Search Results
Results for: 'ED'
By: Administrator, Views: 14038
Anatomic: Body erect, head facing forward, arms by the sides with palms to the front; used as a standard anatomical position of reference Dorsal recumbent: On back with lower extremities flexed and rotated outward; used in application of obstetric forceps, vaginal and rectal examination, and ...
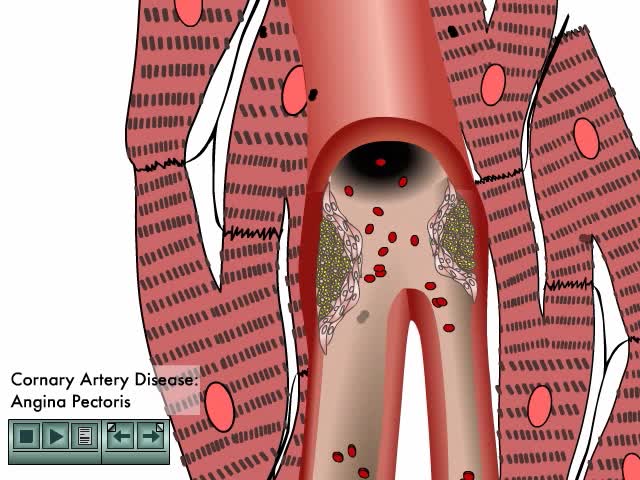
Coronary Heart Disease Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14475
Arteriosclerotic heart disease occurs when arterial vessels are marked by thickening, hardening, and loss of elasticity in arterial walls. Course of cardiovascular disease accelerates due to: Reduced blood flow Rlevated blood lipids Defective endothelial repair
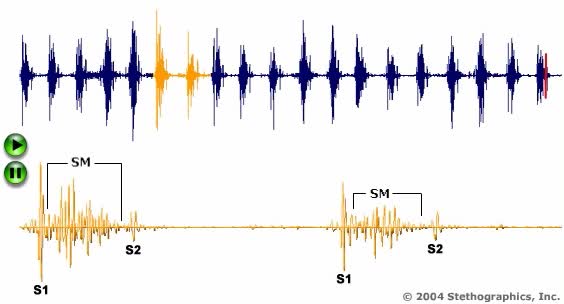
By: Administrator, Views: 531
An electrocardiogram (ECG, EKG) is a commonly used procedure in which the electrical events associated with the beating of the heart are evaluated. (A) Skin electrodes are applied to the chest wall, which send electrical signals to a computer that interprets the signals into graph form.
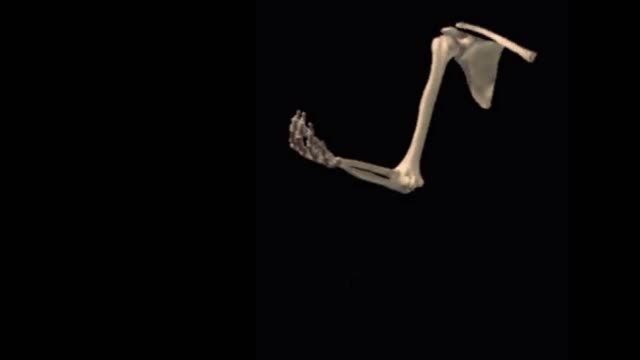
By: Administrator, Views: 660
Normal starting position for elbow flexion is with the subject supine with the shoulder positioned in 0 degrees of flexion, extension and abduction with the arm close to the side of the body
By: Administrator, Views: 13855
Smoking cessation (also known as quitting smoking or simply quitting) is the process of discontinuing tobacco smoking. Tobacco smoke contains nicotine, which is addictive and can cause dependence. Nicotine withdrawal makes the process of quitting often difficult. Seventy percent of smokers wou...
By: Administrator, Views: 15160
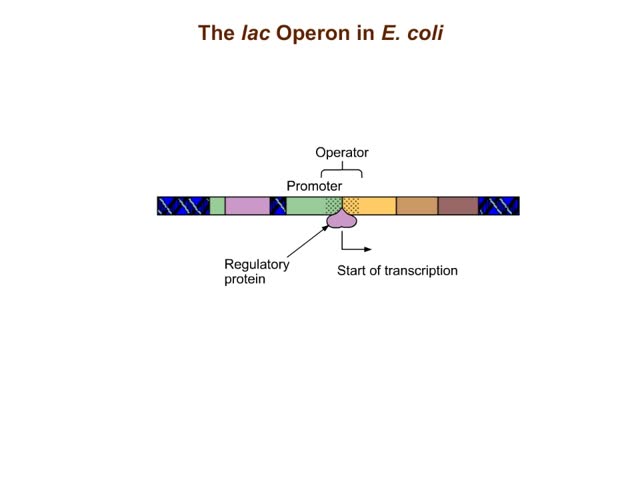
The lac operon (lactose operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is no...
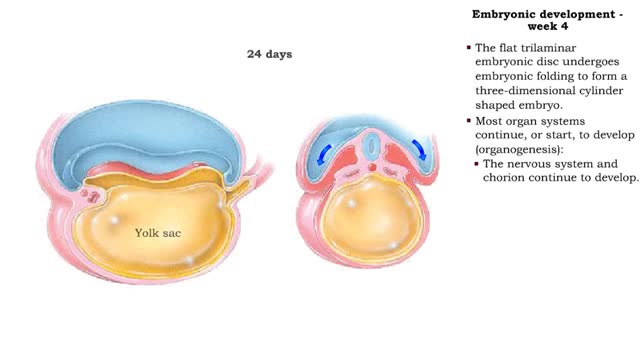
Embryonic development - Week 4
By: HWC, Views: 11166
• The flat trilaminar embryonic disc undergoes embryonic folding to form a three-dimensional cylinder shaped embryo. • Most organ systems continue, or start, to develop (organogenesis): • The nervous system and chorion continue to develop. • The heart and the rest of the cardiovas...
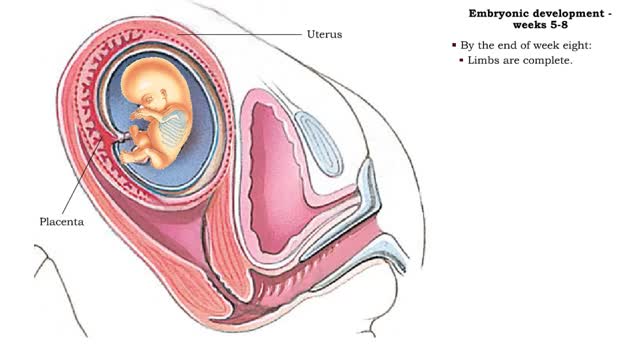
Embryonic development - Weeks 5 to 8
By: HWC, Views: 11219
• The second month of development is characterized by rapid development of the head and limbs as well as continued organogenesis. • During the fifth and sixth weeks growth of the brain, and therefore head, is rapid. • Hands and feets begin to form. • During week seven, even more deve...
Advertisement