Search Results
Results for: 'Communication and regulation - body systems'
By: Administrator, Views: 13587
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with distant spread of the disease, t...
By: HWC, Views: 11807
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
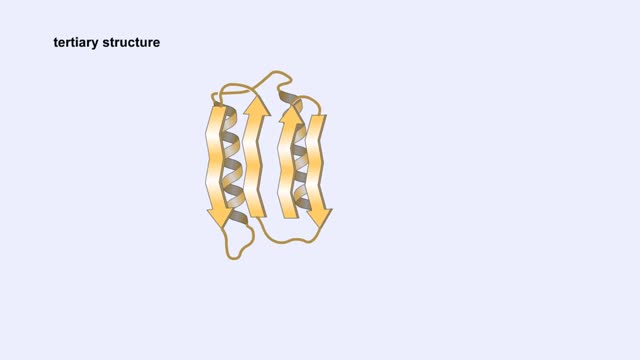
Protein Structure - Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary
By: HWC, Views: 10932
A protein's first order structure, or primary structure, begins with the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain. The 20 different amino acids can be arranged in an infinite number of sequences. For example, the hormone insulin, which regulates the uptake of glucose from the blood into ce...
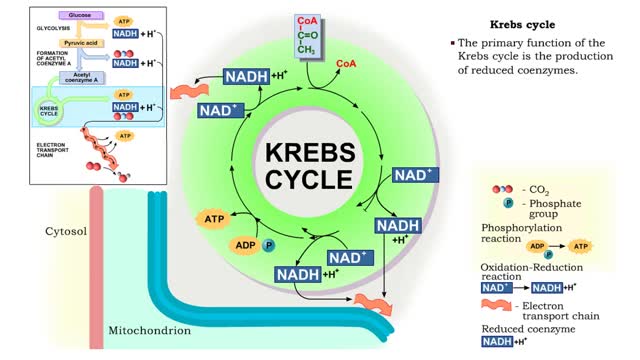
Krebs cycle : Formation of acetyl coenzyme A and Electron transport chain
By: HWC, Views: 11236
The oxidation of glucose to produce ATP is cellular respiration. Four sets of reactions are involved: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Krebs cycle reactions Electron transport chain reactions • The second pathway of glucose catabolism, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, is a transi...
Advertisement