Search Results
Results for: 'The structure and function of the mammalian ribosome'
By: Administrator, Views: 13476
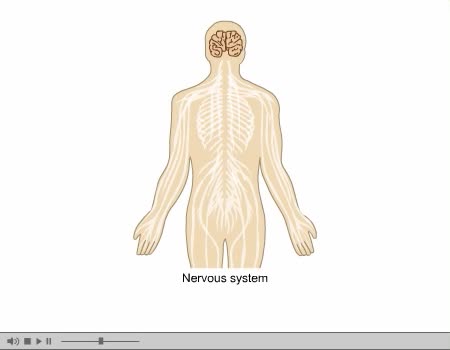
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell. Synapses are essential to neuronal function: neurons are cells that are specialized to pass signals to individual tar...
By: Administrator, Views: 13796
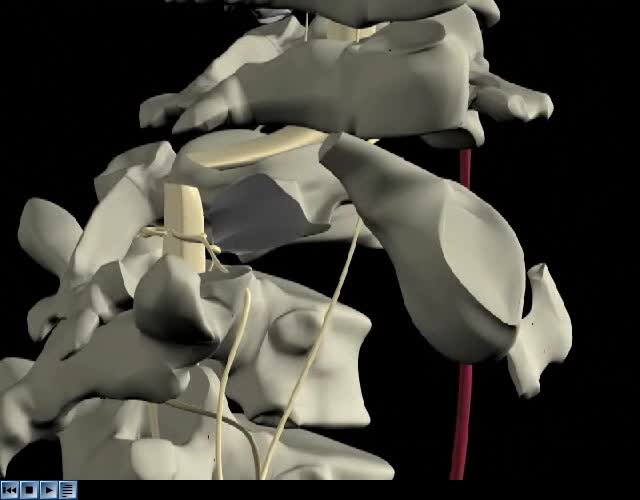
The most common cause of spinal cord injury is trauma. Spinal cord injury is most common in young, white men. Spinal cord injury can be either complete or incomplete. In complete injuries there is no function below the level of injury. In incomplete injuries there is some function remaining...
By: HWC, Views: 10204
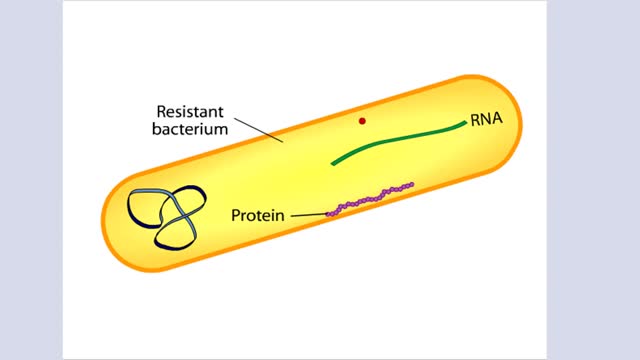
The Crisis in Antibiotic Resistance More than 70 years ago, Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin. A few decades later, when this antibiotic was used in World War II, Fleming's discovery had revolutionized medicine. No longer did people have to die from something as trivial as an infected cut.Y...
Cellular slime mold life cycle Animation
By: HWC, Views: 4804
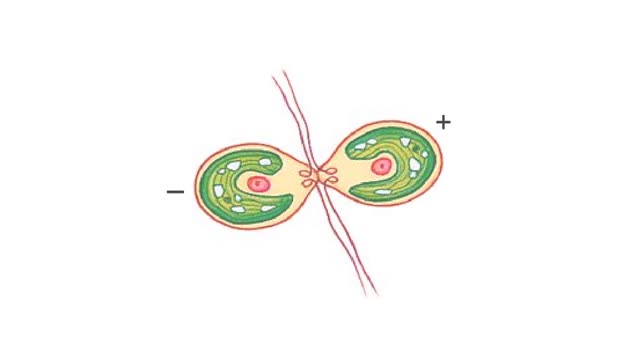
Life cycle of Dictyostelium discoideum, a cellular slime mold Animation. Amoeba-like slime mold cells live in the soil, where they feed on bacteria. The free-living cells grow and reproduce by mitosis. When food dwindles, the amoebas stream toward one another in response to a chemical...
By: Administrator, Views: 518
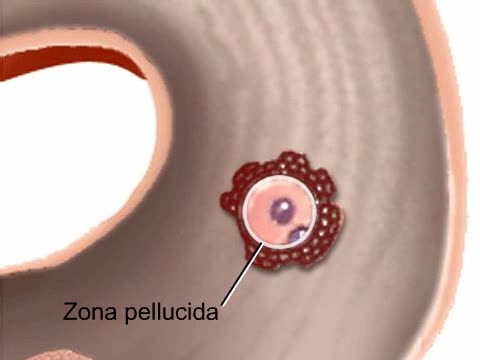
At conception, the gender and other biologic traits of the new individual are determined. The zygote is genetically complete and immediately begins to divide, forming a solid mass of cells called a morula. When the developing embryo (stage of development between weeks 2 and 8) reaches the ute...
By: Administrator, Views: 13602
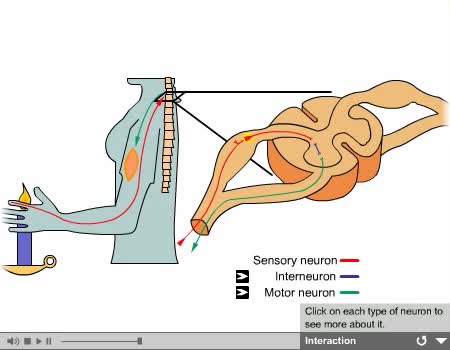
Interneurons: - Are called central or associative neurons. - Located entirely within the central nervous system. - They function to mediate impulses between sensory and motor neurons.
Proteins Defined, Hierarchy & Composition of Cells
By: HWC, Views: 9988
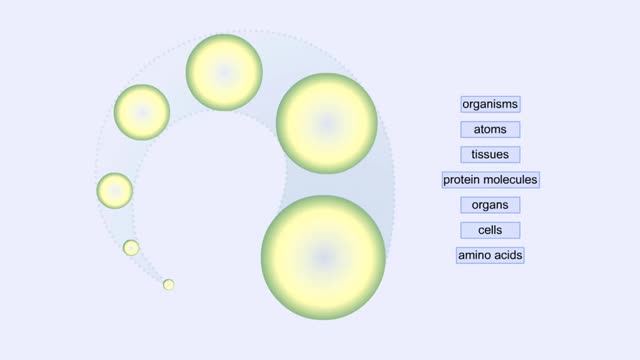
Proteins are long chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Together with the other three biological macromolecules—carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids—proteins are the building blocks of cells. Proteins are the most complex and abundant biological macromolecules in cel...
Mitochondrial Structure & ETC Protein Complexes (Protein Complexes and Electron Transport)
By: HWC, Views: 10118
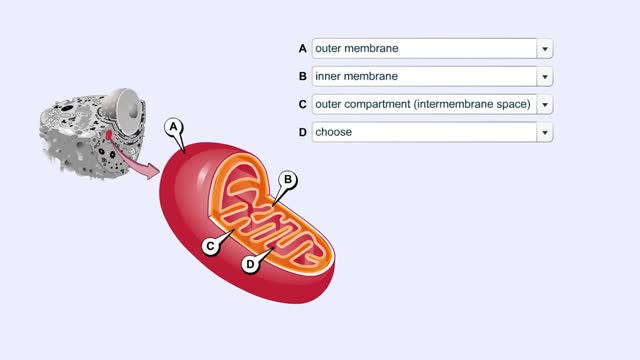
The energy carrying molecules, NADH and FADH2, that were generated in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, now are processed in the mitochondria where their high energy electrons are deposited in an electron chain complex located in the inner mitochondrial membranes. These high-energy electrons now dr...
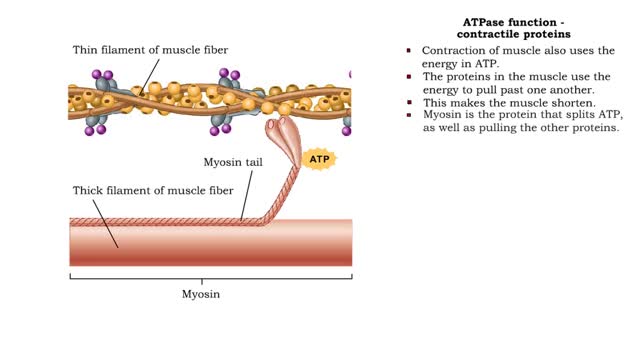
ATPase function - membrane transport, contractile proteins and synthesis
By: HWC, Views: 10913
• Energy from ATP is used to move ions across the cell membrane during active transport. • This membrane protein transports sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell. As such, it is called a sodium-potassium pump. • Because this pump also acts as an enzyme to hydrolyze ATP it i...
Advertisement