Search Results
Results for: 'Na ion and water loss'
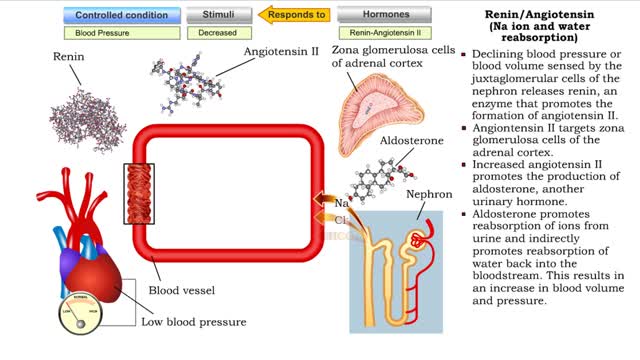
Renin/Angiotensin (water gain from urine & Na ion and water reabsorption)
By: HWC, Views: 10691
• Sensing declining blood pressure or blood volume, juxtaglomerular cells of the nephron release renin, an enzyme that promotes the formation of angiotensin II. • Angiotensin II targets smooth muscle cells in blood vessels that provide blood to the nephron. • Angiotensin II causes thes...
By: Administrator, Views: 13476
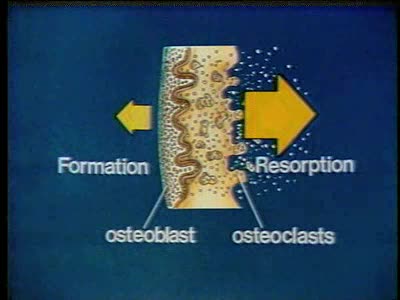
With normal aging, individuals can lose 1.0 to 1.5 inches in height. Loss of more than 1.5 inches in height can be related to vertebral compression fractures and other issues due to osteoporosis.
Global warming and its effect on climate change
By: HWC, Views: 10273
Global warming, habitat destruction, and pollution are all hot topics in the news. Environmentalists are concerned that many of these factors will lead to the loss of species. But how will this happen? One way to think about the environment is as a finely-tuned, high performance engine. If one...
What are Strong & Weak Acids and How they're different?
By: HWC, Views: 9493
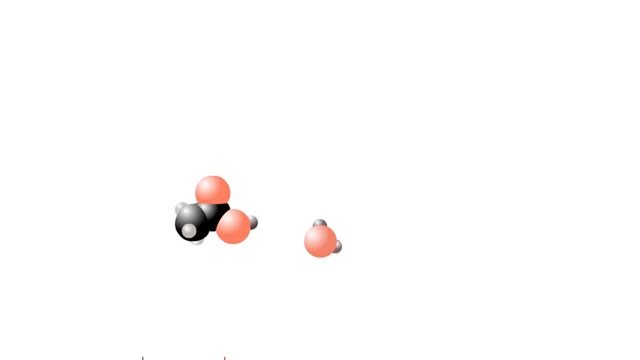
Let's consider the changes that take place when hydrogen chloride, HCI, is added to water. You will need to recognize space-filling models of HCI molecules, hydronium ions (H30+), chloride ions (C11, and water molecules (H20). They are shown at the right. When HC1 molecules dissolve in water, ...
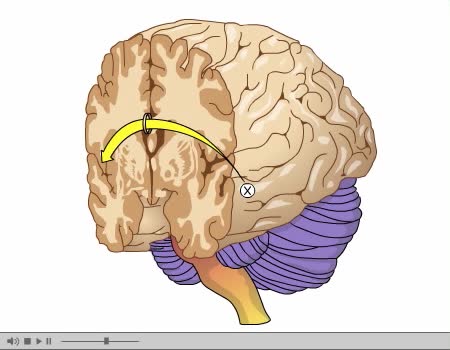
Studying the Left and Right Brain Independently
By: Administrator, Views: 13941
A seizure, technically known as an epileptic seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with loss of consciousness (tonic-clonic seizure), to shakin...
By: HWC, Views: 10004
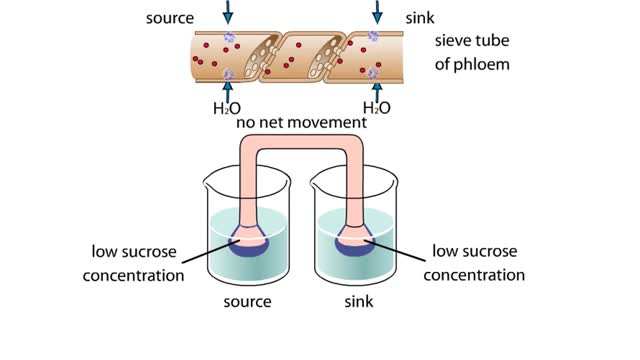
This apparatus of beakers A and funnels simulates the flow of a sucrose solution in the phloem of a plant. The funnels and connecting tube represent a sieve tube of the phloem. Differentially permeable membranes cap the funnels at the source and sink ends, allowing water, but not sucrose, to cros...
Forming urine ( influencing factors), Forming dilute urine & Forming concentrated urine
By: HWC, Views: 11175
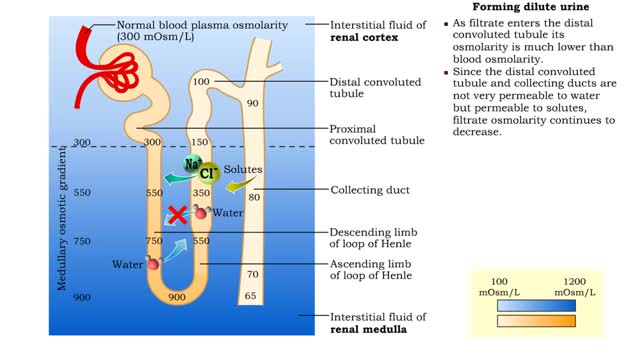
• The amount of urine produced by the nephron depends on : • Body fluid volume. • Body fluid composition. • Dilute urine is formed when the body is normally hydrated. • The medullary osmotic gradient determines the osmolarity of the filtrate. • Filtrate osmolarity increase...
Medullary osmotic gradient - influencing factors
By: HWC, Views: 11121
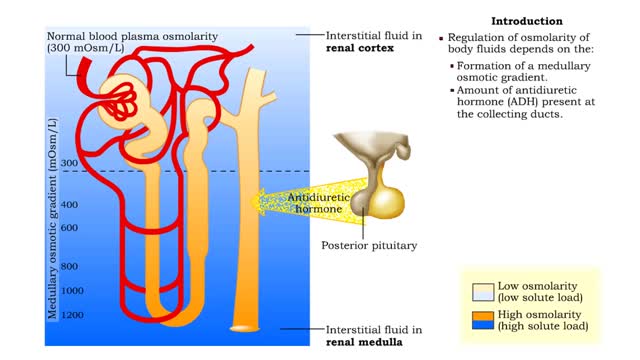
▪ Maintenance of fluid volume and composition, despite changes in water input and output, is crucial to a healthy life. ▪ Regulation of blood's osmolarity, or solute concentration, is a function of the nephron. • Normal osmolarity is maintained by the ability of the nephron to alter uri...
Coronary Heart Disease Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14143
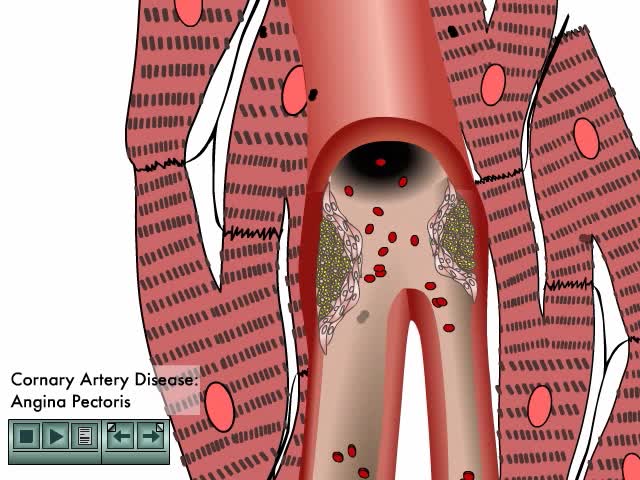
Arteriosclerotic heart disease occurs when arterial vessels are marked by thickening, hardening, and loss of elasticity in arterial walls. Course of cardiovascular disease accelerates due to: Reduced blood flow Rlevated blood lipids Defective endothelial repair
Advertisement