Search Results
Results for: 'blood and systemic cell compartments'
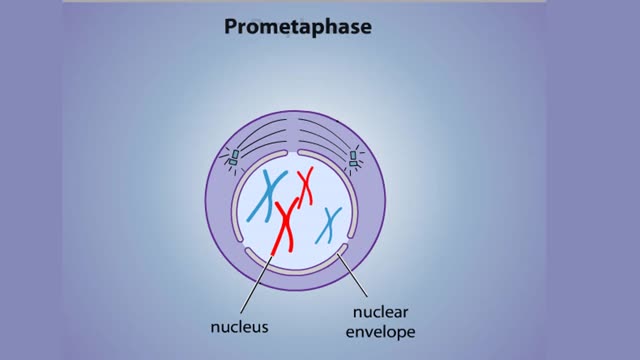
Stages of Mitosis - Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase & Telophase
By: HWC, Views: 10689
In mitosis, the nucleus divides to produce two nuclei that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent nucleus. To prepare for division, the DNA replicates in the preceding interphase. Although the chromosomes are not yet compacted and visible as discrete bodies, we illustrate them ...
By: Administrator, Views: 641
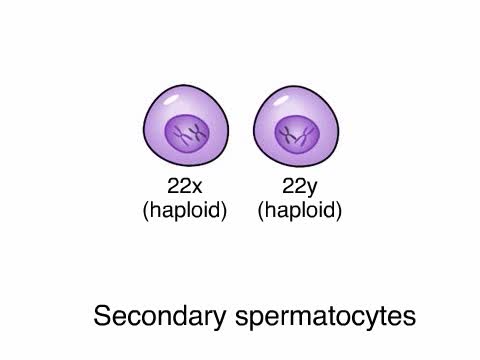
A man’s reproductive system is specifically designed to produce, store, and transport sperm. Unlike the female genitalia, the male reproductive organs are on both the interior and the exterior of the pelvic cavity. They include: the testes (testicles) the duct system: epididymis and vas def...
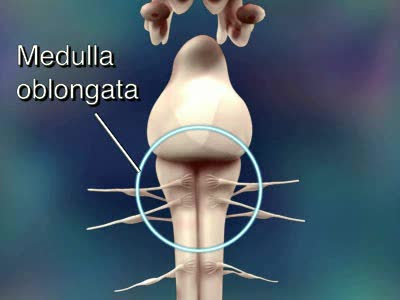
Central Nervous System Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14043
Consists of the brain and spinal cord. CNS receives impulses from throughout the body processes the information responds with an appropriate action Brain and spinal cord can be divided into: gray matter (unsheathed cell bodies and true dendrites) white matter (myelinated nerve fibers) ...
By: Administrator, Views: 13938
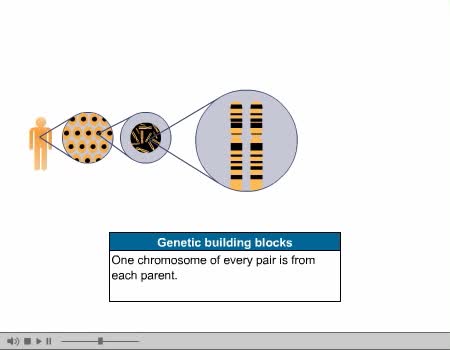
Genetics is a branch of biology concerned with the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms. Gregor Mendel, a scientist and Augustinian friar, discovered genetics in the late 19th-century. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from p...
By: Administrator, Views: 13954
Status epilepticus (SE) is a single epileptic seizure lasting more than five minutes or two or more seizures within a five-minute period without the person returning to normal between them. Previous definitions used a 30-minute time limit. The seizures can be of the tonic–clonic type, with a re...
By: HWC, Views: 11673
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
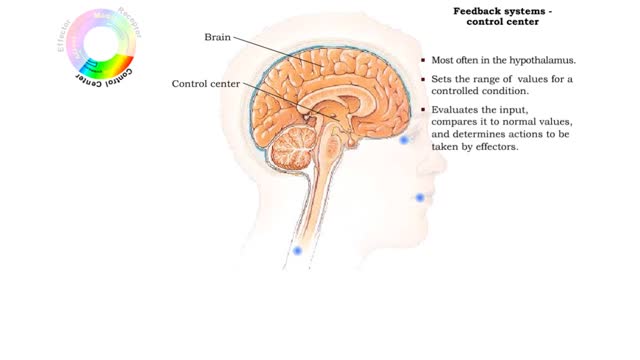
Component of feedback systems & Communication and regulation of body systems
By: HWC, Views: 11083
• Primary responsibility for communication and regulation in the body is shared by the nervous and endocrine systems. • The two systems work alone or together in specialized physiological processes called feedback systems to maintain homeostasis. • Feedback systems - or loops - are ...
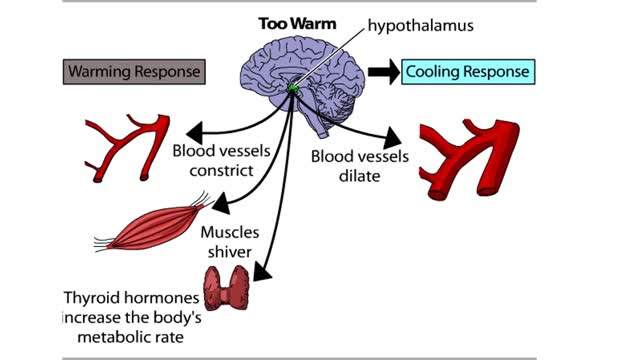
The Hypothalamus: The Body's Thermostat (Human Thermostat)
By: HWC, Views: 10112
Normal body function requires a relatively constant body temperature, which is regulated by the body's thermostat, a region of the brain called the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus generates a temperature set point for the body and appears to be the major site for the integration of temperature inf...
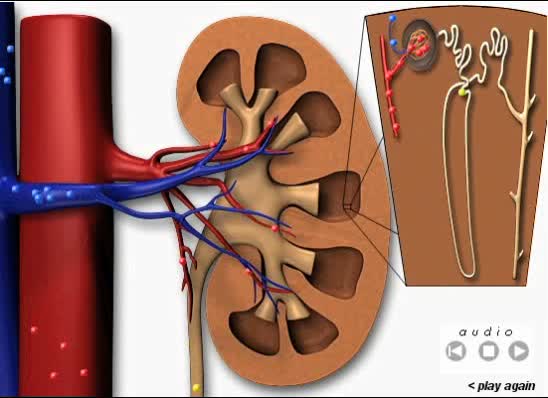
Blood Flow Through the Kidneys
By: Administrator, Views: 13646
Purplish-brown, bean-shaped organs located behind abdominal cavity (retroperitoneal area) on either side of spine, between thoracic vertebrae and lumbar region.
Advertisement