Search Results
Results for: 'Glomerular blood hydrostatic pressure'
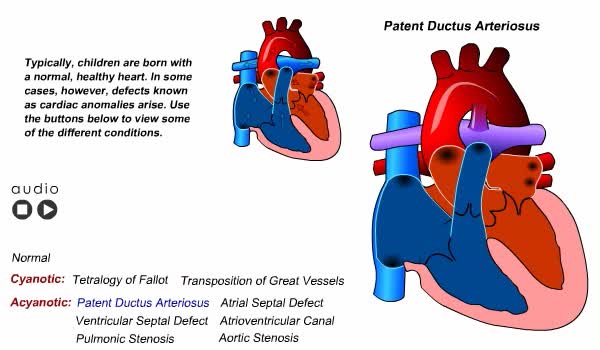
Congenital Heart Defects Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14448
Pulse, blood pressure, and respiration vary according to the child’s age. A newborn’s pulse rate is irregular and rapid, varying from 120 to 140 beats per minute. Blood pressure is low and can vary with the size of the cuff used. Average blood pressure at birth is 80/46. Respirations are ...
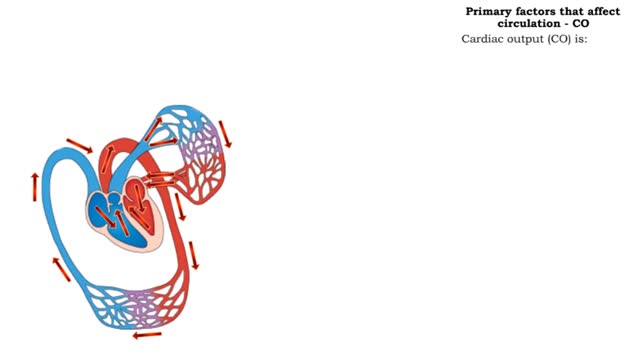
The primary factors that affect circulation - MABP, CO and SVR
By: HWC, Views: 11741
Introduction Blood flow is determined by the relative intensities of factors that drive and resist moving blood. • Cardiac output (CO) equals the mean arterial blood pressure (MABP, a driving force) divided by systemic vascular resistance (SVR, a resisting force). • Hormones and the cen...
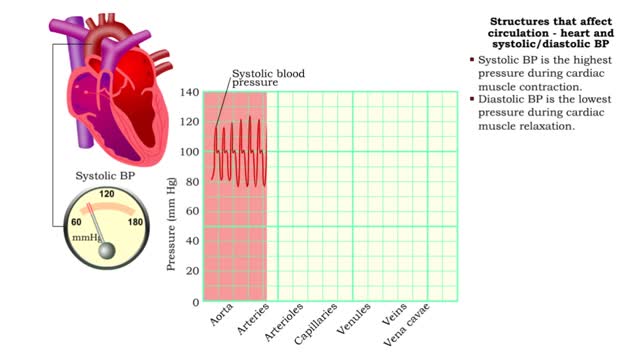
Structures that affect circulation - heart and systolic/diastolic BP
By: HWC, Views: 11298
• Heart generates blood pressure. • Arterioles produce resistance thereby regulating blood flow to tissues. • Veins store blood; kidneys regulate blood volume; both affect venous return and cardiac output. ■ Contractions of the ventricles determine blood pressure, which drives th...
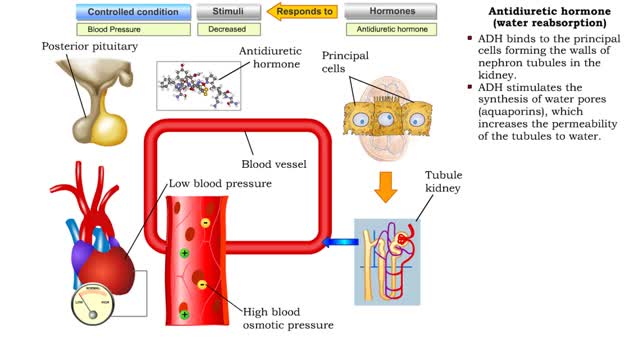
Antidiuretic hormone (vasoconstriction, water reabsorption & sweat inhibition)
By: HWC, Views: 11191
• Dehydration, blood loss, and low amounts of water in the blood can cause blood volume and pressure to decrease. • Neurosecretoxy cells in the posterior pituitary release antidiuretic hormone(ADH). • ADH binds to smooth muscle cells in blood vessel walls, stimulating them to vasoconstr...
By: Administrator, Views: 14522
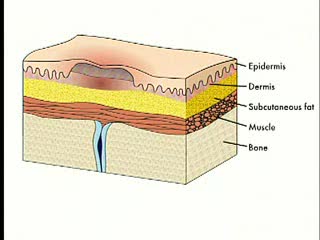
Pressure ulcers, also known as bedsores, decubiti, decubitous ulcers, pressure injuries, and pressure sores, are localized damage to the skin and/or underlying tissue that usually occur over a bony prominence as a result of usually long-term pressure, or pressure in combination with shear or fric...
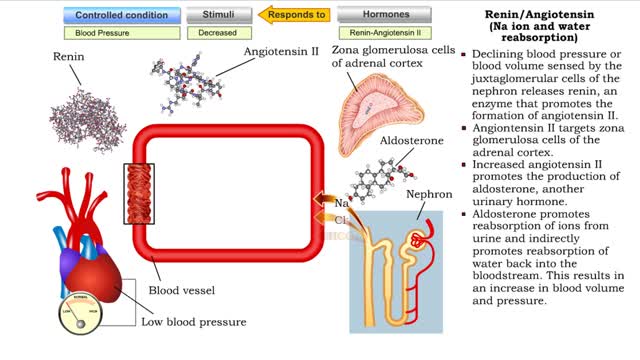
Renin/Angiotensin (water gain from urine & Na ion and water reabsorption)
By: HWC, Views: 11305
• Sensing declining blood pressure or blood volume, juxtaglomerular cells of the nephron release renin, an enzyme that promotes the formation of angiotensin II. • Angiotensin II targets smooth muscle cells in blood vessels that provide blood to the nephron. • Angiotensin II causes thes...
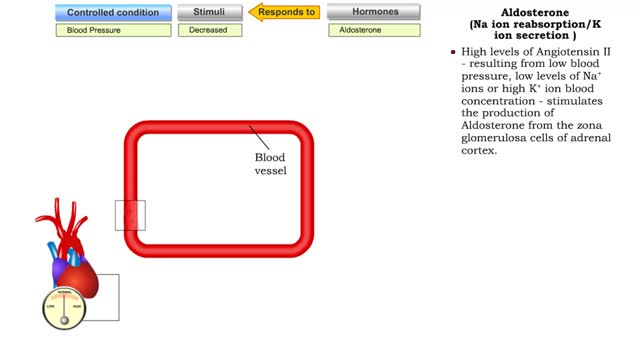
Atrial natriuretic peptide (vasodilation) & Aldosterone
By: HWC, Views: 11086
• Certain situations will cause the body's stress level to rise. • increased blood pressure will stretch the atria of the heart, stimulating the secretion of atria natriuretic peptide (MP). • ANP causes muscle cells in blood vessels to relax. • Blood pressure is lowered as a result ...
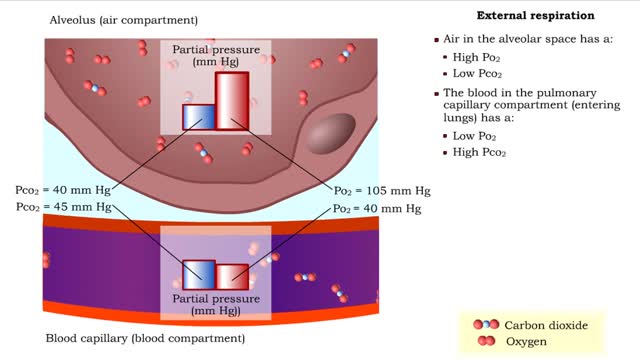
Gas exchange - partial pressure, locations, external and internal respiration
By: HWC, Views: 11524
▪ In a mixture, each individual gas exerts a pressure that is proportional to the concentration of that gas within the mixture. • This part of the total pressure is called a "partial pressure". • A gas moves along the part of the pressure gradient determined by its own concentration. ...
Hormonal regulation of blood pressure - RAA system
By: HWC, Views: 11858
■ Long-term regulation of MABP is under hormonal control. • Hormones that affect blood pressure and volume: the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAA) system, antidiuretic hormone (ADM), and atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP). ■ Most important hormonal regulator of MABP. Activated by drop in...
Advertisement