Search Results
Results for: 'Cardiac conductile cells'
Stroke volume - contractility definition
By: HWC, Views: 10160
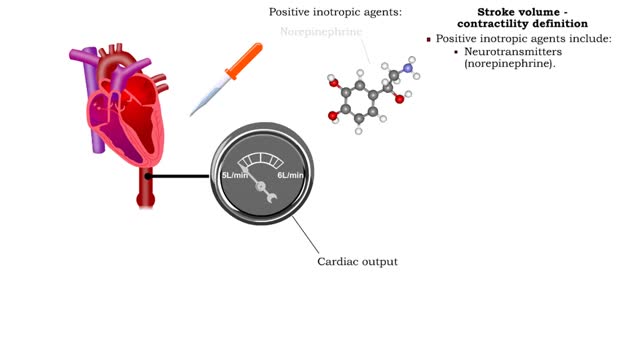
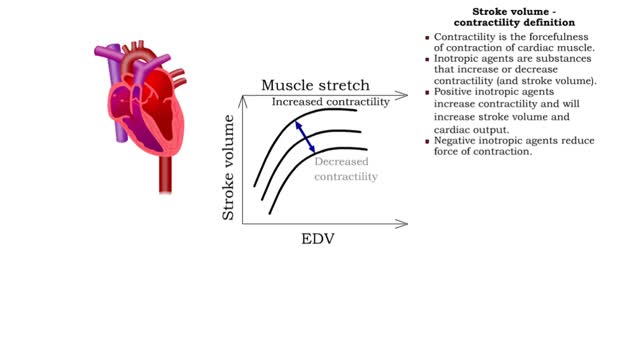
Contractility is the forcefulness of contraction of cardiac muscle. • Inotropic agents are substances that increase or decrease contractility (and stroke volume). • Positive inotropic agents increase contractility and will increase stroke volume and cardiac output. • Negative inotropi...
By: HWC, Views: 10614
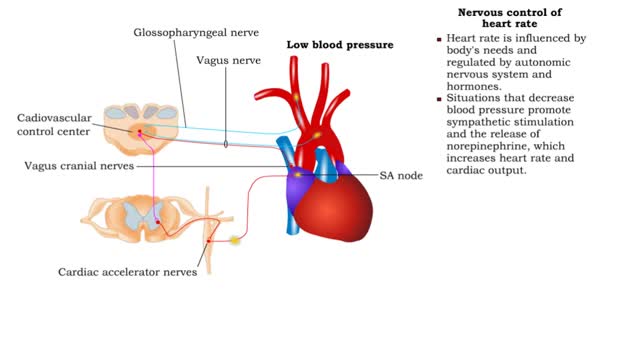
• Heart rate is determined by the rate of depolarizations of the sinoatrial (SA) node. • Cardiac output is directly proportional to heart rate, the greater the heart rate the greater the cardiac output. • Changes in heart rate are associated with exercise, stress or injury. Nervous ...
By: HWC, Views: 10475
Preload definition • Preload is the degree of stretch of cardiac muscles cells prior to contraction. • The amount of stretch is related to the end-diastolic volume[EDV]. • Increased return blood flow from the veins increases end-diastolic volume. Cardiac muscle sarcomeres stretch and ...
Types of synapses - electrical & chemical
By: HWC, Views: 10561
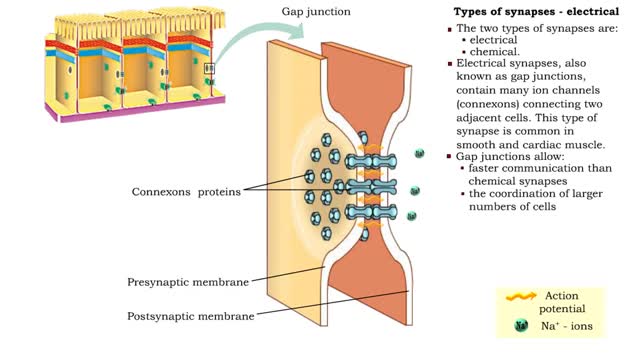
• Neurons communicate with one another or effector cells via synapses that allow information to be filtered and integrated. • The two types of synapses are: • electrical • chemical. • Electrical synapses, also known as gap junctions, contain many ion channels (connexons) conne...
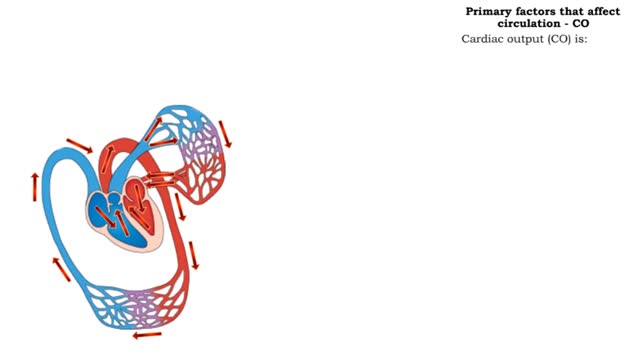
The primary factors that affect circulation - MABP, CO and SVR
By: HWC, Views: 10861
Introduction Blood flow is determined by the relative intensities of factors that drive and resist moving blood. • Cardiac output (CO) equals the mean arterial blood pressure (MABP, a driving force) divided by systemic vascular resistance (SVR, a resisting force). • Hormones and the cen...
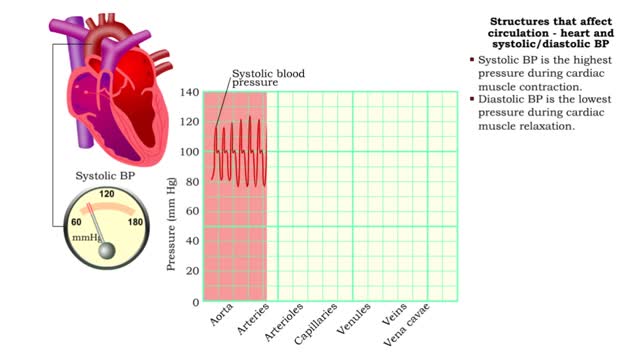
Structures that affect circulation - heart and systolic/diastolic BP
By: HWC, Views: 10479
• Heart generates blood pressure. • Arterioles produce resistance thereby regulating blood flow to tissues. • Veins store blood; kidneys regulate blood volume; both affect venous return and cardiac output. ■ Contractions of the ventricles determine blood pressure, which drives th...
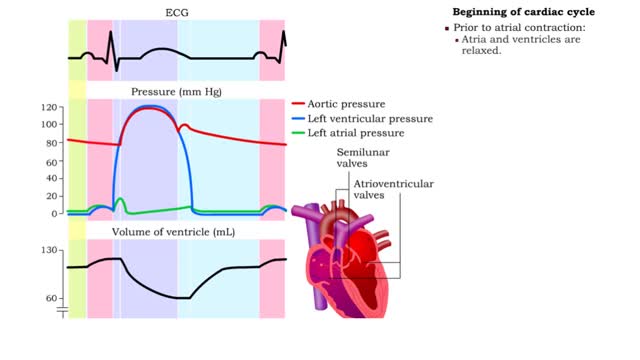
Five phases of cardiac cycle & Atrial contraction
By: HWC, Views: 10584
1. Atrial contraction (atrial systole). 2. Isovolumetric (ventricular) contraction. 3. Ventricular ejection. 4. Isovolumetric (ventricular) relaxation. 5. Passive ventricular filling. Beginning of cardiac cycle • Prior to atrial contraction: • Atria and ventricles are relaxed....
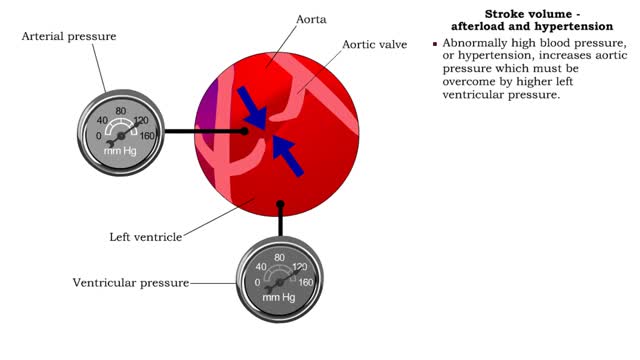
Stroke volume - afterload definition & hypertension
By: HWC, Views: 9930
• Pressure (or other resisting force) that ventricles must overcome to push open semilunar valves and eject blood. ▪ Normally, the left ventricle blood pressure must overcome arterial pressure in the aorta. ▪ Abnormally high blood pressure, or hypertension, increases aortic pressure w...
Advertisement