Search Results
Results for: 'polypeptide chain'
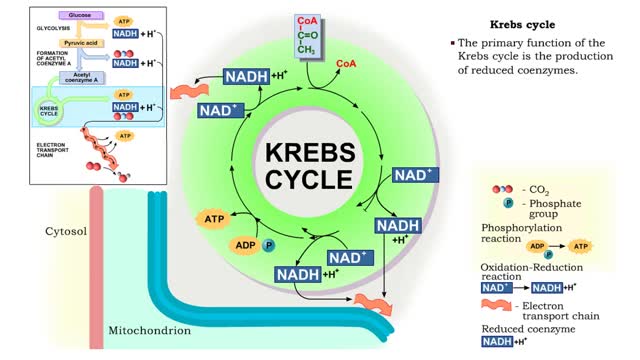
Krebs cycle : Formation of acetyl coenzyme A and Electron transport chain
By: HWC, Views: 11284
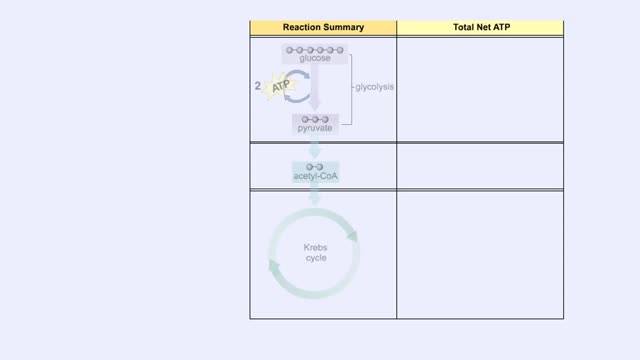
The oxidation of glucose to produce ATP is cellular respiration. Four sets of reactions are involved: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Krebs cycle reactions Electron transport chain reactions • The second pathway of glucose catabolism, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, is a transi...
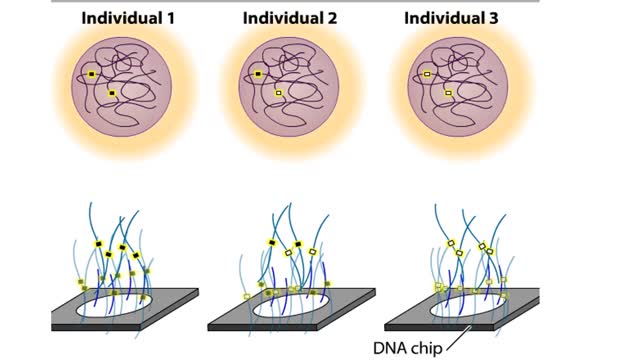
SNP Polymorphysim Microarray Chip - How to Test a Person's DNA
By: HWC, Views: 10422
To test a person's DNA, a researcher first needs a source of tissue. Most of the cells in a blood sample are red blood cells, which lack nuclei, but there are also a number of white blood cells, which do contain nuclei and chromosomal DNA. If we could see a particular DNA sequence in these cel...
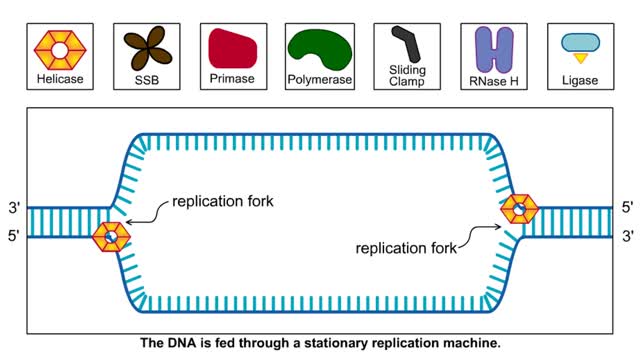
The Lagging Strand in DNA Replication and Replication in Action
By: HWC, Views: 10563
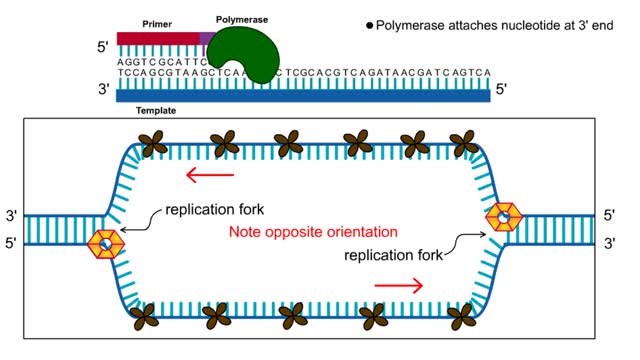
The lagging strand is the strand of nascent DNA whose direction of synthesis is opposite to the direction of the growing replication fork. DNA backbones run in opposite directions, the strands in a DNA molecule are oriented antiparallel to one another. New DNA is made by enzymes called DNA...
By: HWC, Views: 10469
First step: strands are separated • Helicase unwinds the DNA double helix at the replication fork • SSBs coat the single strands to prevent reannealing • Polymerase attaches nucleotide at 3' end • Synthesis is in 5' to 3' direction DNA Polymerase: • Only extends nucleic ac...
ETC Protein Complexes & Chemiosmosis (Total ATP Production and ATP Synthase)
By: HWC, Views: 10766
You will notice that FADH2 donates two electrons further downstream than NADH. This results in only two protons being pumped across the inner membrane. The final electron acceptor for these transported electrons is oxygen. Oxygen receives these electrons, plus protons from the aqueous matrix. ...
Nervous pathway to the Neuromuscular (NMJ)
By: HWC, Views: 11555
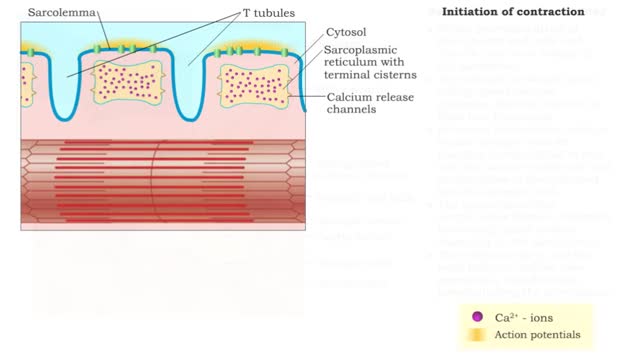
• A nervous impulse, also called an action potential, starts from the brain or spinal cord to signal skeletal muscle cell contraction. Action potentials continue along a motor neuron to the muscle cell. • The signal to contract must cross a synapse - the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) - betwe...
How proteins function? How do proteins work?
By: HWC, Views: 10728
How proteins function is really about how proteins "do work" in cells. How do proteins work? Let's start thinking about protein function by looking at something important to you: your hair. Keratin is a structural protein that is composed of 2 intertwined or helical strands. Keratin is also f...
Lipid catabolism ( ketogenesis and oxidation of glycerol) and Lipid anabolism (lipogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 11406
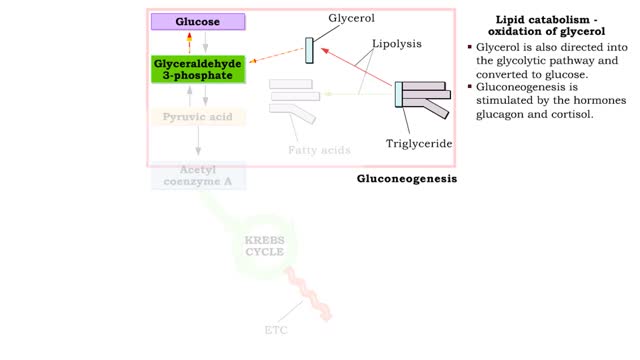
• During excessive beta oxidation, the two-carbon fatty acid fragments are converted into acidic ketone bodies. • Ketosis, the overproduction of ketone bodies, can lead to acidosis (ketoacidosis) of the blood. • After lipolysis, glycerol is converted to pyruvic acid. • Pyruvic aci...
Advertisement