Search Results
Results for: 'Blood colloid osmotic pressure (BCOP)'
By: HWC, Views: 11322
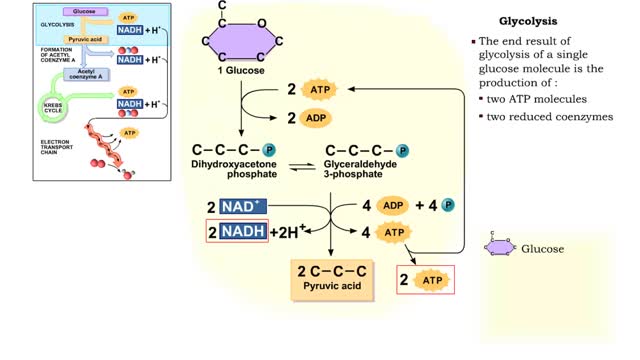
The first reactions involve a single 6-carbon glucose sugar undergoing phosphorylation using two ATP molecules and resulting in two 3-carbon compounds. • The rest of this pathway involves an oxidation reduction reaction, forming two reduced coenzymes, and generation of four ATP molecules. ...
Contraction and Relaxation Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 13925
Muscles are responsible for movement. The types of movement are: - Locomotion, when chemical energy is changed into mechanical energy. - Propulsion of substances through tubes, as in circulation and digestion. - Changes in the sizes of openings, as in the contraction and relaxation of the iris...
Acid-base imbalances - respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11328
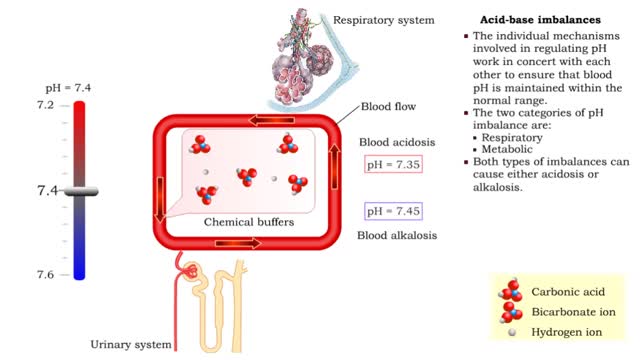
• The individual mechanisms involved in regulating pH work in concert with each other to ensure that blood pH is maintained within the normal range. • The two categories of pH imbalance are: • Respiratory • Metabolic • Both types of imbalances can cause either acidosis or alka...
Labor and Delivery - Infant Cord Apgar
By: Administrator, Views: 458
As soon as your baby is born, a delivery nurse will set one timer for one minute and another for five minutes. When each of these time periods is up, a nurse or physician will give your baby her first "tests," called Apgars. This scoring system (named after its creator, Virginia Apgar) helps t...
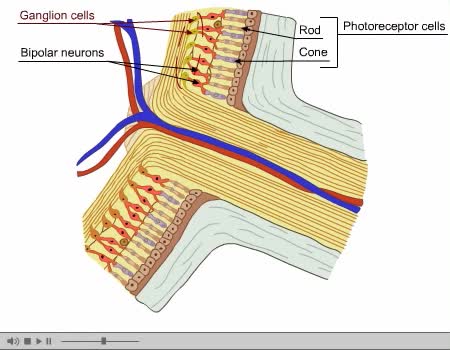
Optic Nerve and Optic Disk Animation (Part 2 of 2)
By: Administrator, Views: 14039
The optic disc or optic nerve head is the point of exit for ganglion cell axons leaving the eye. Because there are no rods or cones overlying the optic disc, it corresponds to a small blind spot in each eye. The ganglion cell axons form the optic nerve after they leave the eye. The optic disc ...
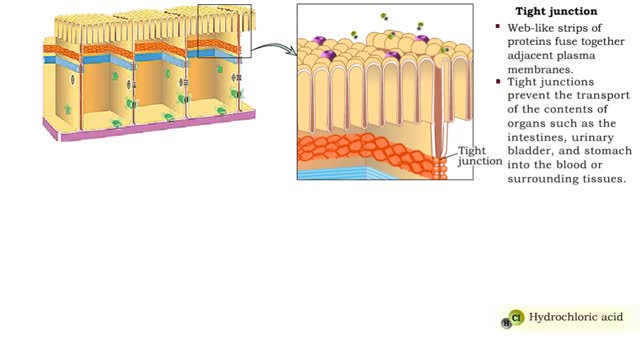
Junction Types - Tight and Adherens Junctions
By: HWC, Views: 11416
Many tissues contain in tercellular junctions between cells. 1. Tight junction 2. Adherens junction 3. Desmosome 4. Hemidesrnosome 5. Gap junction 1. Tight junction • Web-like strips of proteins fuse together adjacent plasma membranes. • Tight junctions prevent the transport...
The pH scale - Strong acids and Weak acids
By: HWC, Views: 11057
The pH scale • Expresses concentration of H+. • range: 0-14. • 7 is neutral. • Less 7 is acid. • greater 7 is basic (alkaline). Strong acids - role in the body ■ In strong acids all molecules dissociate. ■ HC1 is highly acidic and found only in the stomach. • H...
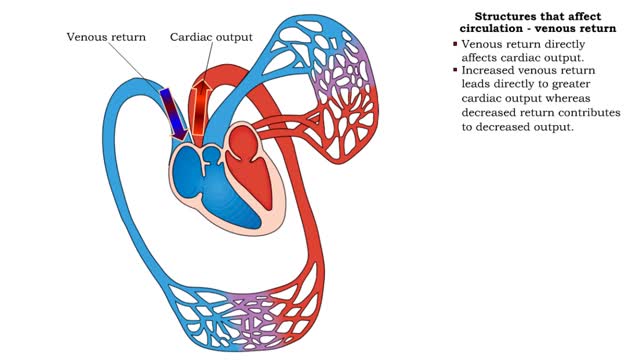
Structures that affect circulation - venous return
By: HWC, Views: 10878
• Venous return directly affects cardiac output. • Increased venous return leads directly to greater cardiac output whereas decreased return contributes to decreased output. • Venous return depends on: • Blood volume regulation by the kidneys. • Venous tone. • Skeletal muscl...
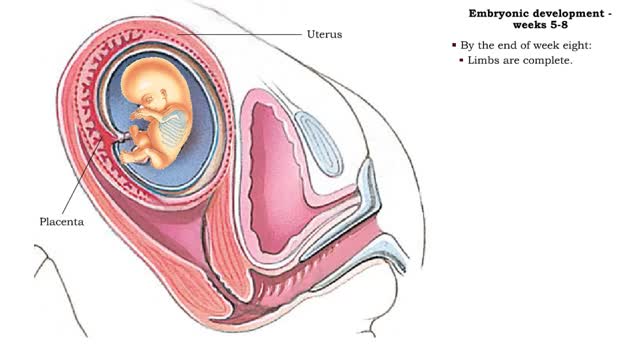
Embryonic development - Weeks 5 to 8
By: HWC, Views: 11195
• The second month of development is characterized by rapid development of the head and limbs as well as continued organogenesis. • During the fifth and sixth weeks growth of the brain, and therefore head, is rapid. • Hands and feets begin to form. • During week seven, even more deve...
Advertisement