Search Results
Results for: 'systemic tissue cells'
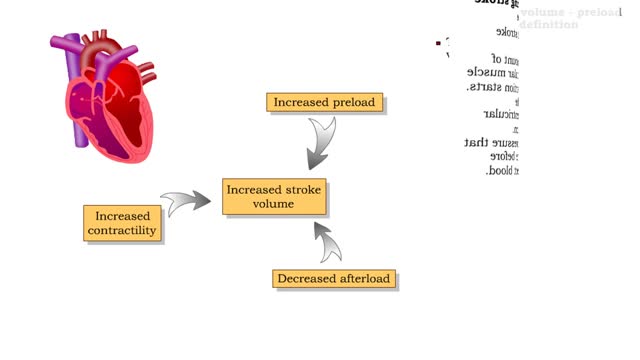
Definitions of stroke volume, preload definition & Factors influencing stroke volume
By: HWC, Views: 10860
• Stroke volume is directly correlated with cardiac output-the greater the stroke volume the greater the cardiac output. • Stroke volume represents the difference in the amount of blood between: • the volume in the ventricles at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume EDV); • the ...
By: Administrator, Views: 13917
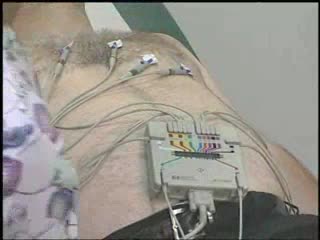
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a test that checks how your heart is functioning by measuring the electrical activity of the heart. With each heartbeat, an electrical impulse (or wave) travels through your heart. This wave causes the muscle to squeeze and pump blood from the heart. Sinoat...
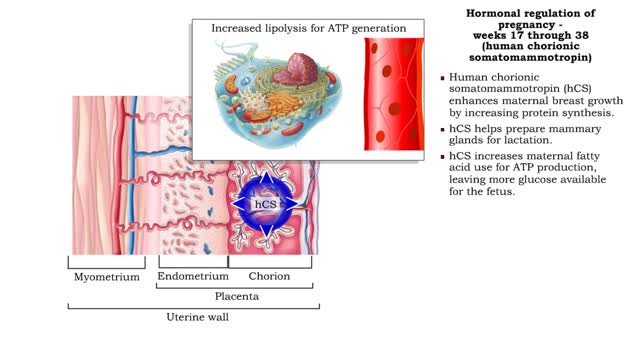
Hormonal regulation of pregnancy - weeks 17 through 38
By: HWC, Views: 11306
• Estrogens increase uterine blood flow, maintaining the endometrium during pregnancy. • High levels of estrogen and progesterone inhibit the synthesis of milk. Progesterone inhibits myometrial contractions of the uterus to prevent premature birth. • Relaxin inhibits myometrial contract...
By: HWC, Views: 9228
During interphase, the chromosomes will be duplicated in preparation for mitosis, which divides the chromosomes, and cytokinesis, which divides the cell's cytoplasm. In early prophase, the duplicated chromosomes begin to condense. Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids joined at the...
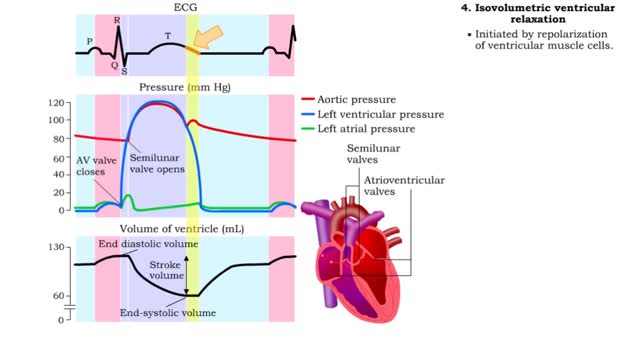
Isovolumetric VC, Ventricular ejection, Isovolumetric & Passive ventricular filling
By: HWC, Views: 10979
• Isovolumetric means that blood volume does not change. • Ventricular blood volume and cell length remain constant. • With valves closed and contraction continuing, ventricular pressure continues to rise. • Ventricular pressure rises above arterial pressure. • Increased ventr...
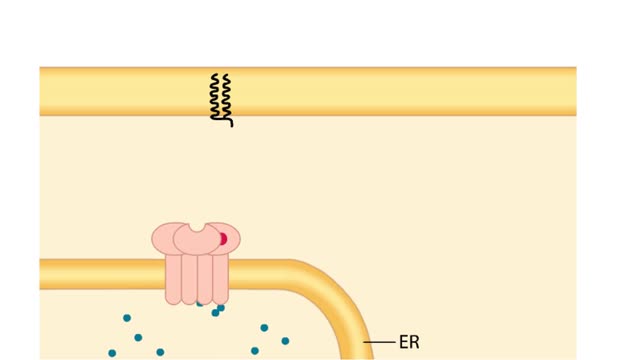
Second Messengers in the Inositol-lipid Signaling Pathway
By: HWC, Views: 10216
Extracellular signals produce specific responses in target cells through the action of intracellular second messengers. Here, we focus on three second messengers, IP3, DAG, and Ca2+, all involved in the inositol-lipid signaling pathway. A hormone-receptor signal on the cell surface leads to the a...
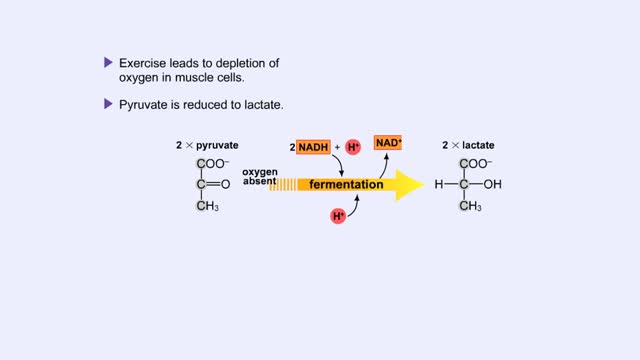
Fermentation - When Oxygen Is Absent, Pyruvate to Lactate & Pyruvate to Ethanol
By: HWC, Views: 10552
Pyruvate is the end product of glycolysis. If oxygen is present, pyruvate enters the mitochondrion where further energy yielding reactions of the Krebs cycle will take place. However, if oxygen is not present, pyruvate will enter a pathway called fermentation. This pathway regenerates NAD+ fro...
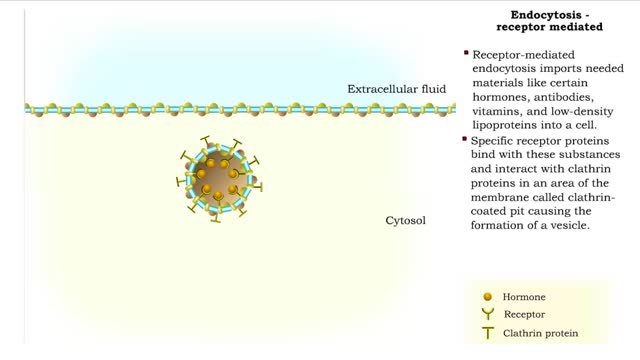
Endocytosis - pinocytosis, receptor mediated and Transcytosis
By: HWC, Views: 10989
Pinocytosis is the process in which a cell "drinks" a tiny droplet Of extracellular fluid, including its solutes. Pinocytosis (Cell Drinking) is the process by which the cell takes in fluids (as well as any small molecules dissolved in those fluids). • The plasma membrane folds inward to...
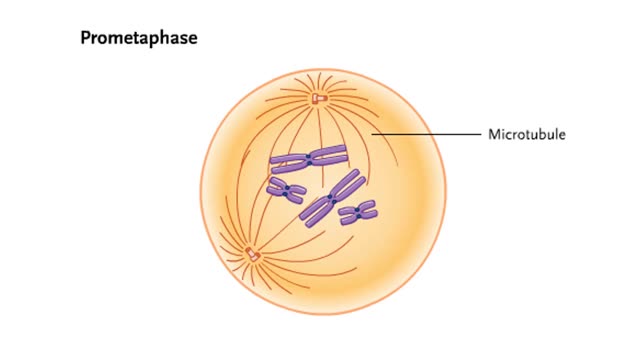
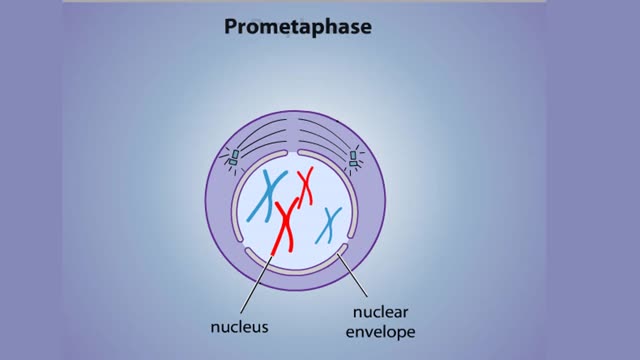
Stages of Mitosis - Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase & Telophase
By: HWC, Views: 10867
In mitosis, the nucleus divides to produce two nuclei that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent nucleus. To prepare for division, the DNA replicates in the preceding interphase. Although the chromosomes are not yet compacted and visible as discrete bodies, we illustrate them ...
Advertisement