Search Results
Results for: 'Transcription A molecular view animation'
Properties of macromolecules (Explained with No Audio)
By: HWC, Views: 10586
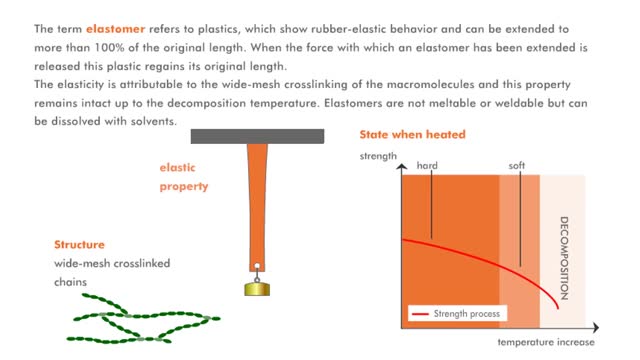
The term thermoplast refers to a plastic, which when heated is soft and deformable, but which rehardens when cooled. The molecular structure of the macromolecules is comparable to a cotton ball in which the individual fibers of the macromolecules are shown. The fibers of the cotton ball can s...
What are Taste Receptors? How Does it Work? Animation
By: HWC, Views: 8522
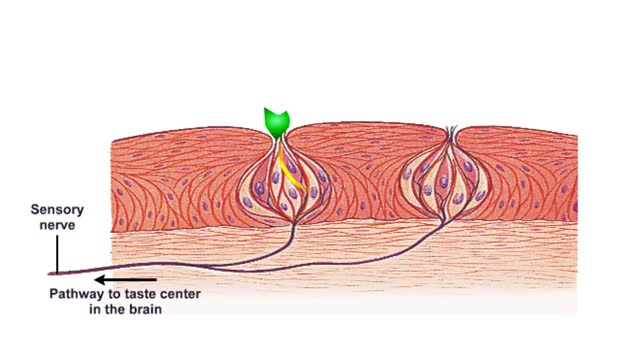
Do you ever wonder how you can taste the foods you eat? It all starts with taste receptors in your muscular tongue. Taste receptor neurons are found in your taste buds but you are not looking at the taste buds. The raised bumps on the surface of the tongue that you see are specialized epith...
Structure of Amino Acid, Peptide Bonds & Polypeptides
By: HWC, Views: 11243
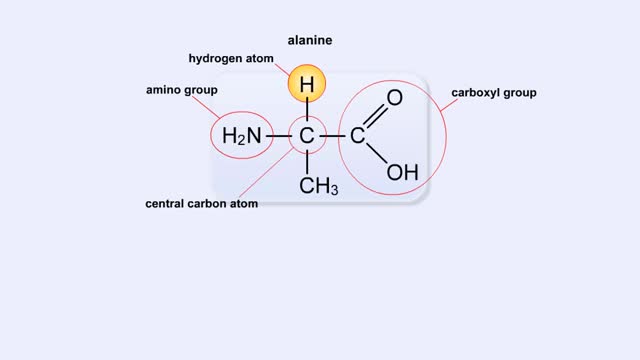
Here are the molecular formulas of three different amino acids. All amino acids share this backbone. The main difference between every amino acid is the side groups seen here, and these side groups give each of the amino acids their different characteristics. But before we get into that, let's ...
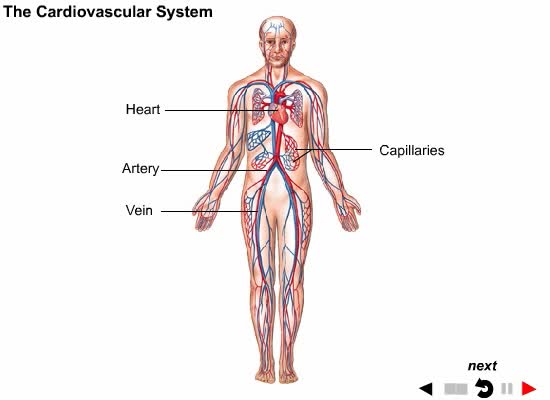
Introduction to Body Systems Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 942
Systems: A group of different organs functioning together for a common purpose.
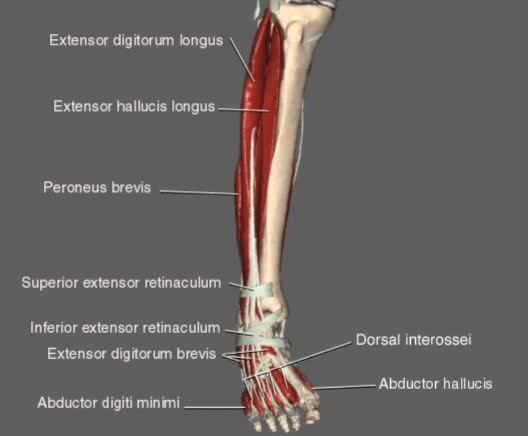
By: Administrator, Views: 494
This animation shows a list of muscles found in the leg used for movement
How proteins function? How do proteins work?
By: HWC, Views: 11327
How proteins function is really about how proteins "do work" in cells. How do proteins work? Let's start thinking about protein function by looking at something important to you: your hair. Keratin is a structural protein that is composed of 2 intertwined or helical strands. Keratin is also f...
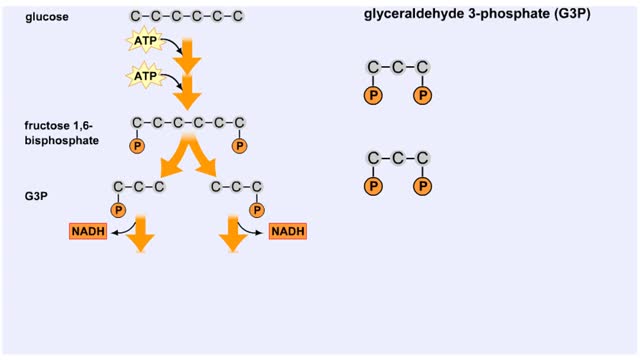
Splitting of Sugar, Oxidation/ Reduction & ATP Generation
By: HWC, Views: 11362
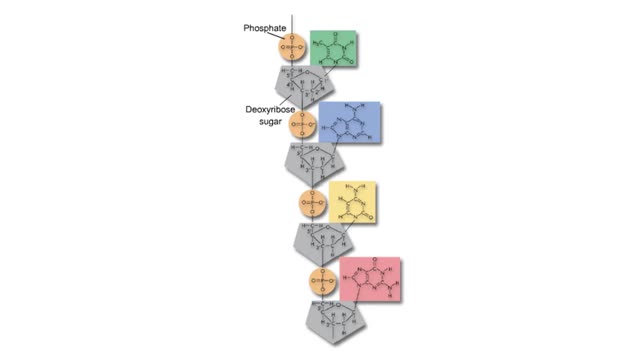
The next reaction shows us the meaning of "glycolysis" or the splitting of glucose. The fructose bisphosphate molecule is split into two molecules each containing 3 carbons as the backbone. FBP is split into two 3-carbon molecules called G3P, or glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. Notice that the phos...
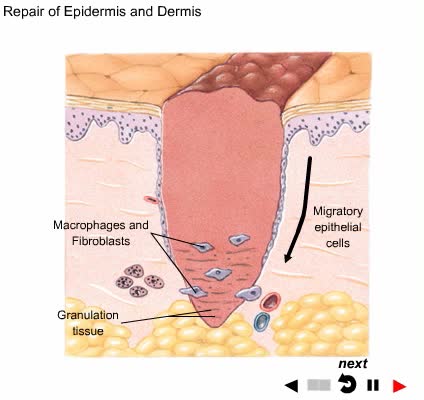
By: Administrator, Views: 14671
A wound is an injury to living tissue caused by a cut, blow, or other impact, typically one in which the skin is cut or broken.
Advertisement