Search Results
Results for: 'Wine Industry and Reverse Osmosis'
By: HWC, Views: 10341
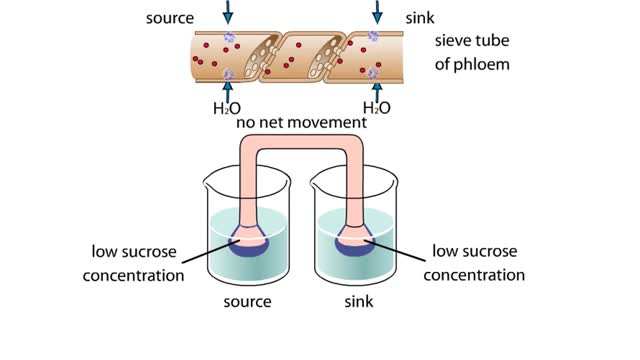
This apparatus of beakers A and funnels simulates the flow of a sucrose solution in the phloem of a plant. The funnels and connecting tube represent a sieve tube of the phloem. Differentially permeable membranes cap the funnels at the source and sink ends, allowing water, but not sucrose, to cros...
Condensation and Hydrolysis Animation
By: HWC, Views: 4871
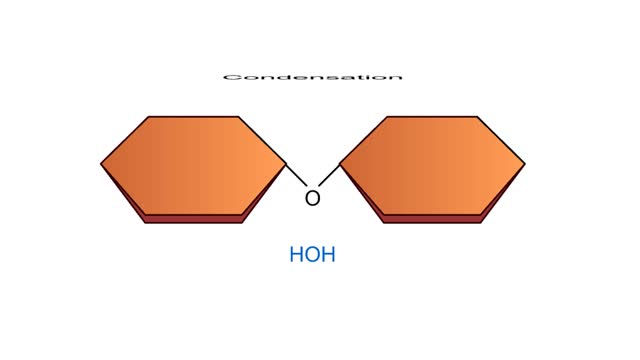
A condensation reaction joins two molecules together to form one larger molecule. An enzyme removes a hydroxyl group from one molecule and a hydrogen atom from another, then speeds the formation of a bond between the two molecules at their exposed sites. Typically the discarded atoms join t...
Primary Active Transport - electrochemical gradient and ion transport / water movement
By: HWC, Views: 11243
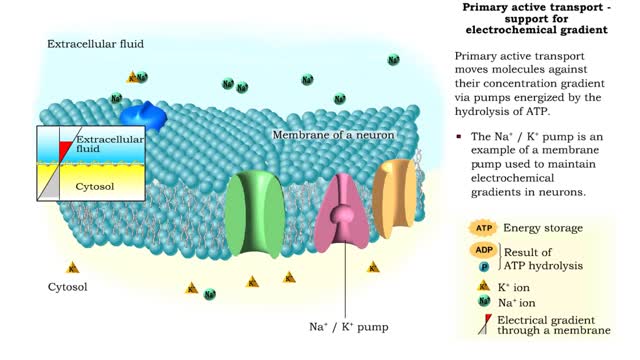
Energy derived from ATP changes the shape of a transporter protein which pumps a substance across a plasma membrane against its concentration gradient An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consis...
The Pressure Flow Model in a Plant
By: HWC, Views: 10443
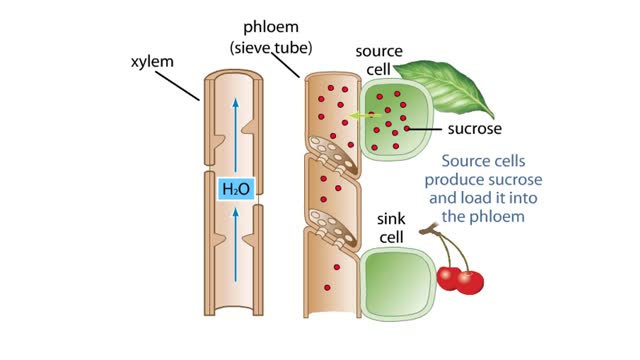
The vascular system of plants has two transport tissues, called xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals, while phloem transports a variety of dissolved substances, including sugars and amino acids, throughout the plant. Water in the xylem always moves up, in the direction from th...
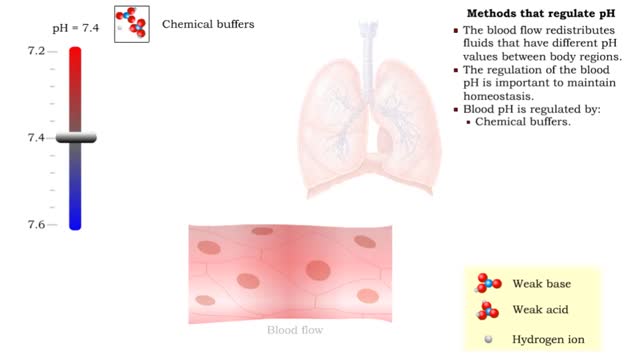
By: HWC, Views: 11175
• The blood flow redistributes fluids that have different pH values between body regions. • The regulation of the blood pH is important to maintain homeostasis. • Blood pH is regulated by: • Chemical buffers. • The respiratory system. • The urinary system. • All thes...
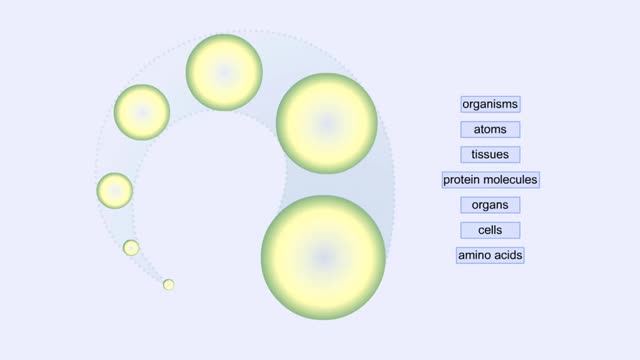
Proteins Defined, Hierarchy & Composition of Cells
By: HWC, Views: 10553
Proteins are long chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Together with the other three biological macromolecules—carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids—proteins are the building blocks of cells. Proteins are the most complex and abundant biological macromolecules in cel...
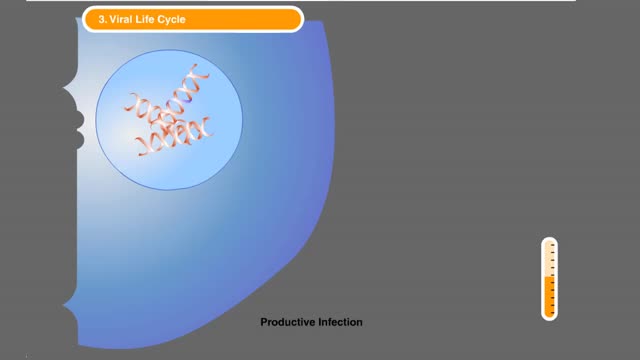
HIV Infection: Viral life cycle
By: HWC, Views: 10478
The series of steps that HIV follows to multiply in the body. The process begins when HIV encounters a CD4 cell. The seven steps in the HIV life cycle are: 1) binding; 2) fusion; 3) reverse transcription; 4) integration; 5) replication; 6) assembly; and 7) budding. Many viruses f...
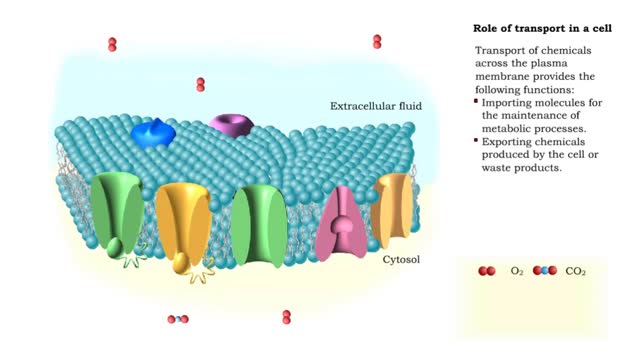
By: HWC, Views: 11198
Transport of chemicals across the plasma membrane provides the following functions: Importing molecules for the maintenance of metabolic processes. Exporting chemicals produced by the cell or waste products. Communicating with other cells, allowing for the generation and conduction of a...
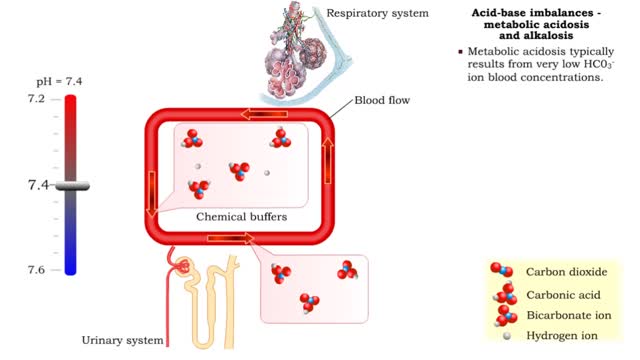
Acid-base imbalances - metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11136
• Metabolic acidosis typically results from very low HCO3- ion blood concentrations. • Metabolic alkalosis typically results from very high HCO3- ion blood concentrations.
Advertisement