Search Results
Results for: 'juxtaglomerular cells'
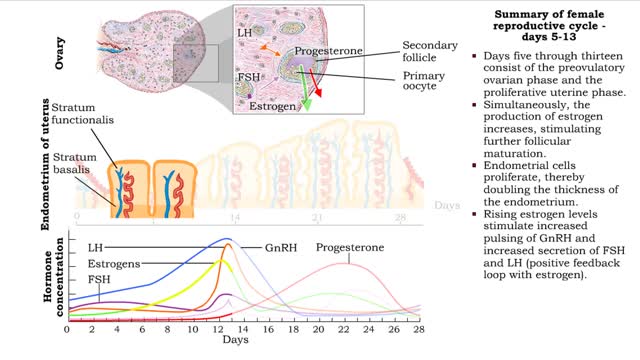
Summary of female reproductive cycle days 1-28
By: HWC, Views: 12068
■ The first five days of the cycle include the menstrual phase. ■ Progesterone and estrogen levels are low. ■ Menses occurs. ■ GnRH pulses more frequently promoting FSH and LH levels to rise. ■ Primary follicles are stimulated to develop. ■ Days five through thirteen consist o...
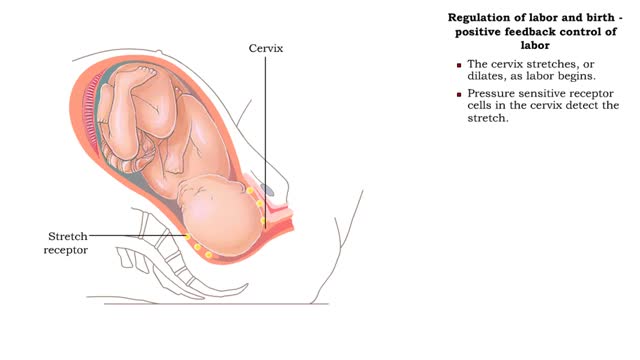
Labor and Childbirth - The Three Stages of Labor: Dilation, Expulsion & Placental مراحل الولادة
By: HWC, Views: 12040
Regulation of labor and birth - effects of estrogen and oxytocin on onset of labor • Just prior to birth, high placental corticotropin-releasing hormone levels stimulate the production of more estrogen. • High estrogen levels overcome the inhibitory effects of progesterone on uterine sm...
By: HWC, Views: 11751
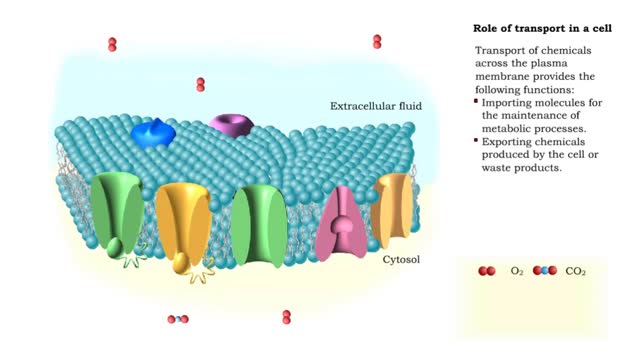
Transport of chemicals across the plasma membrane provides the following functions: Importing molecules for the maintenance of metabolic processes. Exporting chemicals produced by the cell or waste products. Communicating with other cells, allowing for the generation and conduction of a...
By: HWC, Views: 6088
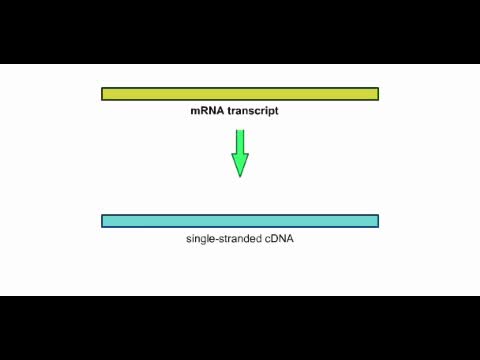
This animation shows how an mRNA transcript can be used to make a cDNA strand.
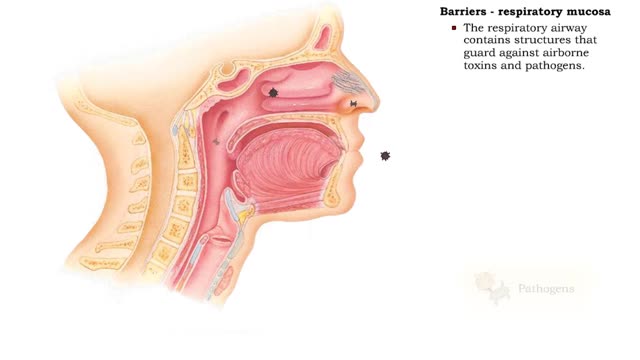
Barriers - eye structures, digestive mucosa, respiratory mucosa & genitourinary mucosa
By: HWC, Views: 11913
• Eyebrows, eyelids, eyelashes and conjunctiva serve to trap microbes preventing their invasion. • Tearing (lacrimation) is a protective mechanism that washes away microbes that attempt to enter the eyes. • Salts, mucus, and lysozymes in tears neutralize substances and bacteria. �...
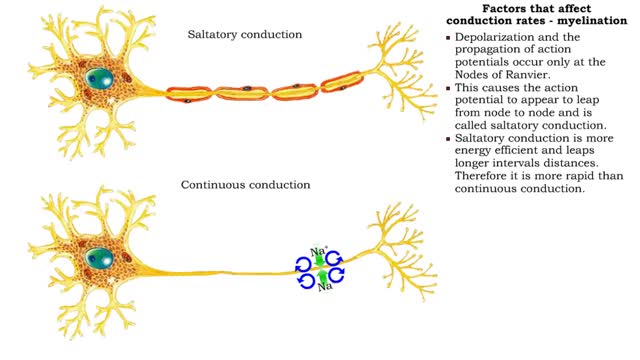
Factors that affect conduction rates (myelination, axon diameter & temperature)
By: HWC, Views: 11744
• Several factors determine the rate of conduction of action potentials: • Myelination • Axon diameter • Temperature • The step-by-step depolarization of an axon is called continuous conduction and occurs along unmyelinated axons. • Neurons in the PNS have many axons that ...
How proteins function? How do proteins work?
By: HWC, Views: 11292
How proteins function is really about how proteins "do work" in cells. How do proteins work? Let's start thinking about protein function by looking at something important to you: your hair. Keratin is a structural protein that is composed of 2 intertwined or helical strands. Keratin is also f...
By: HWC, Views: 11291
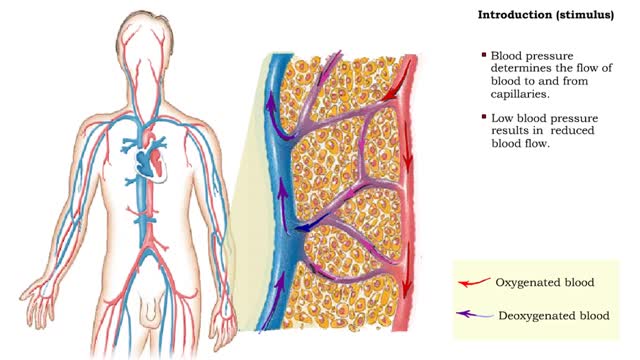
• Blood pressure determines the flow of blood to and from capillaries. • Low blood pressure results in reduced blood flow. • High blood pressure can cause blood vessels to break. In humans, sensitivity is due to portions of the nervous system called receptors. Receptors are typicall...
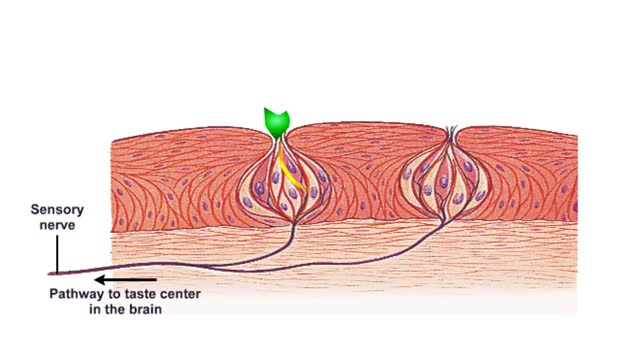
What are Taste Receptors? How Does it Work? Animation
By: HWC, Views: 8493
Do you ever wonder how you can taste the foods you eat? It all starts with taste receptors in your muscular tongue. Taste receptor neurons are found in your taste buds but you are not looking at the taste buds. The raised bumps on the surface of the tongue that you see are specialized epith...
Advertisement