Search Results
Results for: 'polypeptide chain'
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Proteins
By: HWC, Views: 10386
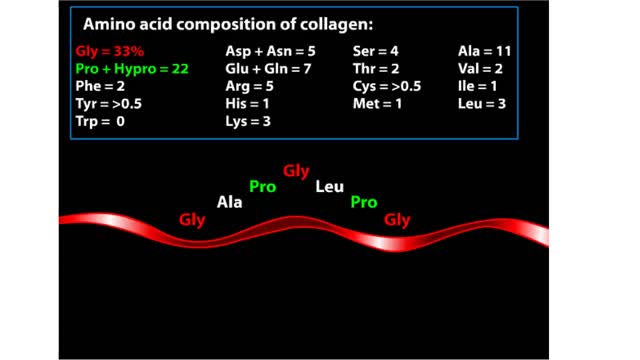
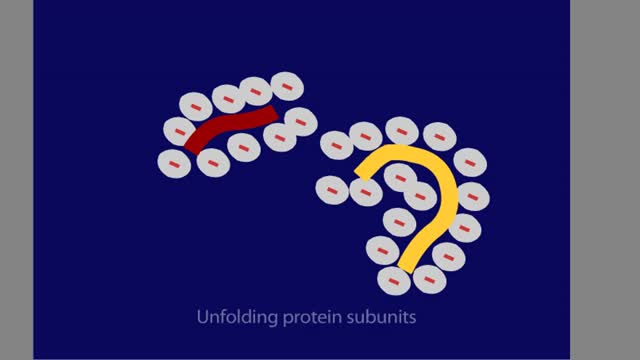
Proteins are chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. The 20 different amino acids used to make all proteins differ only in their side chains, and the properties of these side chains account for the great diversity of protein structure and function. Collagen is an example of how a prote...
Anatomy and Chemical Makeup of a Single Hair (Animation)
By: HWC, Views: 9250
The hair's outer cuticle surrounds hair cells filled with tough keratin macrofibrils. Each macrofibril consists of smaller microfibrils. A microfibril is made up of three keratin polypeptide chains. The chains are linked together by disulfide bonds. A hair consists of keratin chains held...
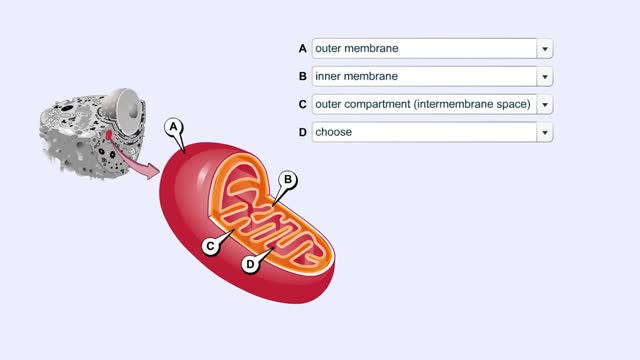
Mitochondrial Structure & ETC Protein Complexes (Protein Complexes and Electron Transport)
By: HWC, Views: 10476
The energy carrying molecules, NADH and FADH2, that were generated in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, now are processed in the mitochondria where their high energy electrons are deposited in an electron chain complex located in the inner mitochondrial membranes. These high-energy electrons now dr...
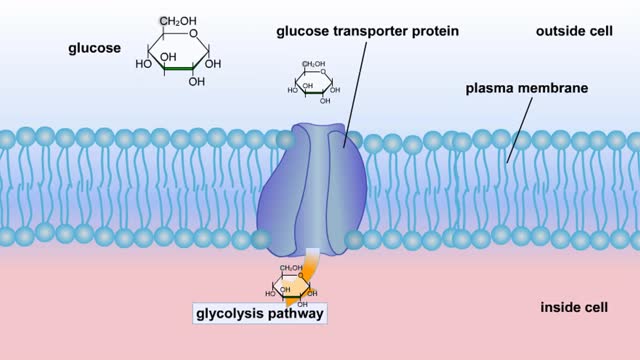
Cellular Respiration & Glucose Mobilization (Glucose transport & Phosphorylation of Glucose)
By: HWC, Views: 10646
Glucose is completely broken down into CO2 and H2O during the process of cellular respiration, which includes 3 stages: 1) glycolysis; 2) the Krebs Cycle; and 3) the electron transport chain. Glucose enters this energy yielding pathway of cellular respiration in the first stage known as...
Power Supply Polyacrylamide Gel Protein Sample
By: HWC, Views: 10167
SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is a powerful tool, which resolves proteins according to their molecular weights. Because proteins differ in size, shape, and charge, a protein sample is first denatured with the anionic detergent SDS. When the sample is heated, the SDS molecules bind to ...
By: HWC, Views: 11164
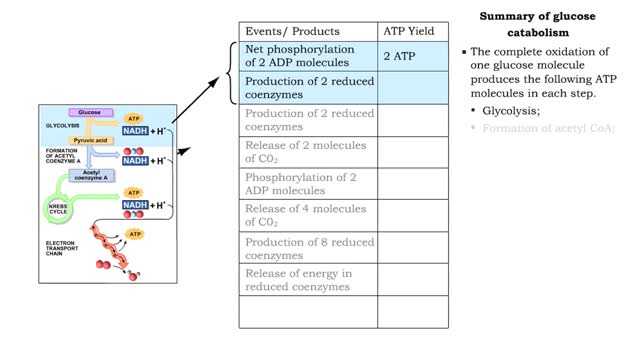
■ The complete oxidation of one glucose molecule produces the following ATP molecules in each step. • Glycolysis; • Formation of acetyl CoA; • Krebs cycle; • Electron transport chain. ■ In addition, glucose catabolism produces six CO2 molecules and water.
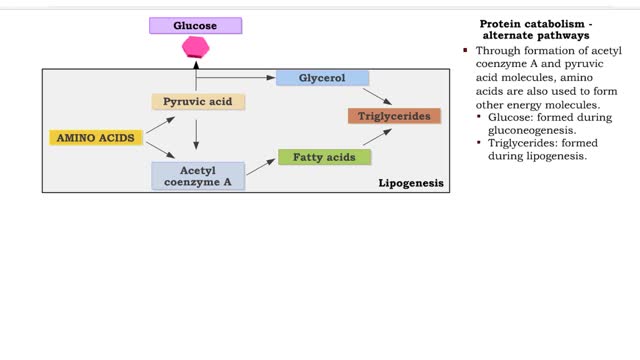
Protein catabolism (Krebs cycle) and Protein anabolism (protein synthesis)
By: HWC, Views: 11427
• Deaminated acids are brought into the Krebs cycle to be oxidized to CO2 and H2O. • Before entering the Krebs cycle, the deaminated acids are converted into intermediate products (pyruvic acid, acetyl coenzyme A, carbonic acids). • In the Krebs cycle, amino acids are oxidized to form r...
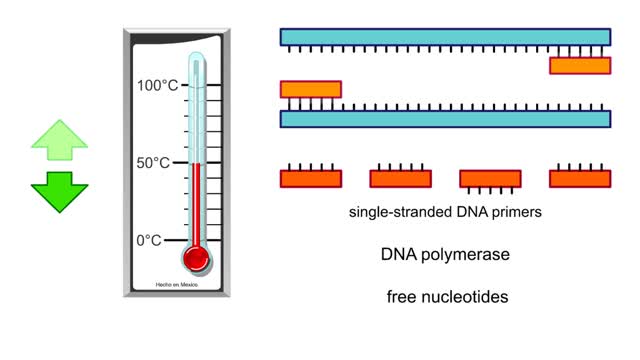
Polymerase chain reaction PCR - Animation
By: HWC, Views: 4821
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method that amplifies fragments of DNA. The purpose of PCR is to create copies of a specific region of DNA. To use this technique, researchers must know the base sequences at either end of the region of interest. They use this information to create...
Digestive chemicals - water, gastric acid, bile & bicarbonate
By: HWC, Views: 10622
• Water is the most abundant molecule in ingested fluids. • Water plays a primary role in hydrolytic digestive reactions. • Helps liquefy and transport digestive foodstuffs down the tract. • Transports secretions from accessory digestive organs to gastrointestinal tract. • Aids ...
Advertisement