Search Results
Results for: 'Diffusion of gases'
By: HWC, Views: 11260
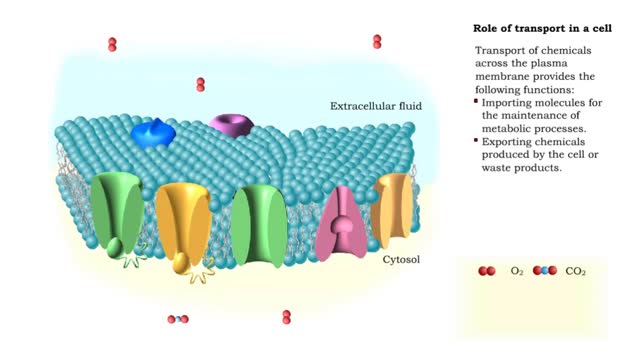
Transport of chemicals across the plasma membrane provides the following functions: Importing molecules for the maintenance of metabolic processes. Exporting chemicals produced by the cell or waste products. Communicating with other cells, allowing for the generation and conduction of a...
By: HWC, Views: 8821
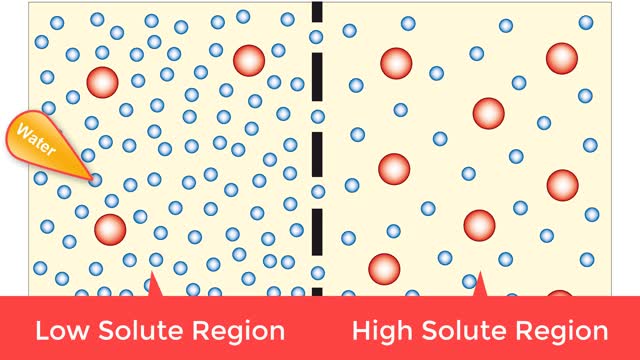
Osmosis is when a solvent, such as water, moves from a low-solute concentration solution to a higher-solute concentration solution through a semipermeable. Osmosis is an example of diffusion (a special case of diffusion) in which the molecules are water, and the concentration gradient occurs a...
By: HWC, Views: 8301
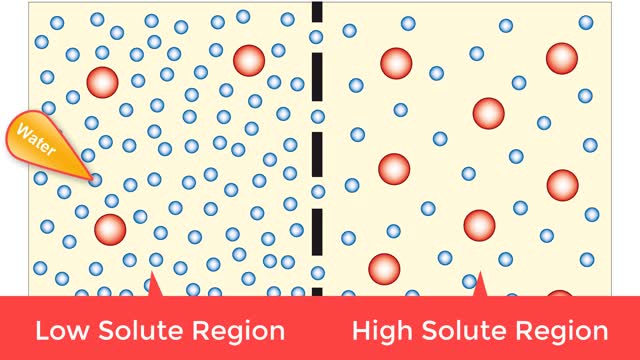
Osmosis is when a solvent, such as water, moves from a low-solute concentration solution to a higher-solute concentration solution through a semipermeable. Osmosis is an example of diffusion (a special case of diffusion) in which the molecules are water, and the concentration gradient occurs a...
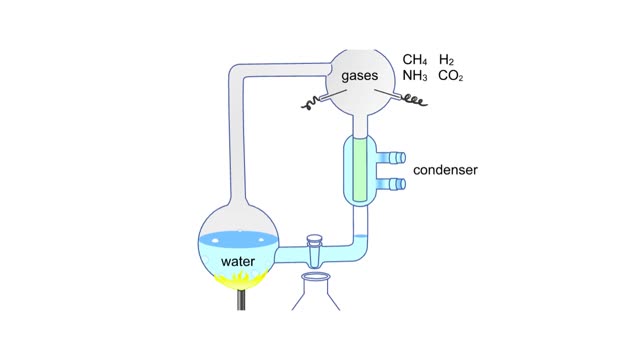
Miller's reaction chamber experiment Animation
By: HWC, Views: 4834
A simple diagram of Stanley Miller and Harold Urey's experimental apparatus. The lower portion of the apparatus was filled with water. The upper portion was filled with a mixture of gases that simulated the earth's early atmosphere. Examples are methane, ammonia, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. ...
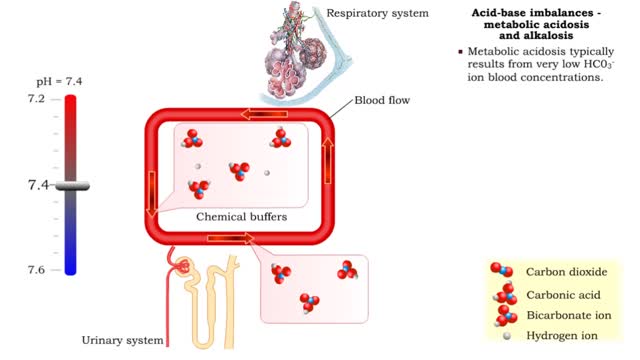
Acid-base imbalances - metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11214
• Metabolic acidosis typically results from very low HCO3- ion blood concentrations. • Metabolic alkalosis typically results from very high HCO3- ion blood concentrations.
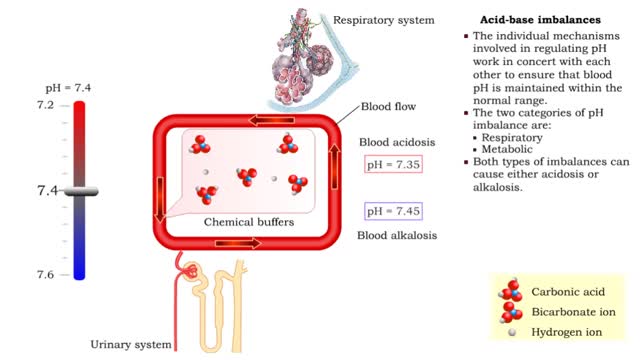
Acid-base imbalances - respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11470
• The individual mechanisms involved in regulating pH work in concert with each other to ensure that blood pH is maintained within the normal range. • The two categories of pH imbalance are: • Respiratory • Metabolic • Both types of imbalances can cause either acidosis or alka...
By: HWC, Views: 11279
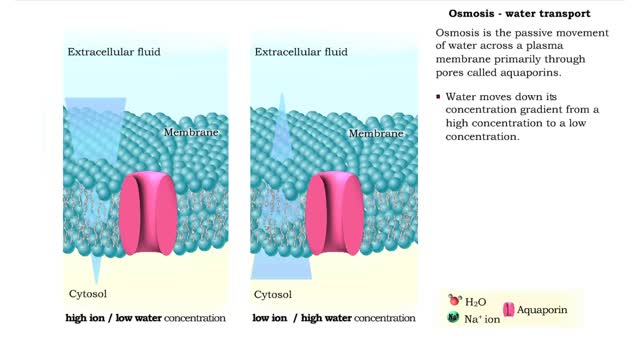
Osmosis is the flow of water down its concentration gradient, across a semi-permeable membrane. Osmosis is an example of diffusion, which is when molecules tend to distribute themselves evenly in a space. what is a semi-permeable membrane? It is a membrane or barrier that allows some molec...
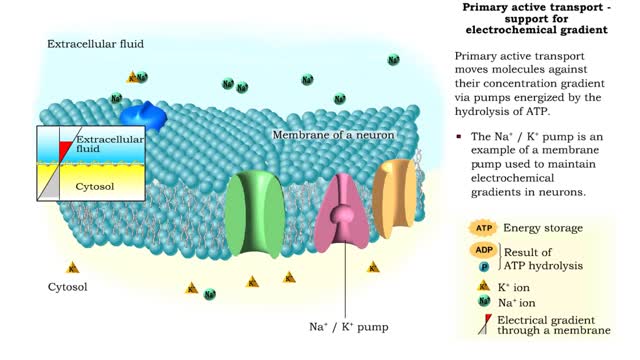
Primary Active Transport - electrochemical gradient and ion transport / water movement
By: HWC, Views: 11317
Energy derived from ATP changes the shape of a transporter protein which pumps a substance across a plasma membrane against its concentration gradient An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consis...
By: HWC, Views: 11741
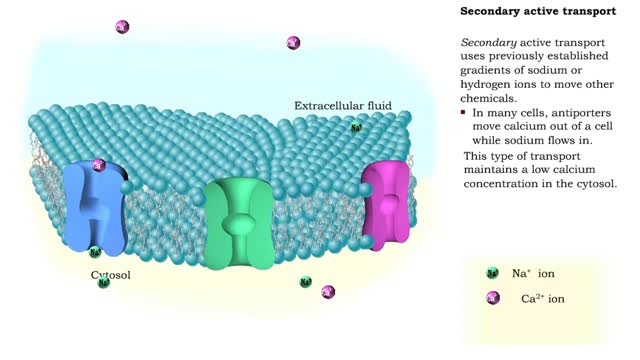
Energy stored (in a hydrogen or sodium concentration gradient) is used to drive other substances against their own concentration gradients Secondary active transport, is transport of molecules across the cell membrane utilizing energy in other forms than ATP. In many cells, antiporters mov...
Advertisement