Search Results
Results for: 'The structure and function of the mammalian ribosome'
Autonomic Nervous System Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 13829
Parasympathetic Division Works to conserve energy and innervate the digestive system. When activated, it: stimulates the salivary and digestive glands. decreases the metabolic rate. slows the heart rate. reduces blood pressure. promotes the passage of material through the intestines along...
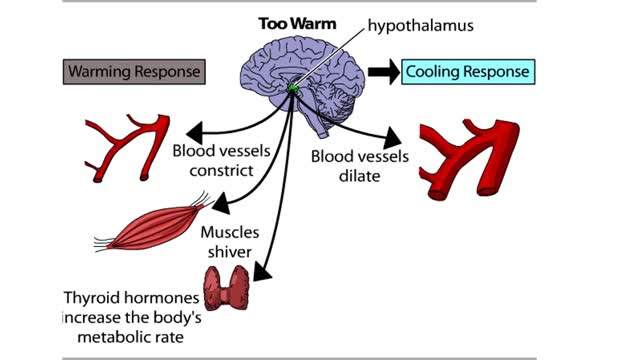
The Hypothalamus: The Body's Thermostat (Human Thermostat)
By: HWC, Views: 9743
Normal body function requires a relatively constant body temperature, which is regulated by the body's thermostat, a region of the brain called the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus generates a temperature set point for the body and appears to be the major site for the integration of temperature inf...
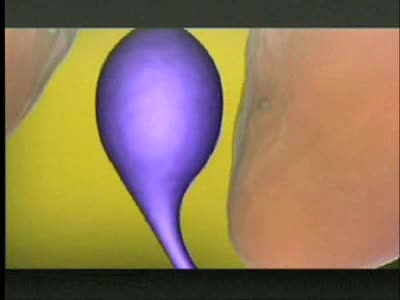
By: Administrator, Views: 413
Caesarean section, also known as C-section, or caesarean delivery, is the use of surgery to deliver babies. A caesarean section is often necessary when a vaginal delivery would put the baby or mother at risk. This may include obstructed labor, twin pregnancy, high blood pressure in the mother, br...
By: Administrator, Views: 13650
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. The two main types are acute otitis media (AOM) and otitis media with effusion (OME). AOM is an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, increased cryi...
By: Administrator, Views: 13845
Herpes simplex is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Infections are categorized based on the part of the body infected. Oral herpes involves the face or mouth. It may result in small blisters in groups often called cold sores or fever blisters or may just cause a sore throat. G...
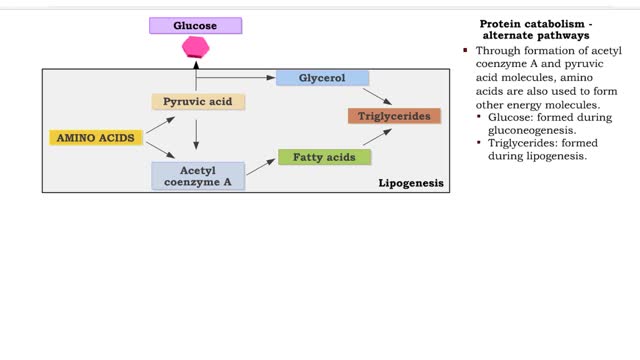
Protein catabolism (Krebs cycle) and Protein anabolism (protein synthesis)
By: HWC, Views: 11037
• Deaminated acids are brought into the Krebs cycle to be oxidized to CO2 and H2O. • Before entering the Krebs cycle, the deaminated acids are converted into intermediate products (pyruvic acid, acetyl coenzyme A, carbonic acids). • In the Krebs cycle, amino acids are oxidized to form r...
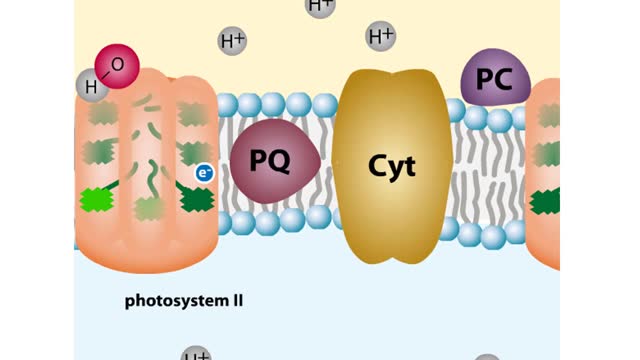
What are the Parts of a Plant Cell?
By: HWC, Views: 9484
Every chloroplast in a plant cell is packed with stacks of flattened sacs called thylakoids. The thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll, as well as most of the other components required for the light reactions of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll-containing structures within the membranes are c...
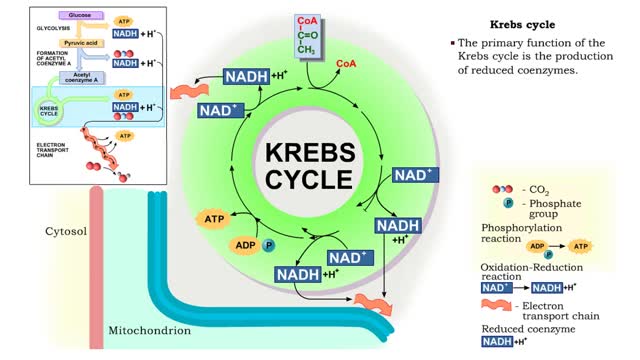
Krebs cycle : Formation of acetyl coenzyme A and Electron transport chain
By: HWC, Views: 10717
The oxidation of glucose to produce ATP is cellular respiration. Four sets of reactions are involved: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Krebs cycle reactions Electron transport chain reactions • The second pathway of glucose catabolism, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, is a transi...
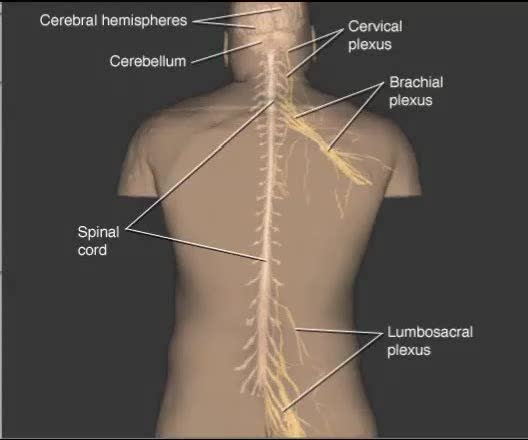
Components of the Nervous System
By: Administrator, Views: 509
The nervous system is the part of an animal that coordinates its actions by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes that impact the body, then works in tandem with the endocrine system to respond to such events. Nervous tissue...
Advertisement