Search Results
Results for: 'Molecules and Membrane'
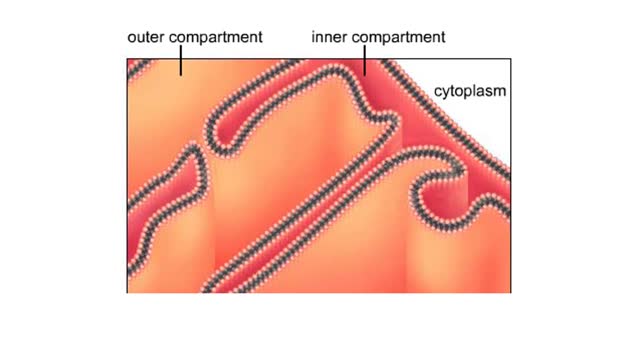
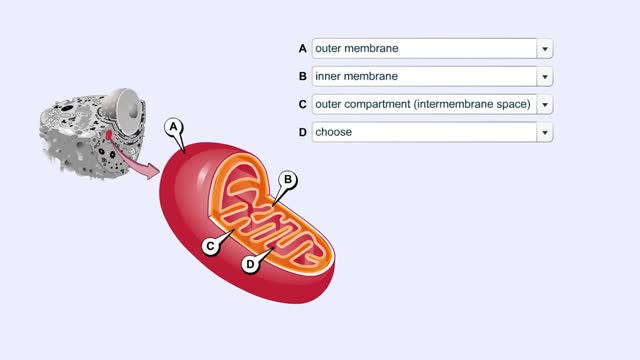
Functional zones in a mitochondrion
By: HWC, Views: 8908
A mitochondrion has a double membrane system. The outer membrane faces the cytoplasm. The inner membrane divides the organelles interior into two compartments. The enzymes that carry out the second stage reactions are in the semifluid matrix inside the inner compartment. Embedded in the ...
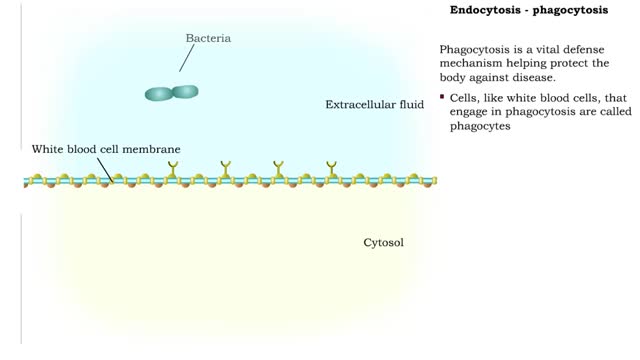
Endocytosis -Types and Phagocytosis
By: HWC, Views: 11084
Endocytosis is the process by which a substance is brought inside a cell without having to pass through the cell membrane. It is the opposite of endocytosis, the process by which substances exit the cell without having to pass through the cell membrane. Exocytosis – membrane-enclosed secret...
By: HWC, Views: 11141
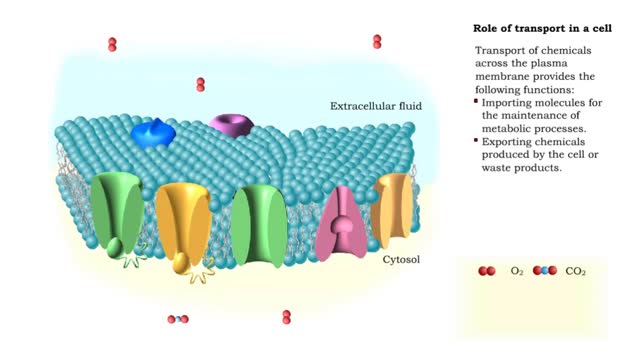
Transport of chemicals across the plasma membrane provides the following functions: Importing molecules for the maintenance of metabolic processes. Exporting chemicals produced by the cell or waste products. Communicating with other cells, allowing for the generation and conduction of a...
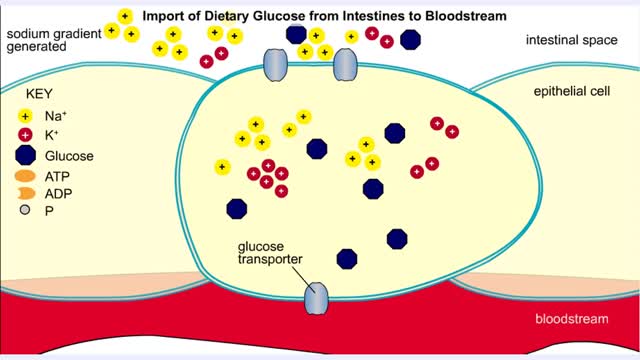
Import of Dietary Glucose from Intestines to Bloodstream
By: HWC, Views: 10443
• Membranes have hydrophobic interiors. which resist the passage of hydrophilic compounds and ions. • However. transporter membrane proteins facilitate the passage of these molecules. • Passive transporters accelerate diffusion of molecules towards equilibrium (decrease a concentrat...
Second Messengers in the Inositol-lipid Signaling Pathway
By: HWC, Views: 10189
Extracellular signals produce specific responses in target cells through the action of intracellular second messengers. Here, we focus on three second messengers, IP3, DAG, and Ca2+, all involved in the inositol-lipid signaling pathway. A hormone-receptor signal on the cell surface leads to the a...
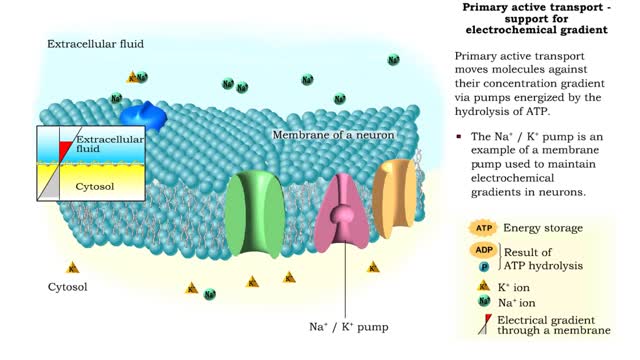
Primary Active Transport - electrochemical gradient and ion transport / water movement
By: HWC, Views: 11206
Energy derived from ATP changes the shape of a transporter protein which pumps a substance across a plasma membrane against its concentration gradient An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consis...
Mitochondrial Structure & ETC Protein Complexes (Protein Complexes and Electron Transport)
By: HWC, Views: 10642
The energy carrying molecules, NADH and FADH2, that were generated in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, now are processed in the mitochondria where their high energy electrons are deposited in an electron chain complex located in the inner mitochondrial membranes. These high-energy electrons now dr...
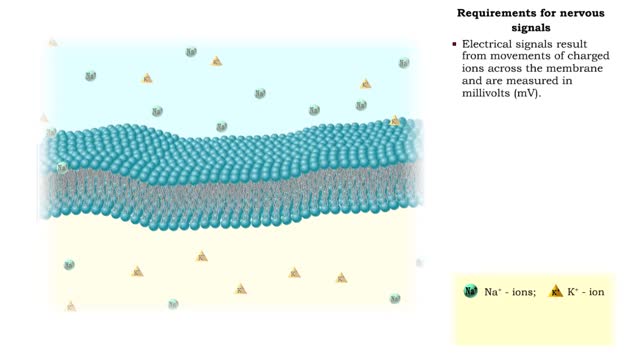
Requirements for nervous signals
By: HWC, Views: 10945
• The function of neurons is to allow communication between cells, thereby maintaining homeostasis. • Electrical signals, called membrane potentials, travel along the membranes of the neurons. • Voltage variability and distance traveled determine the type of nervous signal. 1. Graded...
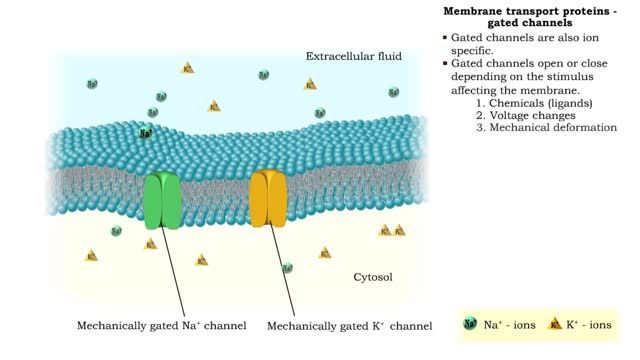
Membrane transport proteins - pores, gated channels and pumps
By: HWC, Views: 11182
• a Three different types of membrane ion transport proteins are required to produce and carry electrical signals: • Pores • Gated channels • Na+/ K+ pump • Pores are always open and allow the diffusion of Na+ and K+ ions across the membrane, down their concentration gradients...
Advertisement