Search Results
Results for: 'acidic ketone'
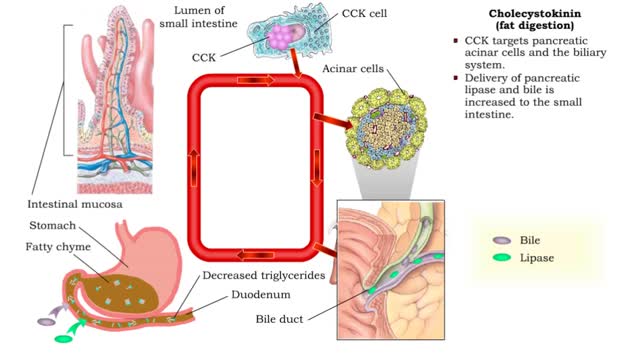
Secretin (inhibiting gastric acid secretion), Cholecystokinin (fat digestion) & Cholecystokinin
By: HWC, Views: 10865
• As chyme approaches the small intestine, secretin also targets acid-producing parietal cells in the gastric mucosa. • Increased secretin inhibits gastric add secretion. • With less gastric acid produced, the chyme going into the intestine is less acidic. • The hormone CCK also reg...
Digestive chemicals - water, gastric acid, bile & bicarbonate
By: HWC, Views: 10753
• Water is the most abundant molecule in ingested fluids. • Water plays a primary role in hydrolytic digestive reactions. • Helps liquefy and transport digestive foodstuffs down the tract. • Transports secretions from accessory digestive organs to gastrointestinal tract. • Aids ...
By: HWC, Views: 10873
Acids and bases are found all around your house. For example, if you open your pantry or refrigerator, you might see a lot of acids. Fruit juice, soda pop, vinegar, and milk are all examples of acids. The word acid actually comes from a Latin term meaning ''sour.'' Many materials, like sugar for ...
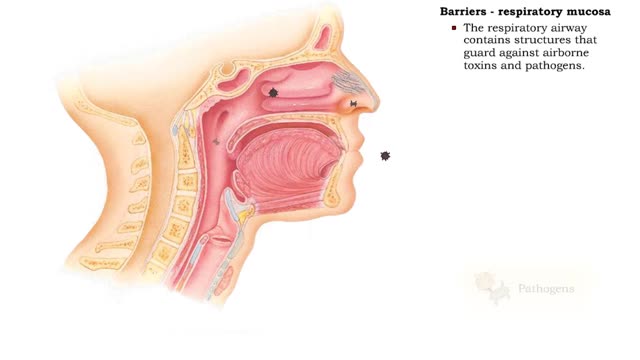
Barriers - eye structures, digestive mucosa, respiratory mucosa & genitourinary mucosa
By: HWC, Views: 11296
• Eyebrows, eyelids, eyelashes and conjunctiva serve to trap microbes preventing their invasion. • Tearing (lacrimation) is a protective mechanism that washes away microbes that attempt to enter the eyes. • Salts, mucus, and lysozymes in tears neutralize substances and bacteria. â€...
Advertisement