine systems. • The two systems work alone or together in specialized physiological processes called feedback systems to maintain homeostasis. • Feedback systems - or loops - are ...
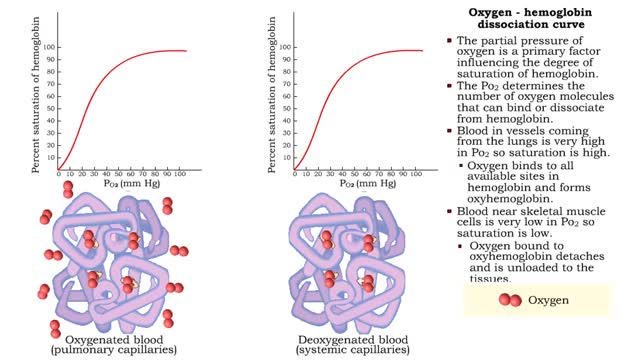
Oxygen - hemoglobin dissociation curve & Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen - acidity
By: HWC, Views: 11526
• The partial pressure of oxygen is a primary factor influencing the degree of saturation of hemoglobin. • The Po2 determines the number of oxygen molecules that can bind or dissociate from hemoglobin. • Blood in vessels coming from the lungs is very high in Po2 so saturation is high. ...
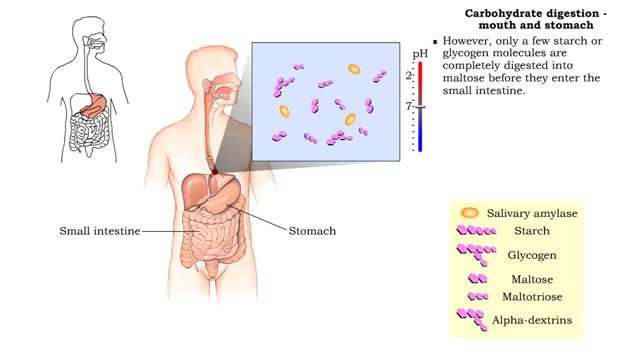
Carbohydrate digestion - mouth and stomach & pancreas and small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 10787
• Digestion of complex carbohydrates (starches and glycogen) involves: • Amylases produced by the salivary glands and pancreas. • Brush-border enzymes in small intestine. • In the mouth, amylase from the parotid and submandibular salivary glands begins carbohydrate digestion. �...
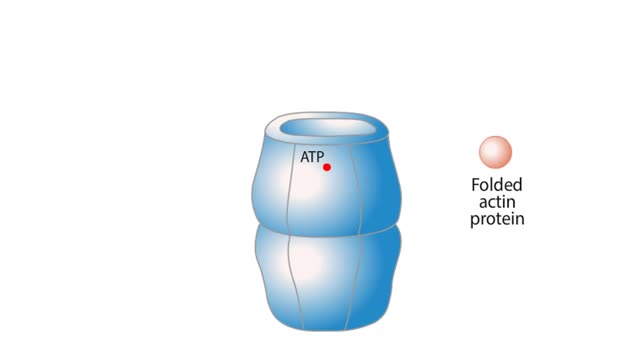
By: HWC, Views: 10573
The life cycle of a typical protein begins with its synthesis on a ribosome. As the polypeptide chain grows, molecules of a chaperone protein bind along its length. This prevents misfolding of the nascent polypeptide. ATP binding causes chaperone release. For most proteins, the polypeptide th...
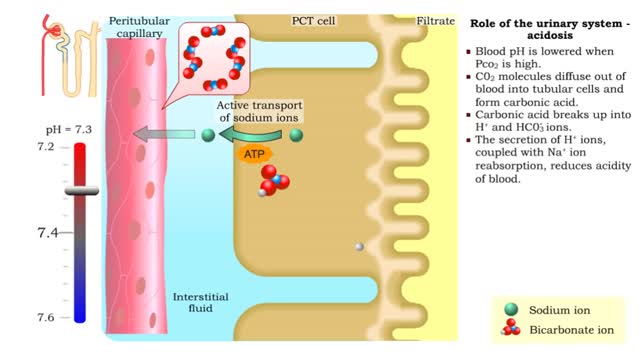
Role of the urinary system - acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11078
• Tubular cells of the proximal convoluted tubule and collecting tubules can alter filtrate pH and therefore blood pH. • These cells can affect blood pH with two coupled mechanisms: • Reabsorption of bicarbonate ions. • Secretion of hydrogen ions. • The reabsorption of bicarbonate...
Advertisement