Search Results
Results for: 'Ethanol Reverse Osmosis Animation'
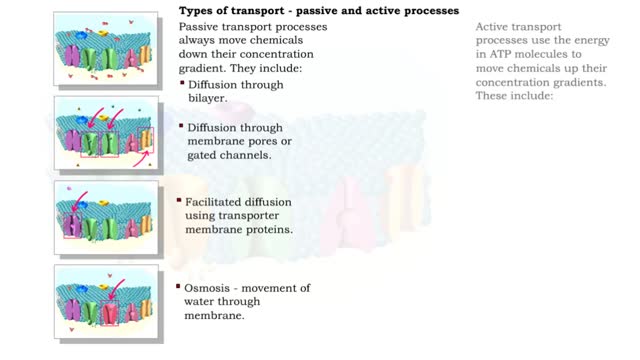
Type of Transport - Active and Passive Processes
By: HWC, Views: 11392
Active transport moves materials from lower to a higher concentration, while passive transport moves materials from higher to lower concentration. Active transport requires energy to proceed, while passive transport does not require the input of extra energy to occur. Transport processes that ...
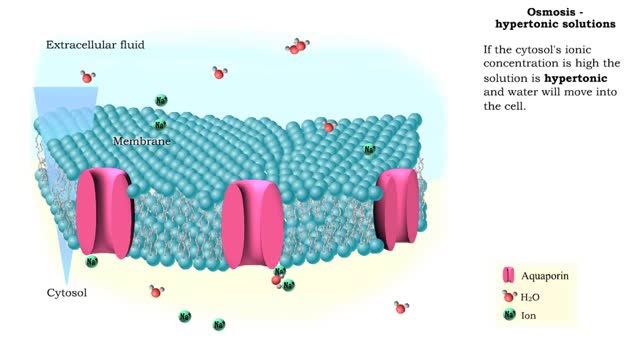
Osmosis - Isotonic, Hypotonic, and Hypertonic Solutions
By: HWC, Views: 11173
Isotonic: Equal Water moves in and out of the cell at an equal rate. The cell remains unchanged. Hypotonic: "hypo" hippo Water moves into the cell, making it swell and get fat (like a hippo). Eventually the cell can rupture and burst (aka lyse). Hypertonic: "like a raisin" Water leaves...
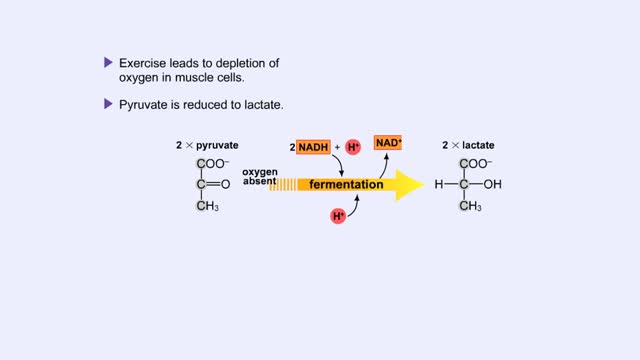
Fermentation - When Oxygen Is Absent, Pyruvate to Lactate & Pyruvate to Ethanol
By: HWC, Views: 10564
Pyruvate is the end product of glycolysis. If oxygen is present, pyruvate enters the mitochondrion where further energy yielding reactions of the Krebs cycle will take place. However, if oxygen is not present, pyruvate will enter a pathway called fermentation. This pathway regenerates NAD+ fro...
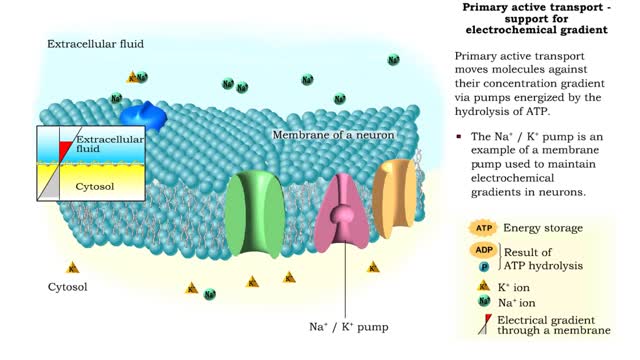
Primary Active Transport - electrochemical gradient and ion transport / water movement
By: HWC, Views: 11257
Energy derived from ATP changes the shape of a transporter protein which pumps a substance across a plasma membrane against its concentration gradient An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consis...
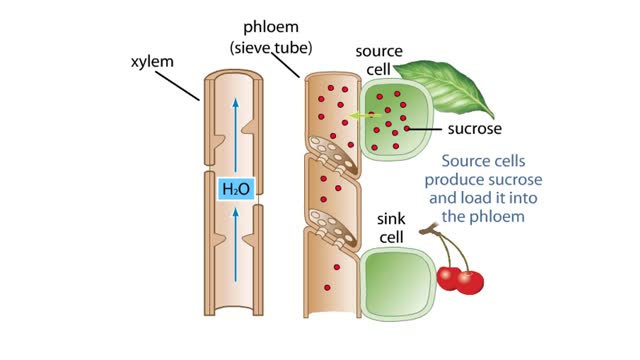
The Pressure Flow Model in a Plant
By: HWC, Views: 10457
The vascular system of plants has two transport tissues, called xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals, while phloem transports a variety of dissolved substances, including sugars and amino acids, throughout the plant. Water in the xylem always moves up, in the direction from th...
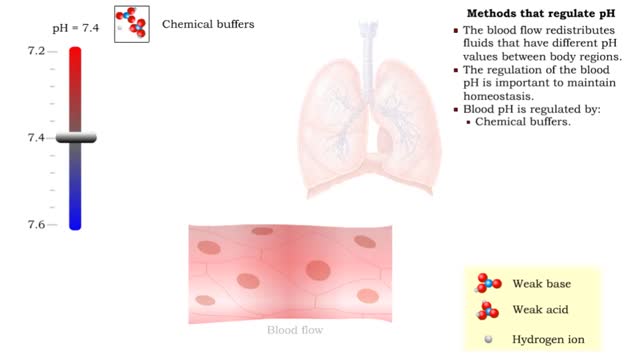
By: HWC, Views: 11185
• The blood flow redistributes fluids that have different pH values between body regions. • The regulation of the blood pH is important to maintain homeostasis. • Blood pH is regulated by: • Chemical buffers. • The respiratory system. • The urinary system. • All thes...
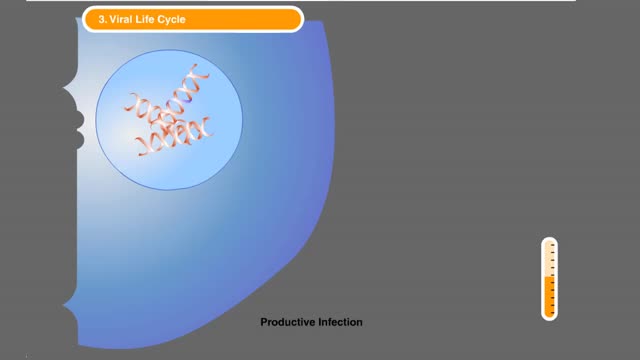
HIV Infection: Viral life cycle
By: HWC, Views: 10492
The series of steps that HIV follows to multiply in the body. The process begins when HIV encounters a CD4 cell. The seven steps in the HIV life cycle are: 1) binding; 2) fusion; 3) reverse transcription; 4) integration; 5) replication; 6) assembly; and 7) budding. Many viruses f...
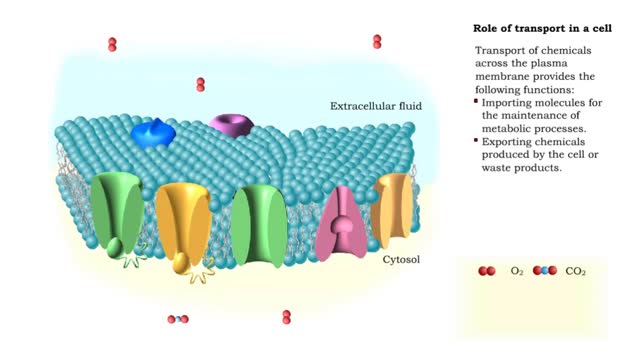
By: HWC, Views: 11212
Transport of chemicals across the plasma membrane provides the following functions: Importing molecules for the maintenance of metabolic processes. Exporting chemicals produced by the cell or waste products. Communicating with other cells, allowing for the generation and conduction of a...
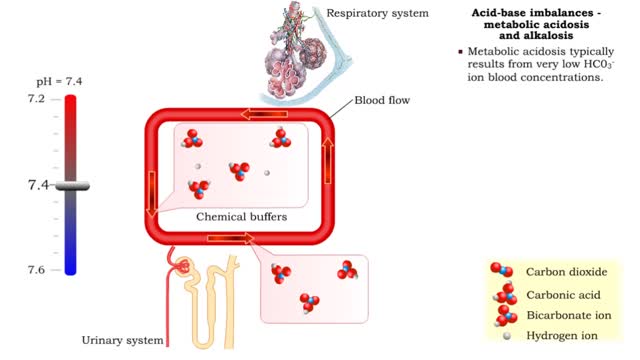
Acid-base imbalances - metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11146
• Metabolic acidosis typically results from very low HCO3- ion blood concentrations. • Metabolic alkalosis typically results from very high HCO3- ion blood concentrations.
Advertisement