Search Results
Results for: 'complex carbohydrates'
By: HWC, Views: 5295
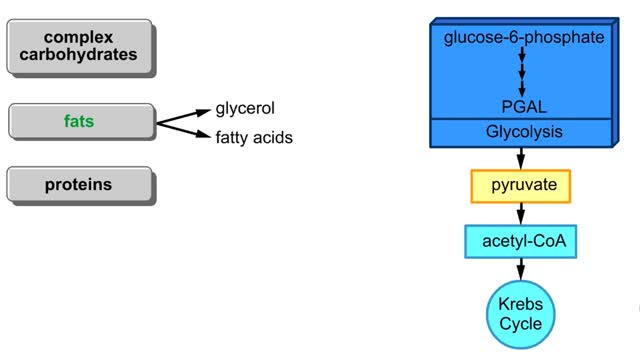
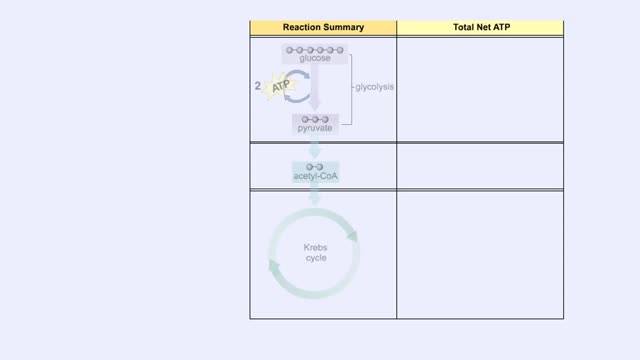
Points at which organic compounds enter the reaction stages of aerobic respiration. Complex carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, such as glucose. They become the substrates for glycolysis. If your body doesn't need to burn glucose for energy, glucose-6-phosphate can be co...
Types of antimicrobial substances (interferons & complement protein)
By: HWC, Views: 11152
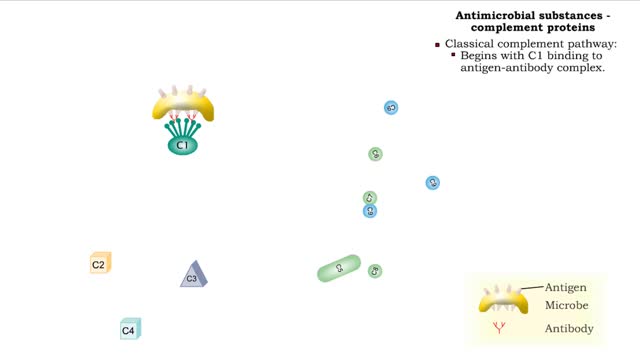
• Found in blood and interstitial fluids. • Discourage microbial growth. • Include interferon and complement proteins. • Produced and released by virus-infected lymphocytes. • Enter new cells and inhibit viral replication. • Act against a large variety of viruses (non-speci...
Michaelis–Menten equation & Kinetic parameters
By: HWC, Views: 10903
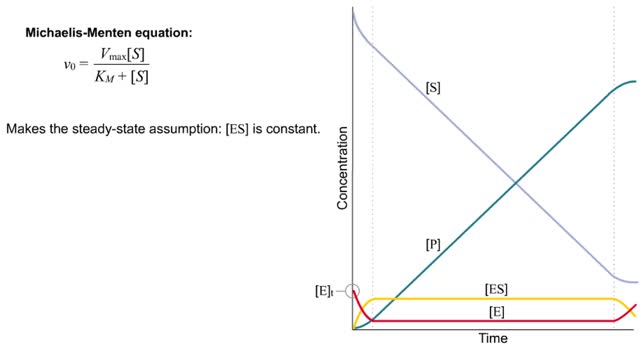
The Michaelis–Menten equation is the rate equation for a one-substrate enzyme-catalyzed reaction. This equation relates the initial reaction rate (v0), the maximum reaction rate (Vmax), and the initial substrate concentration [S] through the Michaelis constant KM—a measure of the substrat...
By: Administrator, Views: 14038
Wound healing is a complex process in which the skin, and the tissues under it, repair themselves after injury. In this article, wound healing is depicted in a discrete timeline of physical attributes constituting the post-trauma repairing process.
By: Administrator, Views: 14100
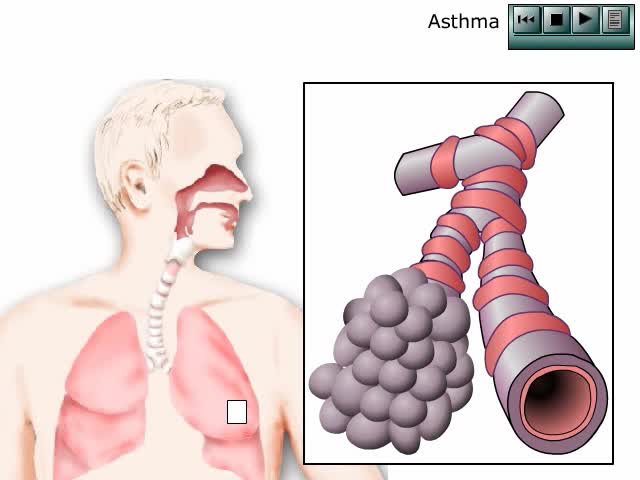
Asthma is a common chronic disease worldwide and affects approximately 26 million persons in the United States. It is the most common chronic disease in childhood, affecting an estimated 7 million children. The pathophysiology of asthma is complex and involves airway inflammation, intermittent ai...
The Pressure Flow Model in a Plant
By: HWC, Views: 10458
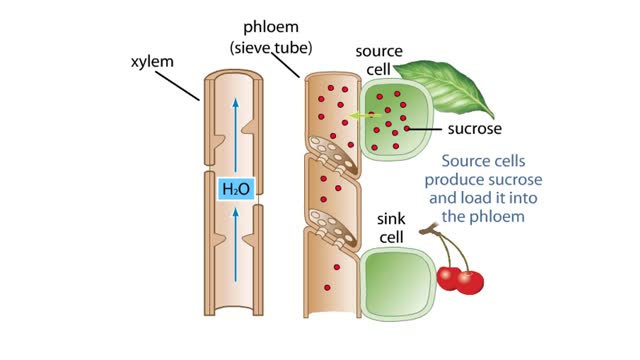
The vascular system of plants has two transport tissues, called xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals, while phloem transports a variety of dissolved substances, including sugars and amino acids, throughout the plant. Water in the xylem always moves up, in the direction from th...
Types of energy transfer reactions: oxidation-reduction reactions and ATP generation reactions
By: HWC, Views: 11715
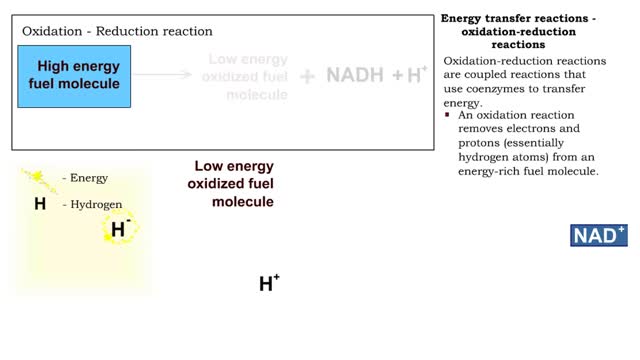
■ Metabolism balances anabolic and catabolic reactions. ■ Anabolism is energy transfer from ATP to simpler molecules in order to build them up into larger, more complex molecules. ■ Catabolism is breaking down larger, more complex molecules, usually to transfer energy from them in order...
ETC Protein Complexes & Chemiosmosis (Total ATP Production and ATP Synthase)
By: HWC, Views: 10775
You will notice that FADH2 donates two electrons further downstream than NADH. This results in only two protons being pumped across the inner membrane. The final electron acceptor for these transported electrons is oxygen. Oxygen receives these electrons, plus protons from the aqueous matrix. ...
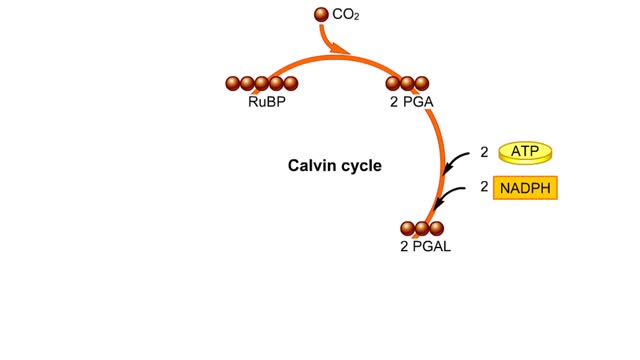
By: HWC, Views: 10899
he light-independent reactions make sugars by way of a cyclic pathway called the Calvin cycle. The cycle begins when rubisco attaches a carbon from carbon dioxide to ribulose bisphosphate. The molecule that forms splits into two molecules of PGA. Each PGA gets a phosphate group from ATP a...
Advertisement