Search Results
Results for: 'Diffusion of gases'
By: HWC, Views: 11469
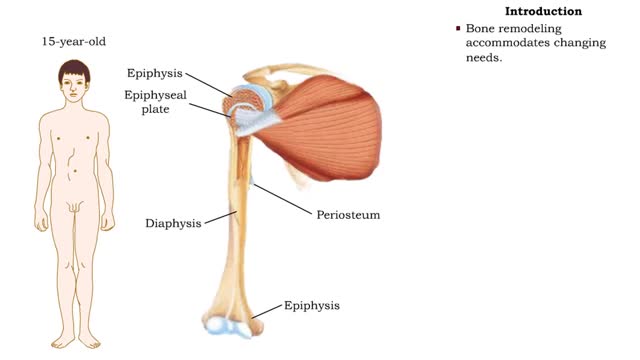
• After birth, bones grow in thickness and length. • Bones grow in diameter via appositional growth at the periosteum. • Epiphyseal plates enable lengthwise growth of long bones, such as the humerus, by interstitial growth. • Bone remodeling accommodates changing needs. • While th...
By: HWC, Views: 11197
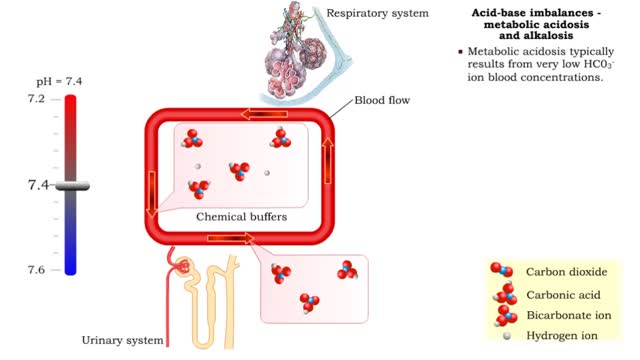
• Dissociation of the chemical substances in the body fluids can result in the production of free hydrogen ions. • The pH scale is used to measure the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. • Normal blood pH values vary around 7.4. • When hydrogen ion concentration increases, t...
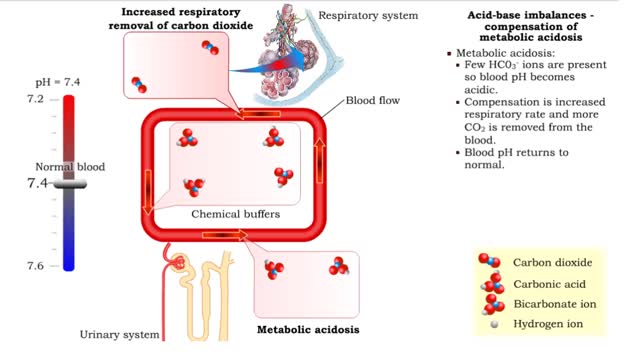
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11319
1. Metabolic acidosis: • Few HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased respiratory rate and more CO2 is removed from the blood. • Blood pH returns to normal. 2. Metabolic alkalosis: • Many HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes alkaline...
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11372
• When one pH balancing system is affected then the other balancing system attempts to correct, or compensate for, the pH imbalance. - Respiratory acidosis: • Excessive CO2 is present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased secretion of H+ into urine and reabsorption ...
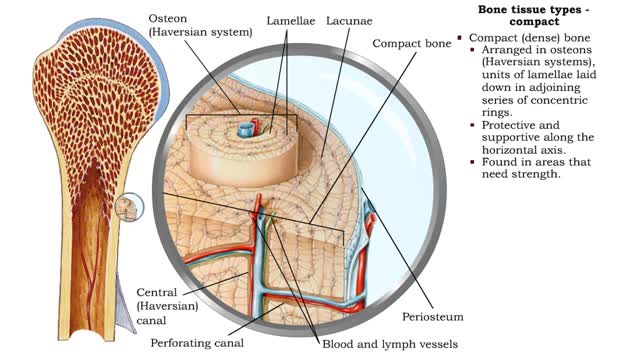
Bone tissue types - compact and spongy
By: HWC, Views: 11117
Bone tissue types • There are two types of bone tissue: compact and spongy. • All the bones of the skeleton have both kinds of bone tissue. • Compact (dense) bone • Arranged in osteons (Haversian systems), units of lamellae laid down in adjoining series of concentric rings. • P...
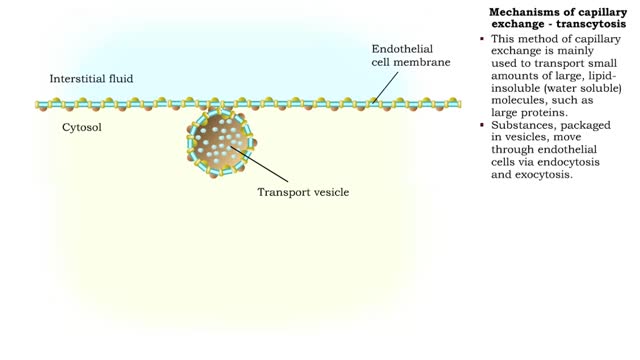
Mechanisms of capillary exchange
By: HWC, Views: 11318
■ The primary role of capillaries is to permit the exchange of nutrients and wastes between the blood and tissue cells (via interstitial fluid). ■ Oxygen and nutrients move from the blood to the cells. ■ Carbon dioxide and other wastes move from the cells to the blood. The three ba...
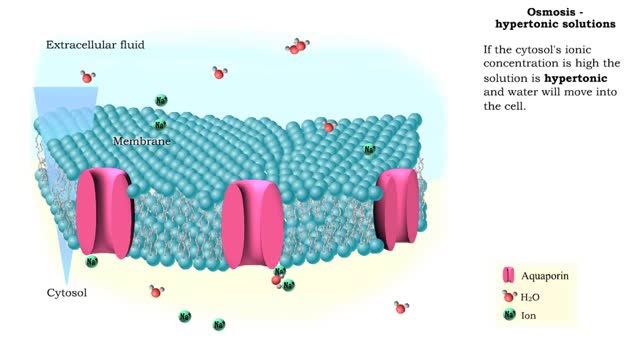
Osmosis - Isotonic, Hypotonic, and Hypertonic Solutions
By: HWC, Views: 11234
Isotonic: Equal Water moves in and out of the cell at an equal rate. The cell remains unchanged. Hypotonic: "hypo" hippo Water moves into the cell, making it swell and get fat (like a hippo). Eventually the cell can rupture and burst (aka lyse). Hypertonic: "like a raisin" Water leaves...
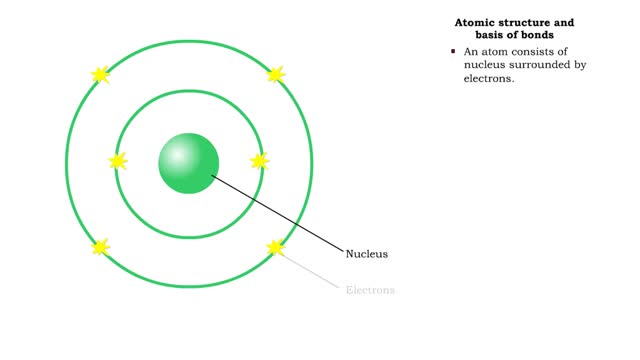
Bond types - Atomic structure and basis of bonds
By: HWC, Views: 11532
• Chemical bonds are fundamental to the structure and function of many types of molecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, gases, salts and water. ■ These molecules are composed of atoms that are held together by three different types of bonds. • The three types ...
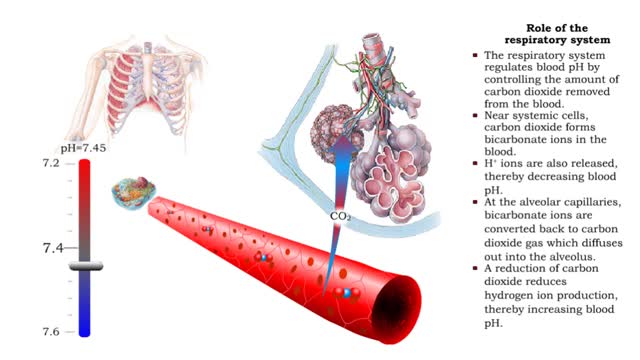
Role of the respiratory system - effect of altered ventilation rates
By: HWC, Views: 11733
• The respiratory system regulates blood pH by controlling the amount of carbon dioxide removed from the blood. • Near systemic cells, carbon dioxide forms bicarbonate ions in the blood. H+ ions are also released, thereby decreasing blood pH. • At the alveolar capillaries, bicarbonate io...
Advertisement