Search Results
Results for: 'Capsular hydrostatic pressure'
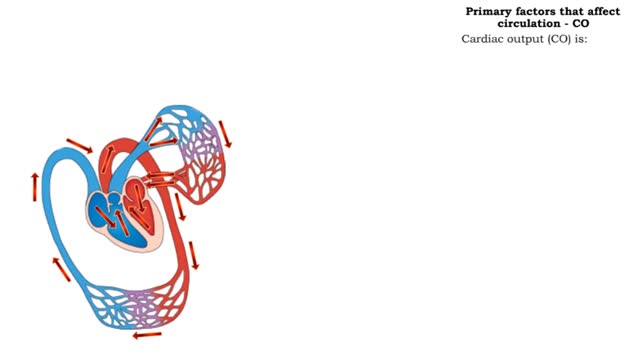
The primary factors that affect circulation - MABP, CO and SVR
By: HWC, Views: 11119
Introduction Blood flow is determined by the relative intensities of factors that drive and resist moving blood. • Cardiac output (CO) equals the mean arterial blood pressure (MABP, a driving force) divided by systemic vascular resistance (SVR, a resisting force). • Hormones and the cen...
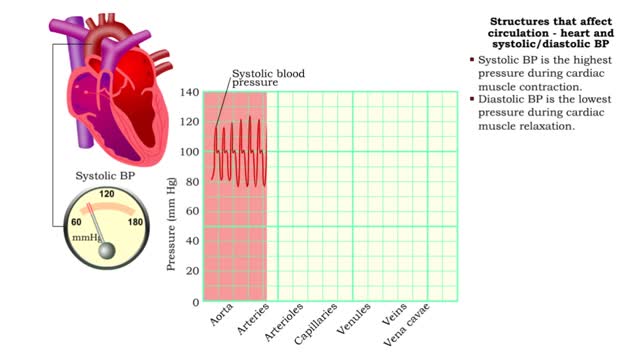
Structures that affect circulation - heart and systolic/diastolic BP
By: HWC, Views: 10680
• Heart generates blood pressure. • Arterioles produce resistance thereby regulating blood flow to tissues. • Veins store blood; kidneys regulate blood volume; both affect venous return and cardiac output. ■ Contractions of the ventricles determine blood pressure, which drives th...
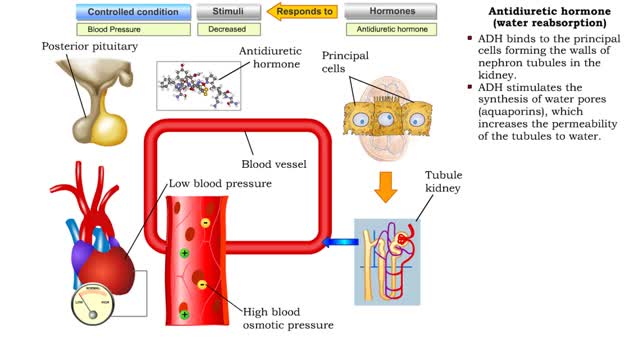
Antidiuretic hormone (vasoconstriction, water reabsorption & sweat inhibition)
By: HWC, Views: 10590
• Dehydration, blood loss, and low amounts of water in the blood can cause blood volume and pressure to decrease. • Neurosecretoxy cells in the posterior pituitary release antidiuretic hormone(ADH). • ADH binds to smooth muscle cells in blood vessel walls, stimulating them to vasoconstr...
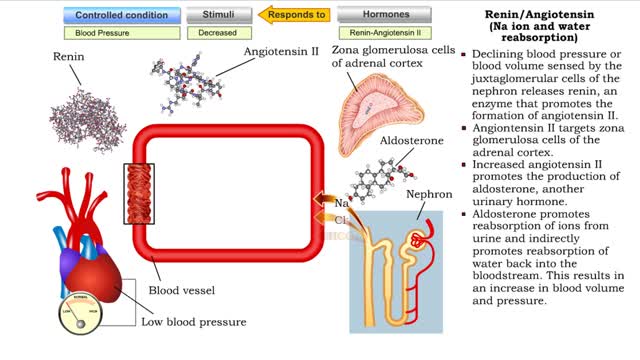
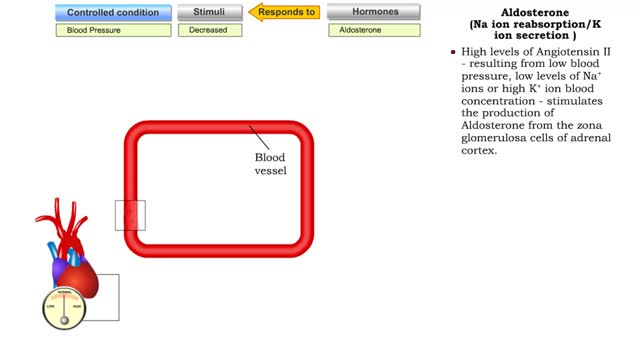
Renin/Angiotensin (water gain from urine & Na ion and water reabsorption)
By: HWC, Views: 10728
• Sensing declining blood pressure or blood volume, juxtaglomerular cells of the nephron release renin, an enzyme that promotes the formation of angiotensin II. • Angiotensin II targets smooth muscle cells in blood vessels that provide blood to the nephron. • Angiotensin II causes thes...
Atrial natriuretic peptide (vasodilation) & Aldosterone
By: HWC, Views: 10455
• Certain situations will cause the body's stress level to rise. • increased blood pressure will stretch the atria of the heart, stimulating the secretion of atria natriuretic peptide (MP). • ANP causes muscle cells in blood vessels to relax. • Blood pressure is lowered as a result ...
Double Vacuum Process (Illustration No Audio)
By: HWC, Views: 9797
In this so-called low-pressure process, the wood is first subjected to a short and relatively weak initial vacuum, after which the treatment vessel is flooded with preservative solution and reduced to normal pressure The double vacuum container is loaded with timber. A partial vacuum is draw...
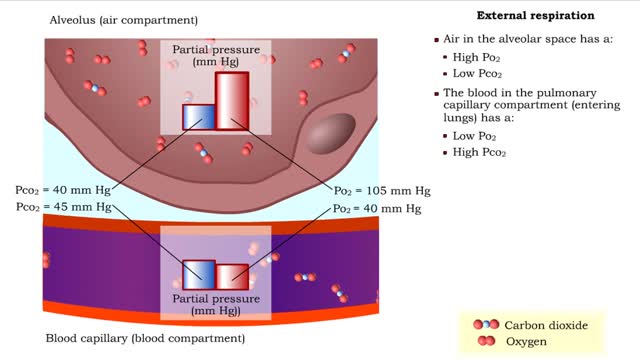
Gas exchange - partial pressure, locations, external and internal respiration
By: HWC, Views: 10887
▪ In a mixture, each individual gas exerts a pressure that is proportional to the concentration of that gas within the mixture. • This part of the total pressure is called a "partial pressure". • A gas moves along the part of the pressure gradient determined by its own concentration. ...
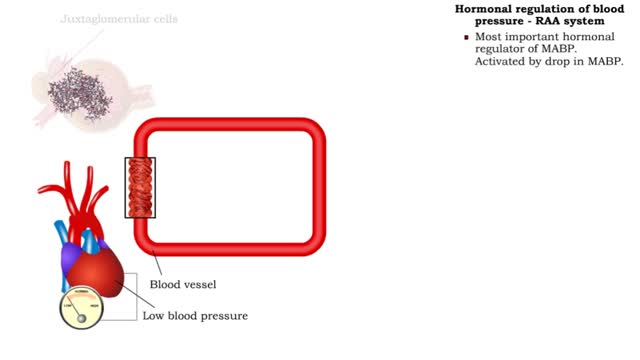
Hormonal regulation of blood pressure - RAA system
By: HWC, Views: 11225
■ Long-term regulation of MABP is under hormonal control. • Hormones that affect blood pressure and volume: the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAA) system, antidiuretic hormone (ADM), and atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP). ■ Most important hormonal regulator of MABP. Activated by drop in...
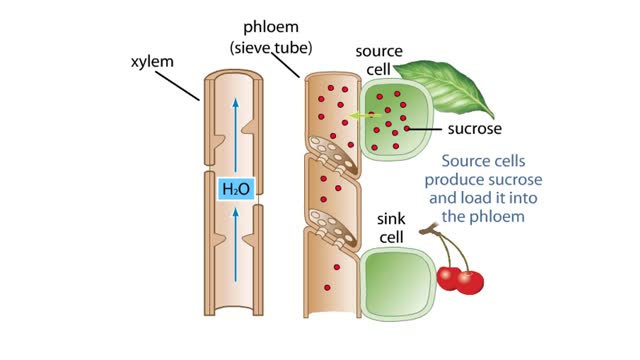
The Pressure Flow Model in a Plant
By: HWC, Views: 10108
The vascular system of plants has two transport tissues, called xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals, while phloem transports a variety of dissolved substances, including sugars and amino acids, throughout the plant. Water in the xylem always moves up, in the direction from th...
Advertisement