Search Results
Results for: 'El'
By: HWC, Views: 11292
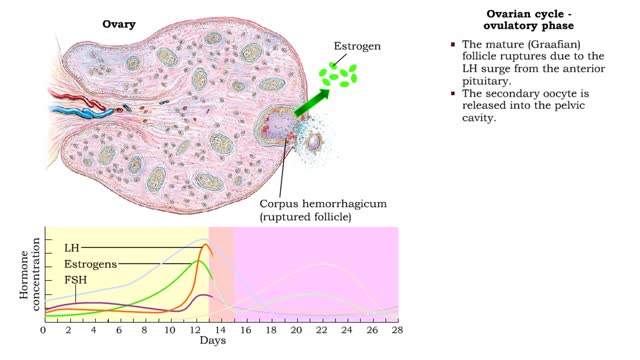
• The ovarian cycle is a monthly sequence of events, consisting of three phases: • Preovulatory • Ovulatory • Post ovulatory Preovulatory phase • prior to ovulation: Primary follicles develop into secondary follicles. • Follicular cells surrounding the primary oocyte In...
Uterine (menstrual) cycle - phases
By: HWC, Views: 10888
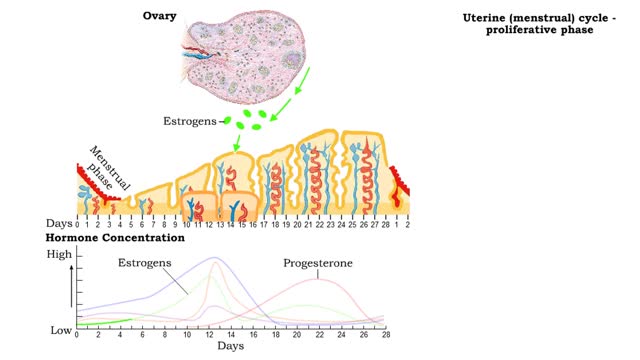
• The uterus goes through a cyclical developmental pattern to be ready for implantation and support of an embryo. • The uterine, or menstrual, cycle is under the control of ovarian horrnones. • The uterine cycle also has three phases: • Menstrual phase • Proliferative phase �...
Summary of female reproductive cycle days 1-28
By: HWC, Views: 11437
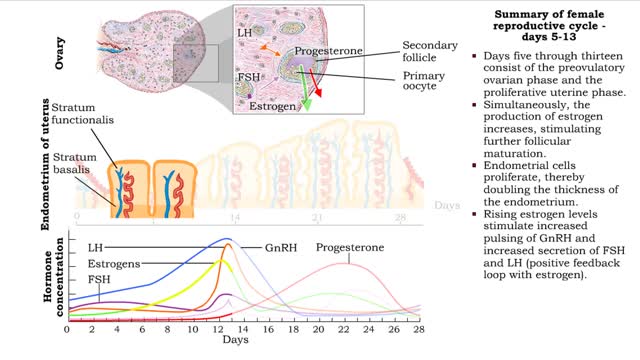
■ The first five days of the cycle include the menstrual phase. ■ Progesterone and estrogen levels are low. ■ Menses occurs. ■ GnRH pulses more frequently promoting FSH and LH levels to rise. ■ Primary follicles are stimulated to develop. ■ Days five through thirteen consist o...
Mechanisms of capillary exchange
By: HWC, Views: 11149
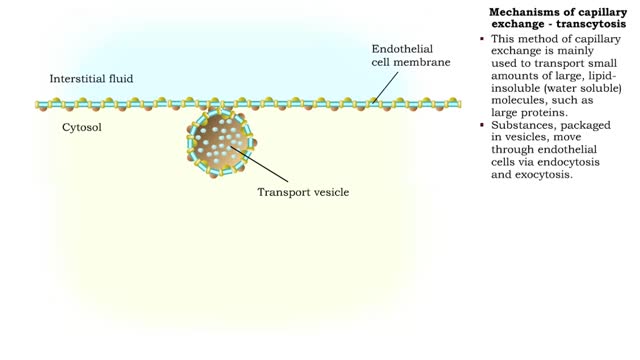
■ The primary role of capillaries is to permit the exchange of nutrients and wastes between the blood and tissue cells (via interstitial fluid). ■ Oxygen and nutrients move from the blood to the cells. ■ Carbon dioxide and other wastes move from the cells to the blood. The three ba...
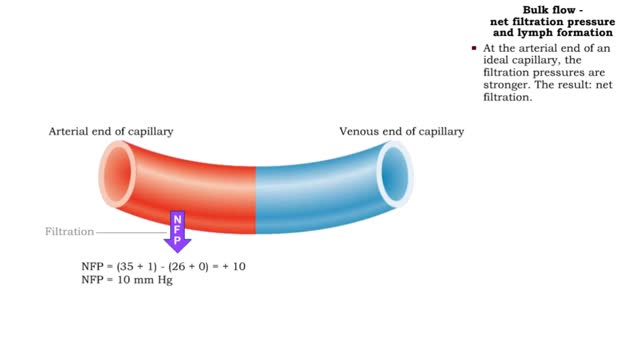
Bulk flow - Factors that influence bulk flow
By: HWC, Views: 11161
• Bulk flow helps regulate the relative volumes of blood and interstitial fluid. • Flow from blood to interstitium is called filtration. ■ Flow from interstitium to blood is called reabsorption. ■ Four factors determine the net direction of capillary exchange. ■ These factors in...
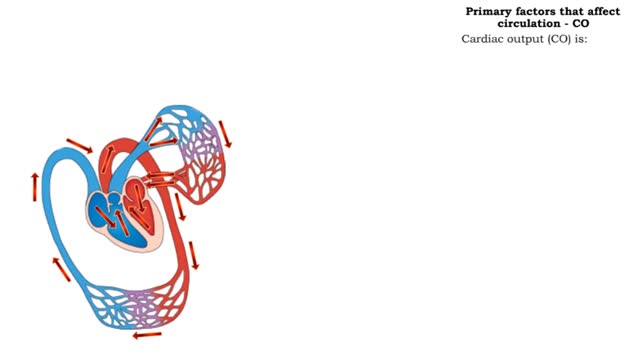
The primary factors that affect circulation - MABP, CO and SVR
By: HWC, Views: 11340
Introduction Blood flow is determined by the relative intensities of factors that drive and resist moving blood. • Cardiac output (CO) equals the mean arterial blood pressure (MABP, a driving force) divided by systemic vascular resistance (SVR, a resisting force). • Hormones and the cen...
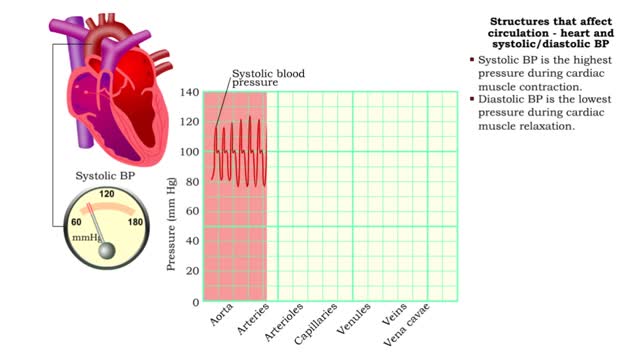
Structures that affect circulation - heart and systolic/diastolic BP
By: HWC, Views: 10903
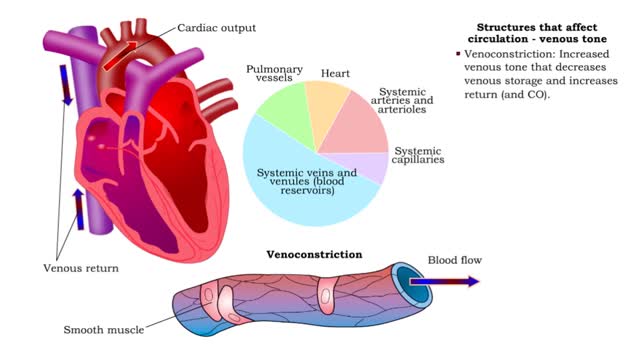
• Heart generates blood pressure. • Arterioles produce resistance thereby regulating blood flow to tissues. • Veins store blood; kidneys regulate blood volume; both affect venous return and cardiac output. ■ Contractions of the ventricles determine blood pressure, which drives th...
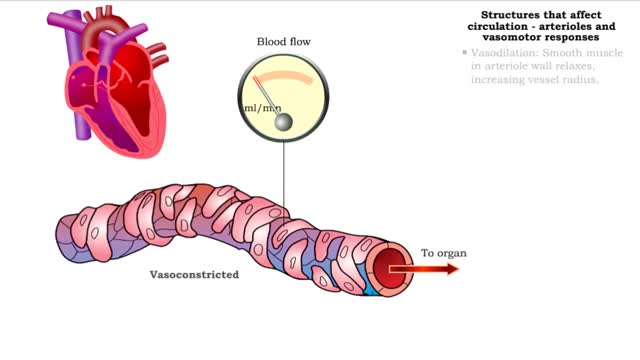
Structures that affect circulation - arterioles and vasomotor responses and venous return
By: HWC, Views: 10985
■ Small arteries and arterioles determine SVR. • Blood pressure drops significantly as blood passes through arterioles. • Decreasing arteriole radius and decreased wall elasticity are the main reasons for increased SVR. ■ Small changes in arteriole radius can cause large changes in ...
Structures that affect circulation - kidneys and blood volume and skeletal muscle pumping
By: HWC, Views: 11606
• Kidneys regulate blood volume and blood osmolarity via salt and water reabsorption. • Increased reabsorption increases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Decreased reabsorption Increases urine production, which decreases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Systemi...
Advertisement