Search Results
Results for: 'Cardiac muscle sarcomeres'
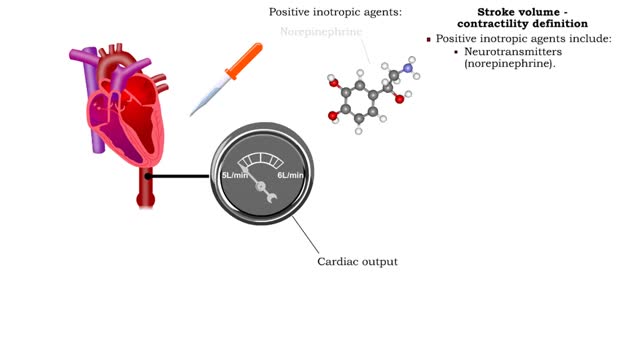
Stroke volume - contractility definition
By: HWC, Views: 10711
Contractility is the forcefulness of contraction of cardiac muscle. • Inotropic agents are substances that increase or decrease contractility (and stroke volume). • Positive inotropic agents increase contractility and will increase stroke volume and cardiac output. • Negative inotropi...
By: Administrator, Views: 13897
Three basic types of muscles: - Skeletal - Smooth - Cardiac Composed of striated or smooth muscle tissue and classified according to their functions and appearance. Skeletal Muscle: - Also known as voluntary or striated muscle. - Controlled by the conscious part of the brain and attach...
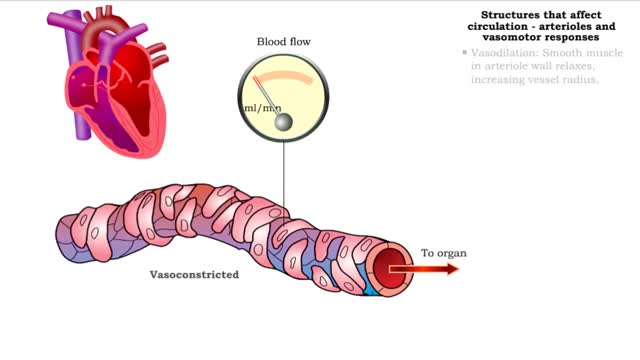
Structures that affect circulation - arterioles and vasomotor responses and venous return
By: HWC, Views: 11078
■ Small arteries and arterioles determine SVR. • Blood pressure drops significantly as blood passes through arterioles. • Decreasing arteriole radius and decreased wall elasticity are the main reasons for increased SVR. ■ Small changes in arteriole radius can cause large changes in ...
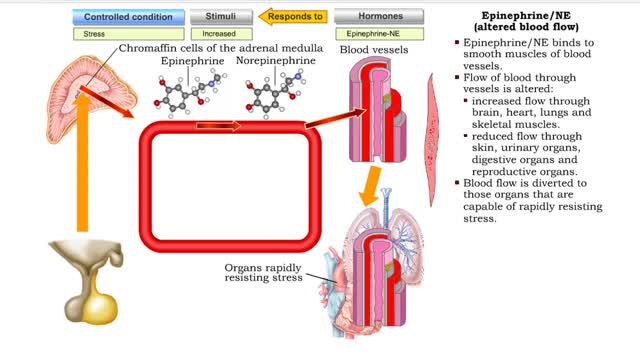
Epinephrine/NE (heart rate, altered blood flow, glycogenolysis & bronchodilation)
By: HWC, Views: 10910
• Stressors trigger increased sympathetic stimulation from the hypothalamus to the chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla. • This causes the immediate release of epinephrine and norepinephrine (NE). • Epinephrine/NE binds to the cardiac muscles of the heart. • Cardiac muscle cells ...
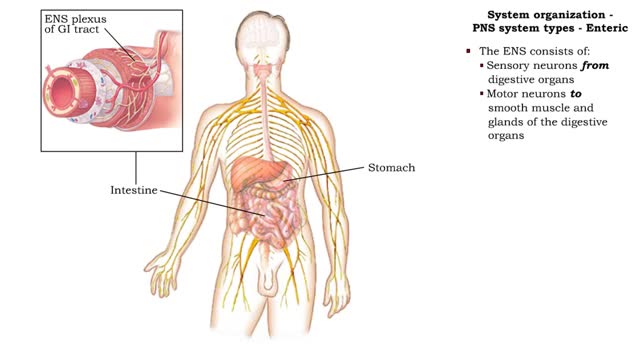
System organization - PPM system types (Somatic, Autonomic & Enteric) and Reflex arc types
By: HWC, Views: 11242
• The PNS consists of all nervous tissue outside of the CNS. • It is divided into three functional components: • Somatic nervous system (SNS) • Autonomic nervous system (ANS) • Enteric nervous system (ENS) • The SNS consists of: • Sensory neurons from skeletal muscles ...
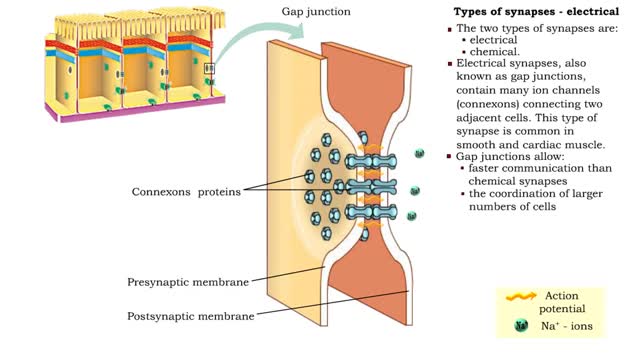
Types of synapses - electrical & chemical
By: HWC, Views: 11117
• Neurons communicate with one another or effector cells via synapses that allow information to be filtered and integrated. • The two types of synapses are: • electrical • chemical. • Electrical synapses, also known as gap junctions, contain many ion channels (connexons) conne...
By: HWC, Views: 10796
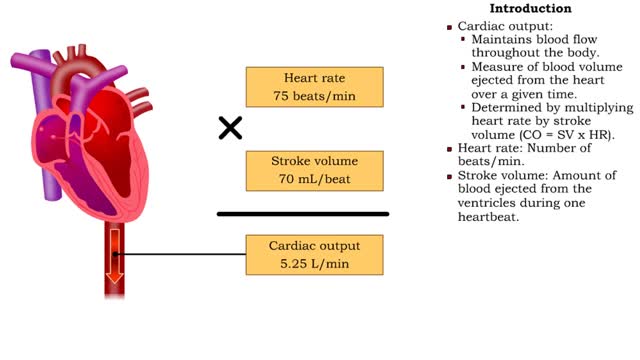
• Cardiac output: • Maintains blood flow throughout the body. • Measure of blood volume ejected from the heart over a given time. • Determined by multiplying heart rate by stroke volume (CO = SV x HR). • Heart rate: Number of beats/min. • Stroke volume: Amount of blood eject...
By: Administrator, Views: 14182
Diastole and systole are two phases of the cardiac cycle. They occur as the heart beats, pumping blood through a system of blood vessels that carry blood to every part of the body. Systole occurs when the heart contracts to pump blood out, and diastole occurs when the heart relaxes after contract...
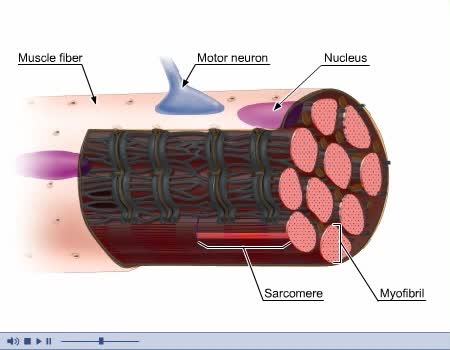
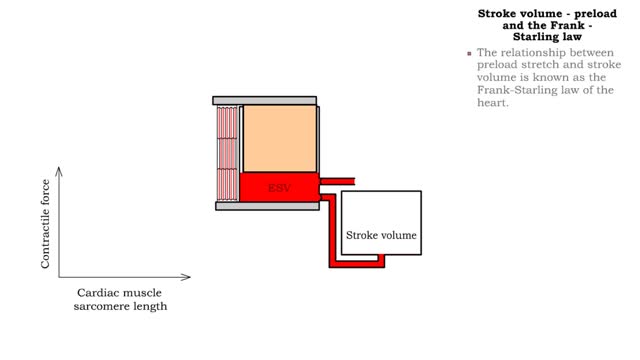
Stroke volume - preload, sarcomere length and Frank -Starling law
By: HWC, Views: 10697
• Sarcomere length affects muscle tension and the force of contraction. • Increased muscle stretch (increased sarcomere length) at the beginning of contraction increases tension produced during the contraction. • A more forceful contraction ejects more blood, thus increasing stroke volu...
Advertisement