Search Results
Results for: 'Sodium atoms and chloride atoms'
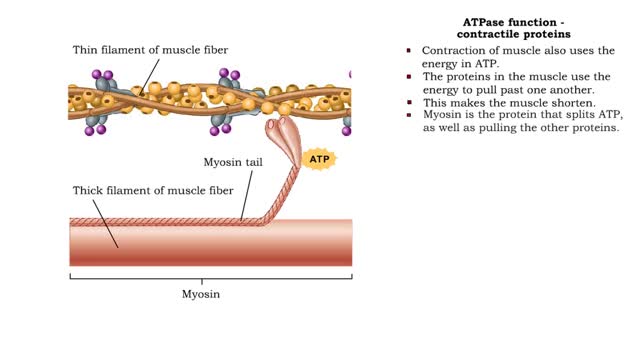
ATPase function - membrane transport, contractile proteins and synthesis
By: HWC, Views: 10915
• Energy from ATP is used to move ions across the cell membrane during active transport. • This membrane protein transports sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell. As such, it is called a sodium-potassium pump. • Because this pump also acts as an enzyme to hydrolyze ATP it i...
By: HWC, Views: 10348
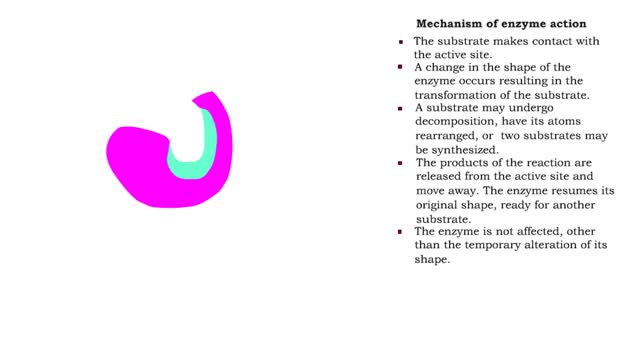
■ The substrate makes contact with the active site. ■ A change in the shape of the enzyme occurs resulting in the transformation of the substrate. ■ A substrate may undergo decomposition, have its atoms rearranged, or two substrates may be synthesized. ■ The products of the reaction...
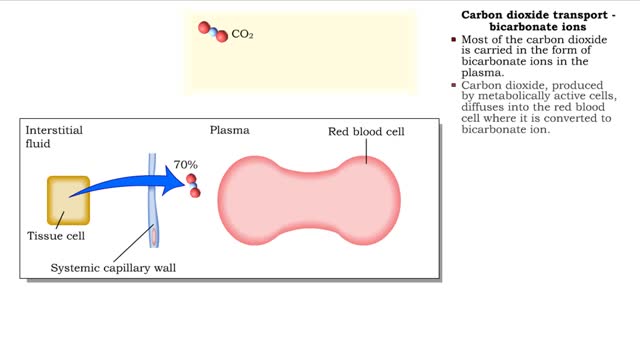
Methods of carbon dioxide transport - carbaminohemoglobin and bicarbonate ions
By: HWC, Views: 10567
• Carbon dioxide is transported three ways: • As bicarbonate ions in the plasma. • Bound to hemoglobin. • As a dissolved gas in the plasma. • A small percent of carbon dioxide is transported as a dissolved gas. • Some of the carbon dioxide is bound to hemoglobin, in the fo...
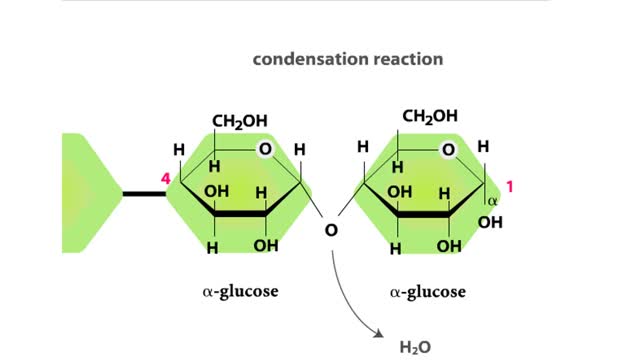
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Carbohydrates
By: HWC, Views: 10101
Carbohydrates include simple sugars (monosaccharides) as well as large polymers (polysaccharides). Glucose is a hexose, a sugar composed of six carbon atoms, usually found in ring form. A starch macromolecule is a polysaccharide composed of thousands of glucose units. Glucose molecules can be ...
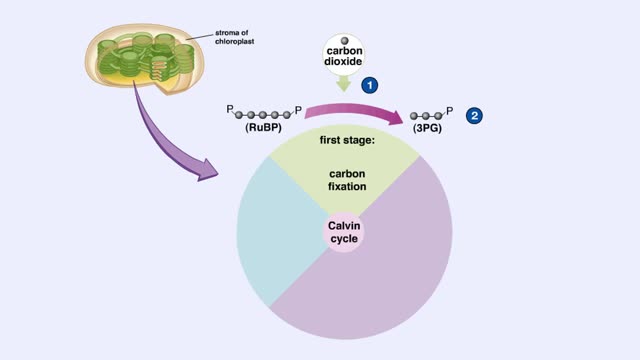
Calvin cycle (The light-independent reactions )
By: HWC, Views: 10321
The light-independent reactions of photosynthesis occur in the stroma of the chloroplast. Carbon dioxide enters the leaf through tiny pores or stomata and diffuses into the chloroplast. The first stage of the Calvin cycle is the attachment of a carbon dioxide molecule to a 5-carbon ribulose bi...
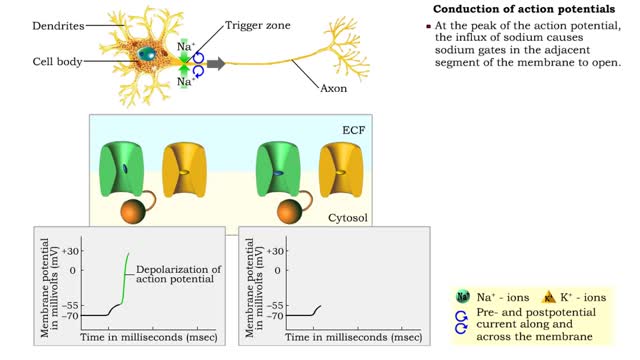
Conduction of action potentials
By: HWC, Views: 10680
• Action potentials must be rapidly conducted over long distances in order for the nervous system to communicate with other cells. • Propagation of an action potential uses processes similar to those that generate the potential at the trigger zone. • a When a graded potential reaches ...
Types of Transport - Uniport, Antiport and Symport (Glucose and Na+K+ Transporters)
By: HWC, Views: 10214
Some transport proteins bind and transport molecules very selectively. Uniport is the transport of one solute molecule. Symport is the transports of two solute molecules in the same direction. Antiport is the transports of two solute molecules in opposite directions. 1. Glucose bin...
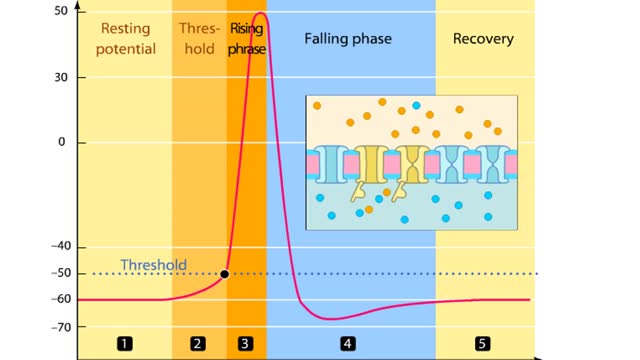
Phases of an Action Potential - Resting Potential, Threshold, Rising, Falling, & Recovery Phases
By: HWC, Views: 9935
In this tutorial, we will review the phases of an action potential measured from a small area of a neuron's membrane. The action potential can be divided into five phases: the resting potential, threshold, the rising phase, the falling phase, and the recovery phase. When the neuron is at rest,...
Advertisement