Search Results
Results for: 'catalyze reactions'
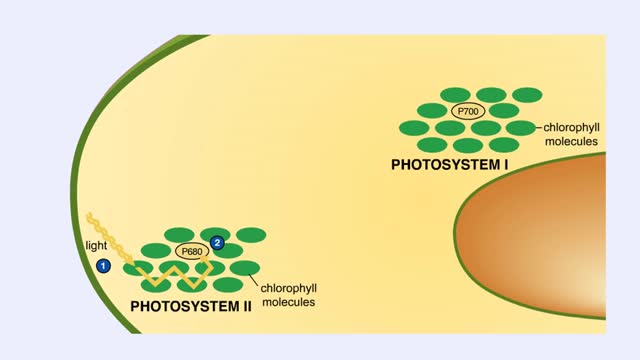
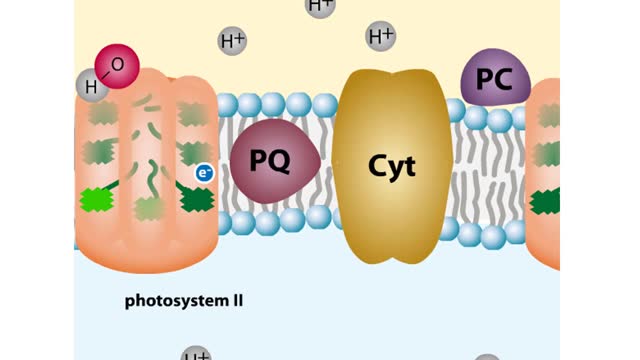
Chloroplast Structure & Light Dependent Reactions (Photosystem 1 and 2 Cyclic Electron Flow)
By: HWC, Views: 10279
The leaf is the principle photosynthetic organ of the plant. This is a cross section of a leaf. The rectangular-shaped cells are part of the photosynthetic tissue called the palisade mesophyll. Each photosynthetic cell can contain several hundred organelles known as chloroplasts. The chlorop...
By: Administrator, Views: 13497
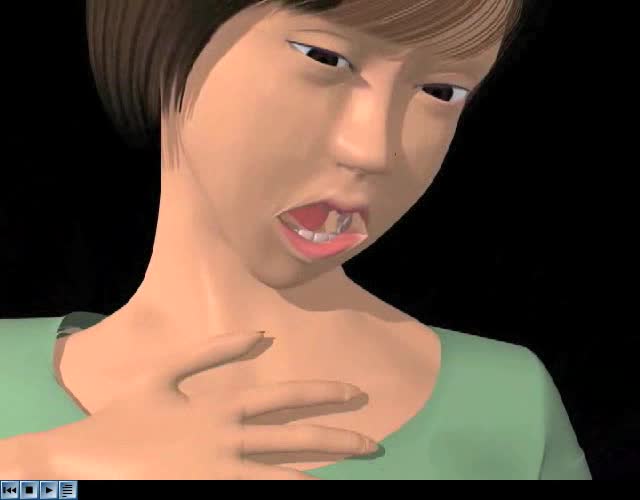
Anaphylaxis is a serious, life-threatening allergic reaction. The most common anaphylactic reactions are to foods, insect stings, medications and latex. If you are allergic to a substance, your immune system overreacts to this allergen by releasing chemicals that cause allergy symptoms.
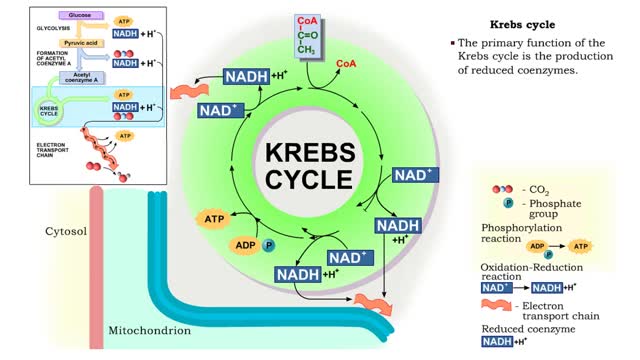
Krebs cycle : Formation of acetyl coenzyme A and Electron transport chain
By: HWC, Views: 10916
The oxidation of glucose to produce ATP is cellular respiration. Four sets of reactions are involved: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Krebs cycle reactions Electron transport chain reactions • The second pathway of glucose catabolism, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, is a transi...
What are the Parts of a Plant Cell?
By: HWC, Views: 9707
Every chloroplast in a plant cell is packed with stacks of flattened sacs called thylakoids. The thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll, as well as most of the other components required for the light reactions of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll-containing structures within the membranes are c...
By: Administrator, Views: 13703
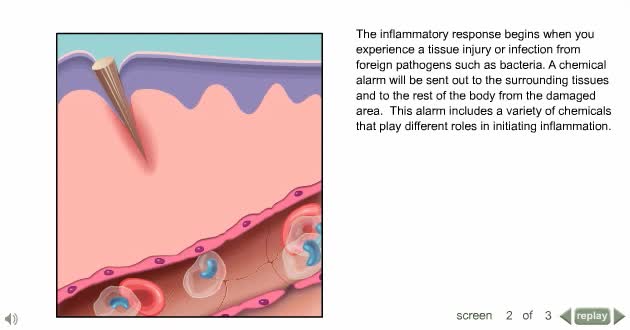
Inflammation is caused by a number of physical reactions triggered by the immune system in response to a physical injury or an infection. Inflammation does not necessarily mean that there is an infection, but an infection can cause inflammation.
Digestive chemicals - water, gastric acid, bile & bicarbonate
By: HWC, Views: 10457
• Water is the most abundant molecule in ingested fluids. • Water plays a primary role in hydrolytic digestive reactions. • Helps liquefy and transport digestive foodstuffs down the tract. • Transports secretions from accessory digestive organs to gastrointestinal tract. • Aids ...
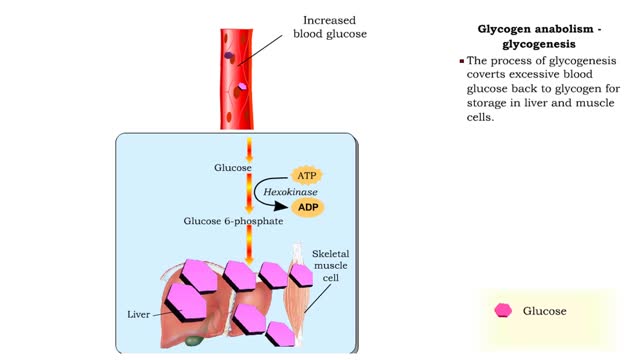
Glucose anabolism reactions: Glycogenolysis and Gluconeogenesis
By: HWC, Views: 11077
• Glucose not needed immediately is stored as glycogen. The process that creates it is glycogenesis. • When ATP is needed for body activities, stored glycogen is broken down by a process called glycogenolysis. • Glucose can be formed through two different anabolic reactions: • Glycog...
By: HWC, Views: 10214
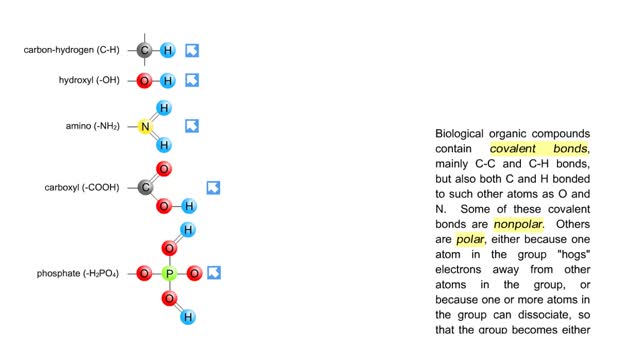
Biological organic compounds contain covalent bonds, mainly C-C and C-H bonds, but also both C and H bonded to such other atoms as O and N. Some of these covalent bonds are nonpolar. Others are polar, either because one atom in the group "hogs" electrons away from other atoms in the group, or...
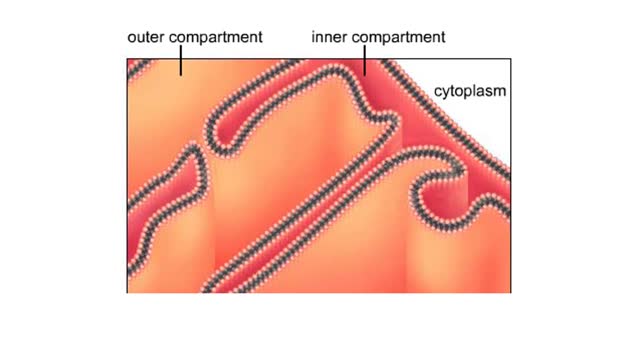
Functional zones in a mitochondrion
By: HWC, Views: 8540
A mitochondrion has a double membrane system. The outer membrane faces the cytoplasm. The inner membrane divides the organelles interior into two compartments. The enzymes that carry out the second stage reactions are in the semifluid matrix inside the inner compartment. Embedded in the ...
Advertisement