Search Results
Results for: 'Mechanisms for chromosome movement Animation'
By: Administrator, Views: 14376
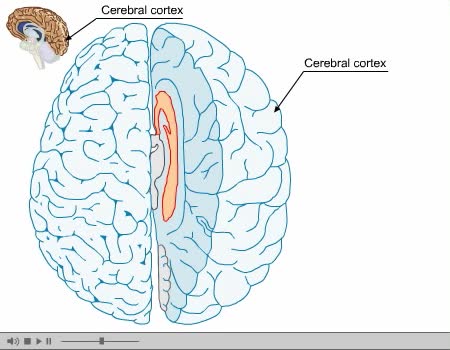
The cerebral cortex (plural cortices), also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain, in humans and other mammals. It is separated into two cortices, by the longitudinal fissure that divides the cerebrum into the left and right cerebral hemisp...
Cell mediated immune response to a viral infection Animation
By: HWC, Views: 6972
Intracellular pathogens are the targets of cell-mediated immune response. The process begins when a virus infects a macrophage. Another macrophage engulfs the same virus or an antigen from it. In both cells, enzymes cleave the viral antigens into small bits. The fragments move to the cell sur...
By: Administrator, Views: 15510
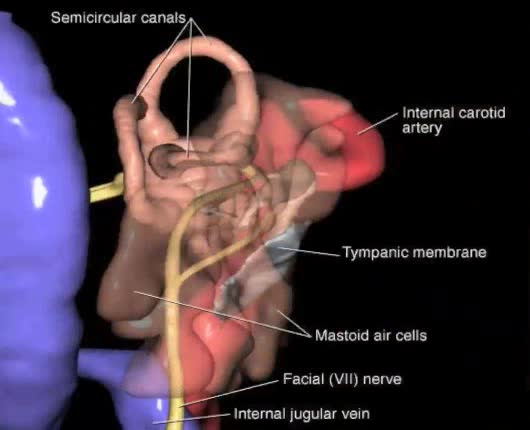
The ear is generally described as having three distinct divisions, each with distinct functions: External ear Middle ear Inner ear The ear contains structures for both the sense of hearing and the sense of balance. Eighth cranial nerve: Also called the acoustic or auditory nerve. Carries...
Transferring genes into plants Animation
By: HWC, Views: 8453
Researchers extract DNA from an organism that has a trait they want to introduce into a plant. The genetic donor can be a bacterial cell, a plant cell. or even an animal cell. The desired gene will be transferred into a plasmid, a small circle of bacterial DNA. The gene is cut out of th...
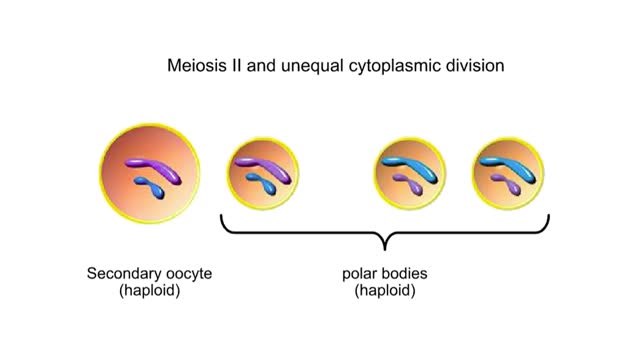
Egg and Sperm Formations in Animals Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5467
Inside the ovaries of a female animal are diploid germ cells called oogonia. An oogonium grows to become a primary oocyte. This large cell is still diploid. Meiosis I followed by unequal cytoplasmic division produces one large secondary oocyte and a smaller polar body. Both are haploid. ...
By: Administrator, Views: 14008
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung affecting primarily the small air sacs known as alveoli. Typically symptoms include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and trouble breathing. Severity is variable. In adults, bacteria are the most common causes of ...
By: HWC, Views: 11807
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
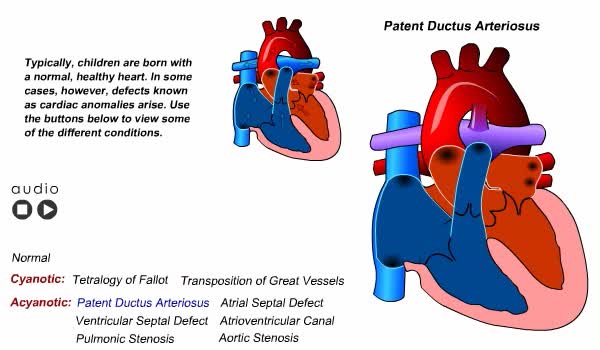
Congenital Heart Defects Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14151
Pulse, blood pressure, and respiration vary according to the child’s age. A newborn’s pulse rate is irregular and rapid, varying from 120 to 140 beats per minute. Blood pressure is low and can vary with the size of the cuff used. Average blood pressure at birth is 80/46. Respirations are ...
By: Administrator, Views: 14016
Types of fractures: - Colles' - Pott's - Compression - Vertebral compression - Epiphyseal - Stress - Hip Closed, or simple–A completely internal break that does not involve a break in the skin (x-ray of the tibia and fibula). Note the break in the fibula (smaller bone). Open, or co...
Advertisement