Search Results
Results for: 'ED'
By: HWC, Views: 11063
• Dissociation of the chemical substances in the body fluids can result in the production of free hydrogen ions. • The pH scale is used to measure the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. • Normal blood pH values vary around 7.4. • When hydrogen ion concentration increases, t...
By: HWC, Views: 11122
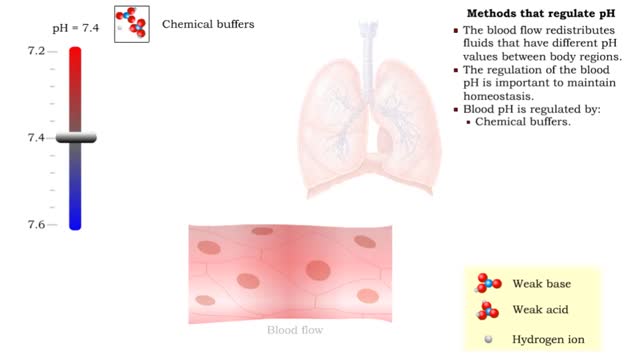
• The blood flow redistributes fluids that have different pH values between body regions. • The regulation of the blood pH is important to maintain homeostasis. • Blood pH is regulated by: • Chemical buffers. • The respiratory system. • The urinary system. • All thes...
Chemical Buffers - protein buffer, phosphate buffer system and bicarbonate buffer system
By: HWC, Views: 11169
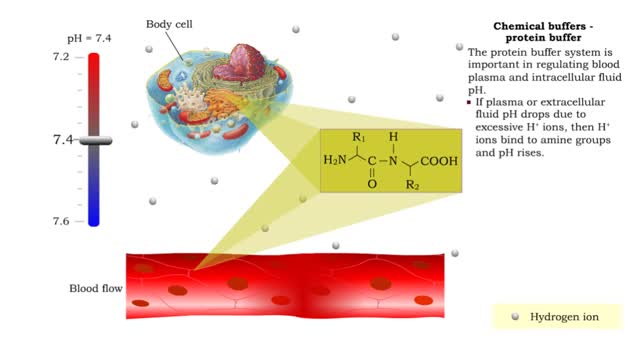
• There are a variety of chemicals in body fluids that prevent the fluids from undergoing large changes in. • These chemicals buffer or regulate fluctuations in H+ concentration. • Chemical buffers: • Bind to H+ ions when there are too many in a solution so pH remains normal. •...
Role of the respiratory system - effect of altered ventilation rates
By: HWC, Views: 11583
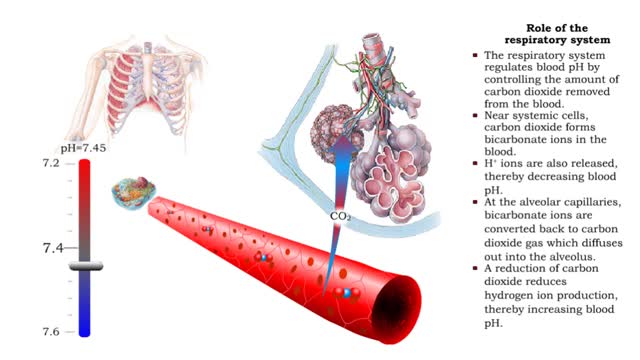
• The respiratory system regulates blood pH by controlling the amount of carbon dioxide removed from the blood. • Near systemic cells, carbon dioxide forms bicarbonate ions in the blood. H+ ions are also released, thereby decreasing blood pH. • At the alveolar capillaries, bicarbonate io...
Role of the urinary system - acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11130
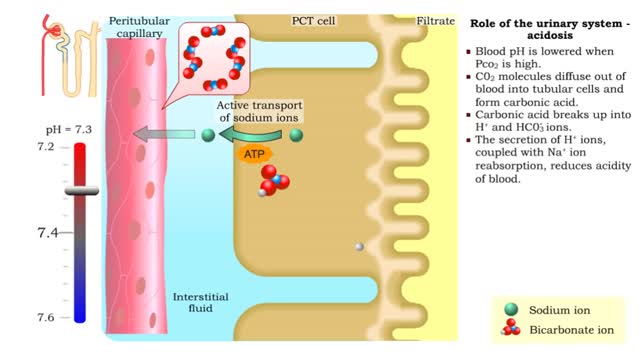
• Tubular cells of the proximal convoluted tubule and collecting tubules can alter filtrate pH and therefore blood pH. • These cells can affect blood pH with two coupled mechanisms: • Reabsorption of bicarbonate ions. • Secretion of hydrogen ions. • The reabsorption of bicarbonate...
Acid-base imbalances - respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11328
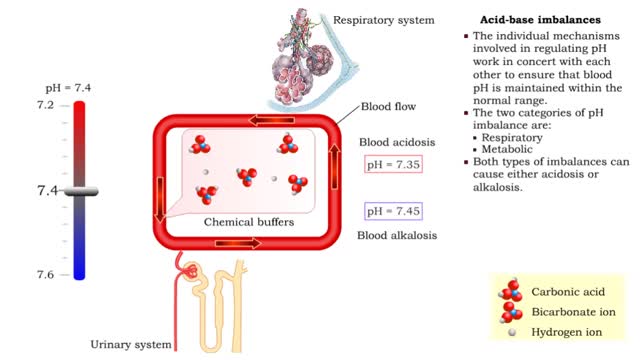
• The individual mechanisms involved in regulating pH work in concert with each other to ensure that blood pH is maintained within the normal range. • The two categories of pH imbalance are: • Respiratory • Metabolic • Both types of imbalances can cause either acidosis or alka...
Acid-base imbalances - metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11062
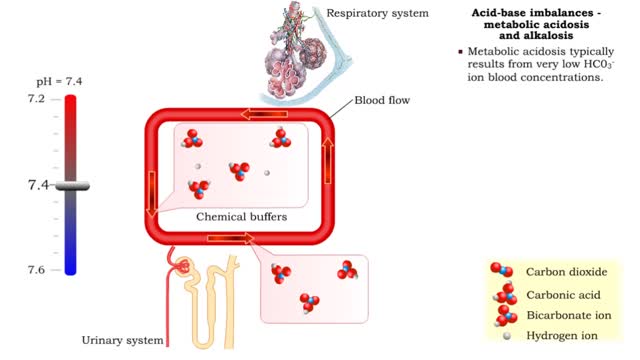
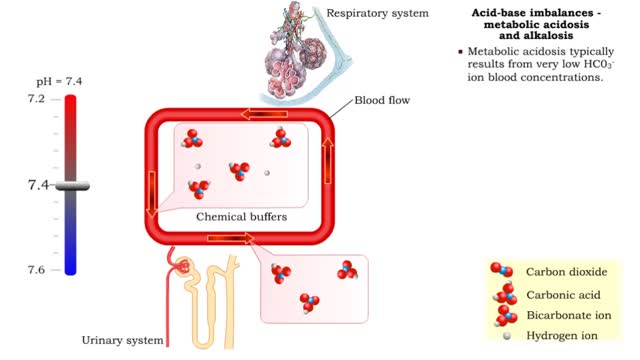
• Metabolic acidosis typically results from very low HCO3- ion blood concentrations. • Metabolic alkalosis typically results from very high HCO3- ion blood concentrations.
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11221
• When one pH balancing system is affected then the other balancing system attempts to correct, or compensate for, the pH imbalance. - Respiratory acidosis: • Excessive CO2 is present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased secretion of H+ into urine and reabsorption ...
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11182
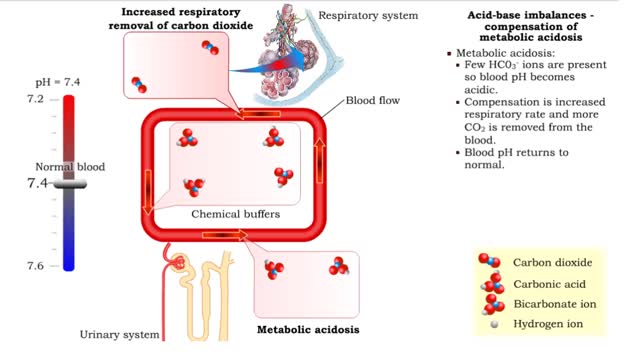
1. Metabolic acidosis: • Few HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased respiratory rate and more CO2 is removed from the blood. • Blood pH returns to normal. 2. Metabolic alkalosis: • Many HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes alkaline...
Advertisement