Search Results
Results for: 'Stomach peristalsis'
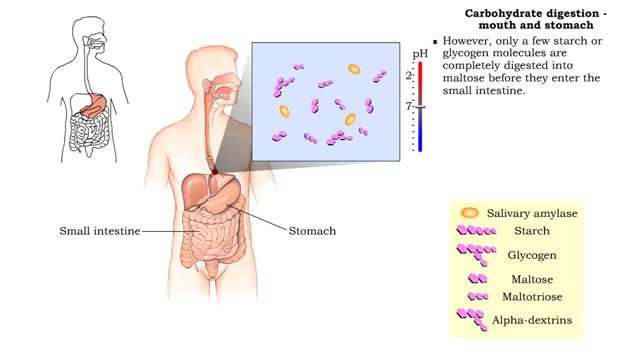
Carbohydrate digestion - mouth and stomach & pancreas and small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 11175
• Digestion of complex carbohydrates (starches and glycogen) involves: • Amylases produced by the salivary glands and pancreas. • Brush-border enzymes in small intestine. • In the mouth, amylase from the parotid and submandibular salivary glands begins carbohydrate digestion. â€...
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
By: Administrator, Views: 14301
Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, is a digestive disorder that affects the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), the ring of muscle between the esophagus and stomach. Many people, including pregnant women, suffer from heartburn or acid indigestion caused by GERD.
By: Administrator, Views: 14580
Digestive system contains both primary and accessory organs for the conversion of food and fluids into a semiliquid that can be absorbed for the body to use. Three main functions: - Digestion - Absorption - Elimination With aging: - Digestive system becomes less motile. - Glandular sec...
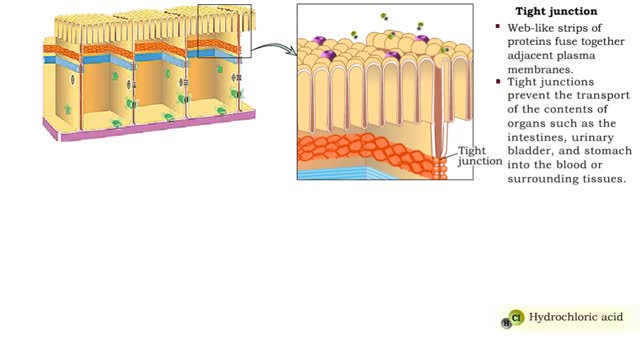
Junction Types - Tight and Adherens Junctions
By: HWC, Views: 11745
Many tissues contain in tercellular junctions between cells. 1. Tight junction 2. Adherens junction 3. Desmosome 4. Hemidesrnosome 5. Gap junction 1. Tight junction • Web-like strips of proteins fuse together adjacent plasma membranes. • Tight junctions prevent the transport...
The pH scale - Strong acids and Weak acids
By: HWC, Views: 11422
The pH scale • Expresses concentration of H+. • range: 0-14. • 7 is neutral. • Less 7 is acid. • greater 7 is basic (alkaline). Strong acids - role in the body ■In strong acids all molecules dissociate. ■HC1 is highly acidic and found only in the stomach. • H...
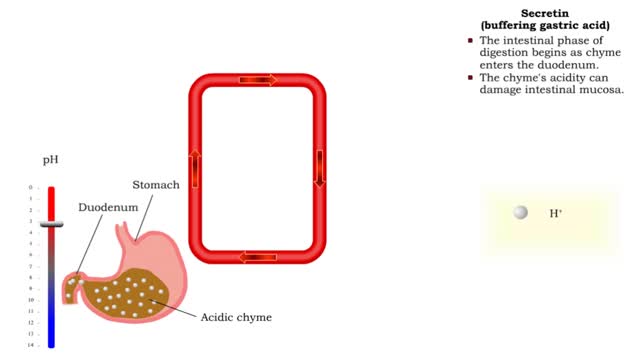
Gastrin (gastric emptying) & Secretin (buffering gastric acid)
By: HWC, Views: 10882
• Gastrin also binds to the smooth muscle cells in the stomach causing: • Increased gastric motility. • Opening of pyloric sphincter. • Increased gastric emptying. • The intestinal phase of digestion begins as chyme enters the duodenum. • The chyme's acidity can damage int...
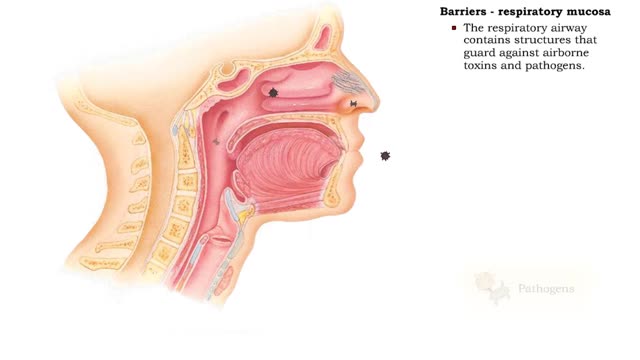
Barriers - eye structures, digestive mucosa, respiratory mucosa & genitourinary mucosa
By: HWC, Views: 11601
• Eyebrows, eyelids, eyelashes and conjunctiva serve to trap microbes preventing their invasion. • Tearing (lacrimation) is a protective mechanism that washes away microbes that attempt to enter the eyes. • Salts, mucus, and lysozymes in tears neutralize substances and bacteria. â€...
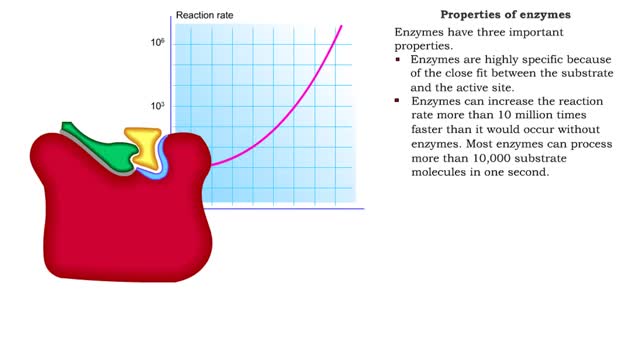
Enzyme structure - Properties of enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 11287
â– Enzymes are proteins that catalyze reactions. â– Some enzymes have two parts: a protein or apoenzyme and a non-protein or cofactor. â– Cofactor can be a metal ion or another organic molecule called a coenzyme. â– Coenzymes often come from vitamins. â– Cofactors affect the shape of...
By: Administrator, Views: 15991
Hyperglycemia means high (hyper) glucose (gly) in the blood (emia). Your body needs glucose to properly function. Your cells rely on glucose for energy. Hyperglycemia is a defining characteristic of diabetes—when the blood glucose level is too high because the body isn't properly using or doesn...
Advertisement