Search Results
Results for: 'Secondary and Tertiary Levels of Protein Structures Animation'
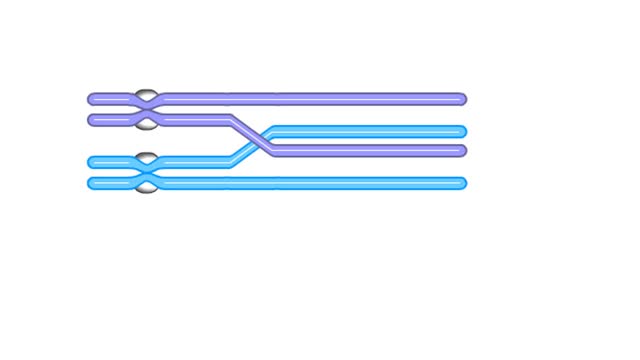
Homologous chromosomes during prophase I - Animation
By: HWC, Views: 8698
The chromosomes were duplicated during interphase and the sister chromatids are now in thin threadlike form. Each chromosome becomes zippered to its homologue, so that all four chromatids are closely aligned. The chromosomes are tightly aligned, but we will show them as separate so that y...
By: Administrator, Views: 14299
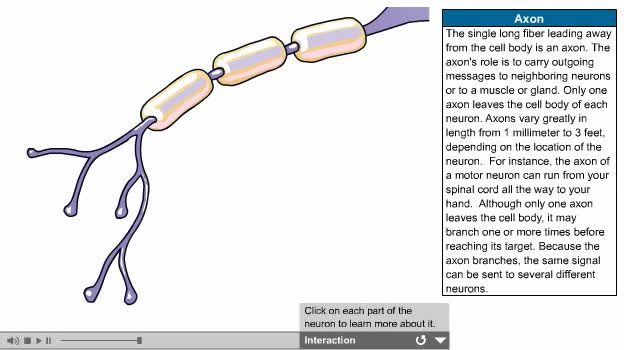
There are several types of neurons, three of which are: Motor neurons, Sensory neurons, Interneurons. The nervous system is usually described as having two interconnected divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). CNS: Includes the brain and spinal...
By: Administrator, Views: 13972
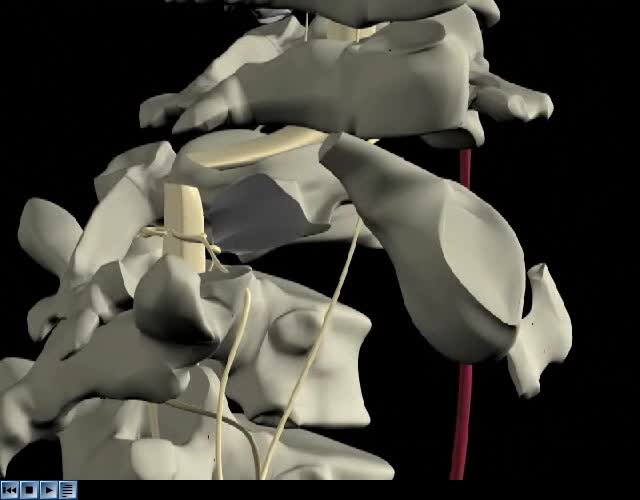
The most common cause of spinal cord injury is trauma. Spinal cord injury is most common in young, white men. Spinal cord injury can be either complete or incomplete. In complete injuries there is no function below the level of injury. In incomplete injuries there is some function remaining...
Nervous pathway to the Neuromuscular (NMJ)
By: HWC, Views: 11248
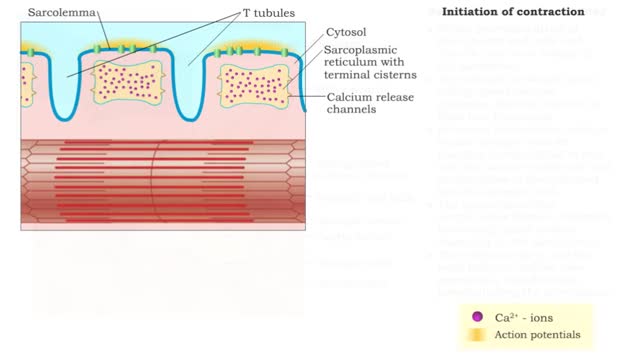
• A nervous impulse, also called an action potential, starts from the brain or spinal cord to signal skeletal muscle cell contraction. Action potentials continue along a motor neuron to the muscle cell. • The signal to contract must cross a synapse - the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) - betwe...
By: HWC, Views: 7592
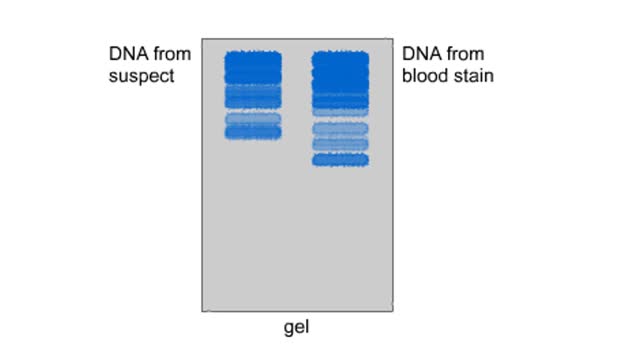
DNA fingerprinting enables a scientist to compare the DNA from two biological samples, such as a blood stain and a suspect's blood. A restriction enzyme is added to the samples to be compared. The enzyme cuts the DNA into smaller fragments. The DNA fragments are placed on an electrophor...
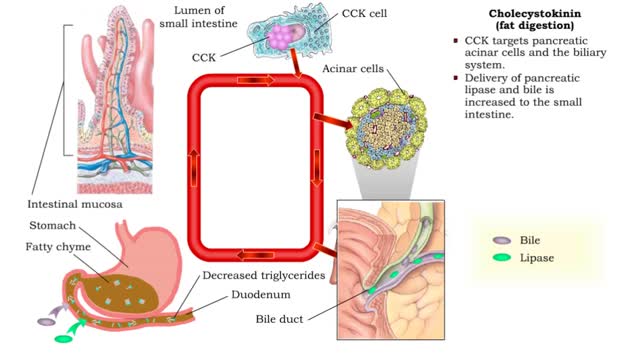
Secretin (inhibiting gastric acid secretion), Cholecystokinin (fat digestion) & Cholecystokinin
By: HWC, Views: 10601
• As chyme approaches the small intestine, secretin also targets acid-producing parietal cells in the gastric mucosa. • Increased secretin inhibits gastric add secretion. • With less gastric acid produced, the chyme going into the intestine is less acidic. • The hormone CCK also reg...
Chronology of leptin research (A history of leptin research)
By: HWC, Views: 7789
In 1950. researchers at Jackson Laboratories noticed that one of their mice had become extremely obese—it had an insatiable appetite. Intrigued, they bred a strain of mice showing this characteristic. In the late 1960s, researchers surgically connected the bloodstreams of a normal mouse and a...
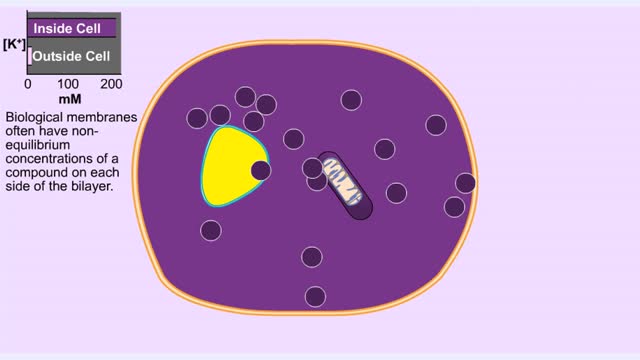
Membrane Protein and Facilitated Transport (Passive Vs Active)
By: HWC, Views: 10334
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins span the membrane, with hydrophobic amino acids interacting with the lipid bilayer and hy...
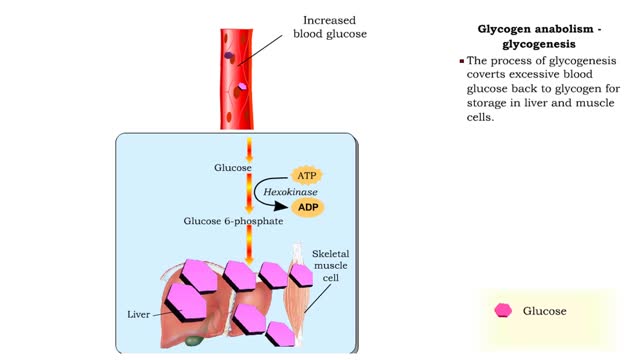
Glucose anabolism reactions: Glycogenolysis and Gluconeogenesis
By: HWC, Views: 11085
• Glucose not needed immediately is stored as glycogen. The process that creates it is glycogenesis. • When ATP is needed for body activities, stored glycogen is broken down by a process called glycogenolysis. • Glucose can be formed through two different anabolic reactions: • Glycog...
Advertisement