Search Results
Results for: 'Body fluid volume'
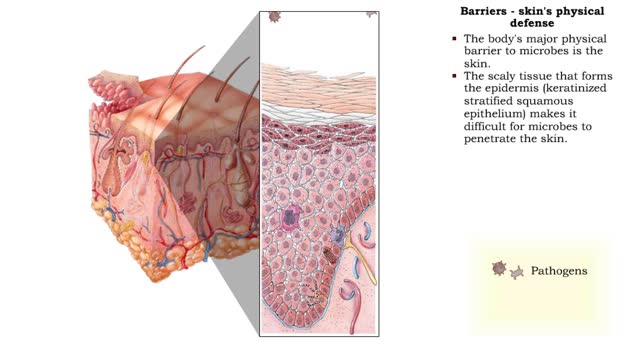
Non-specific disease resistance mechanisms & Skin's defense barriers
By: HWC, Views: 11733
• Non-specific disease resistance acts quickly to fight a wide variety of invaders. • Mechanisms include: • Barriers • Antimicrobial substances • Cellular defenses • Inflammation • Fever Barriers - types • Physical and chemical bathers prevent invasion by micro...
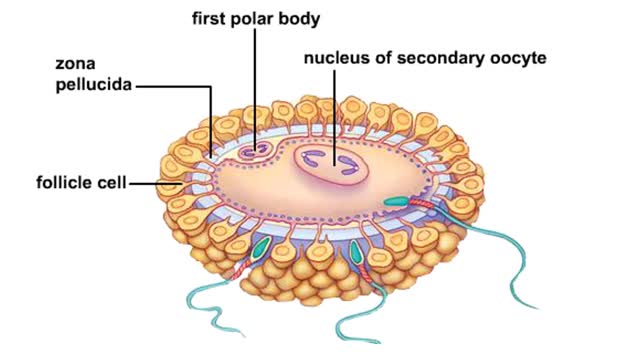
Rh blood type and complications during pregnancy & Fertilization
By: HWC, Views: 9219
Complications can arise if an Rh- woman is impregnated by an Rh+ man. The fetus maybe Rh+. During childbirth, some of the fetal Rh+ cells may leak into the maternal bloodstream. The woman's immune system views the Rh+ as foreign and makes antibodies against it. If the woman becomes pr...
By: Administrator, Views: 14684
Types of fractures: - Colles' - Pott's - Compression - Vertebral compression - Epiphyseal - Stress - Hip Closed, or simple–A completely internal break that does not involve a break in the skin (x-ray of the tibia and fibula). Note the break in the fibula (smaller bone). Open, or co...
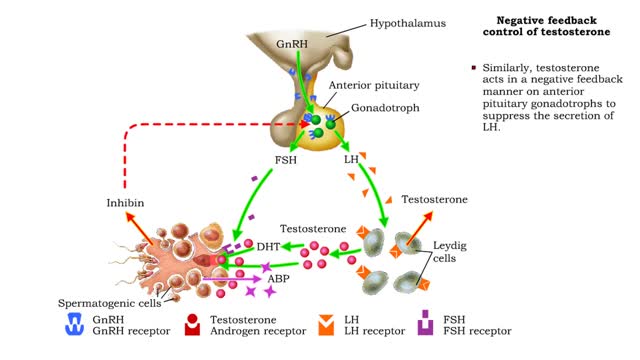
Male Reproductive System - Testosterone
By: HWC, Views: 12337
• Under the influence of FSH and testosterone, Sertoli cells produce androgen-binding protein (ABP) that binds to testosterone and maintains high levels of the hormone near spermatogenic cells. • Testosterone stimulates the final stages of spermatogenesis. • In addition, testosterone is...
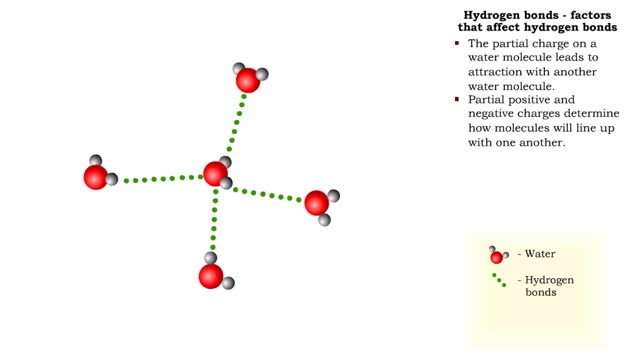
Hydrogen bonds - role in the body
By: HWC, Views: 11977
A hydrogen bond is the electromagnetic attraction between polar molecules in which hydrogen is bound to a larger atom, such as oxygen or nitrogen. This is not a sharing of electrons, as in a covalent bond. Instead, this is an attraction between the positive and negative poles of charged atoms. ...
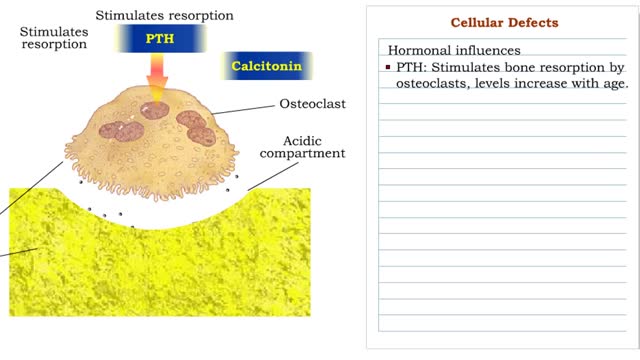
Cellular Defects - Osteoblasts, Osteoclasts and Osteocytes
By: HWC, Views: 11345
â– Metabolically active bone-building cells that secrete astroid. â– Cover surfaces of newly formed bone and respond to growth stimuli â– Less responsive to growth factors as the body ages. â– Contribute to hone loss once their reproductive and biosynthetic potential lessens....
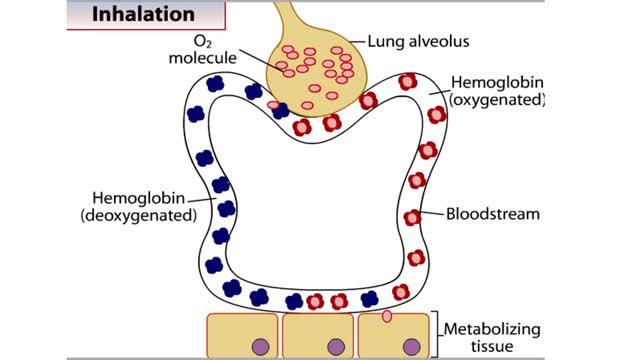
How Hemoglobin Picks Up and Delivers Oxygen
By: HWC, Views: 11118
All of the cells in our bodies require oxygen (02) for survival and must release carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste product. The respiratory and circulatory systems work together as delivery systems for these gases. The lungs exchange these gases between the environment and the bloodstream. The bloo...
Introduction to Eating Disorders
By: Administrator, Views: 14600
An eating disorder is a mental disorder defined by abnormal eating habits that negatively affect a person's physical or mental health. They include binge eating disorder where people eat a large amount in a short period of time, anorexia nervosa where people eat very little and thus have a low bo...
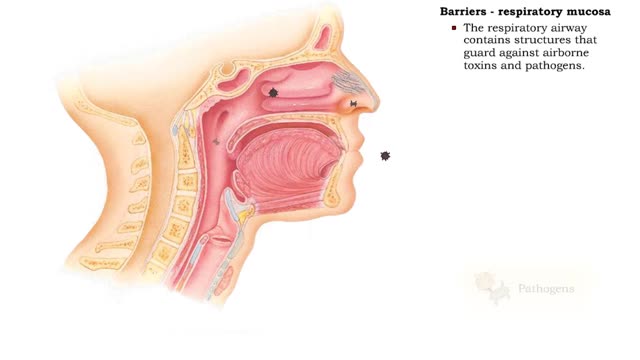
Barriers - eye structures, digestive mucosa, respiratory mucosa & genitourinary mucosa
By: HWC, Views: 12015
• Eyebrows, eyelids, eyelashes and conjunctiva serve to trap microbes preventing their invasion. • Tearing (lacrimation) is a protective mechanism that washes away microbes that attempt to enter the eyes. • Salts, mucus, and lysozymes in tears neutralize substances and bacteria. â€...
Advertisement