Search Results
Results for: 'digestion'
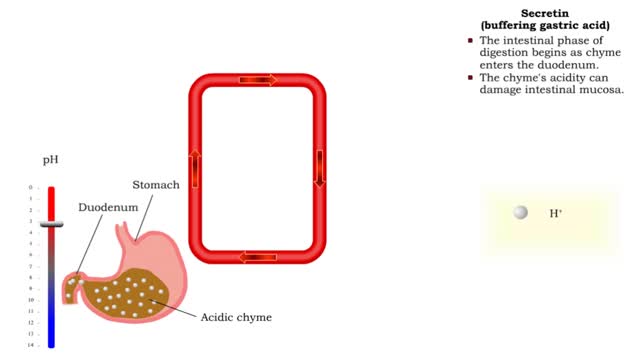
Gastrin (gastric emptying) & Secretin (buffering gastric acid)
By: HWC, Views: 10432
• Gastrin also binds to the smooth muscle cells in the stomach causing: • Increased gastric motility. • Opening of pyloric sphincter. • Increased gastric emptying. • The intestinal phase of digestion begins as chyme enters the duodenum. • The chyme's acidity can damage int...
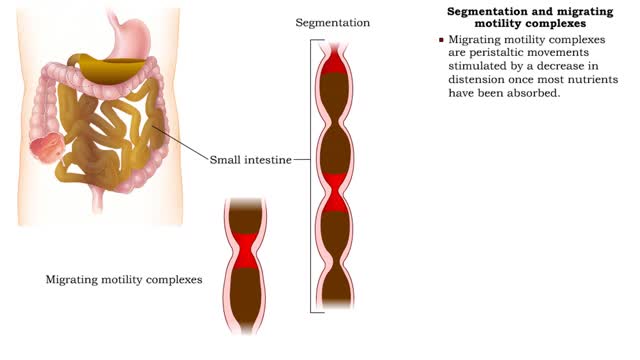
Segmentation and migrating motility complexes & Gastroileal reflex
By: HWC, Views: 10771
• Within a few hours, most of the stomach contents are in the duodenum. • Distension of stretch receptors in the small intestine activates a reflex that stimulates segmentation, a mixing movement. • During segmentation, sections of the intestine are constricted. • This movement incr...
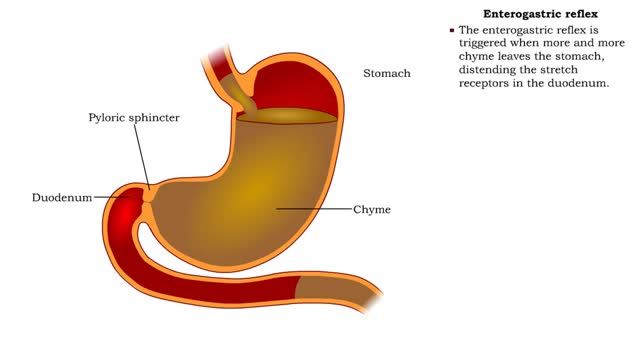
Stomach peristalsis & Enterogastric reflex
By: HWC, Views: 10305
• Food enters, distending the stomach. • Stretch receptors activate enteric reflexes that promote peristaltic movements. • These movements, called mixing waves, begin to mix the food with stomach secretions. • Mixing waves force the digesting food (chyme) toward and through the pylo...
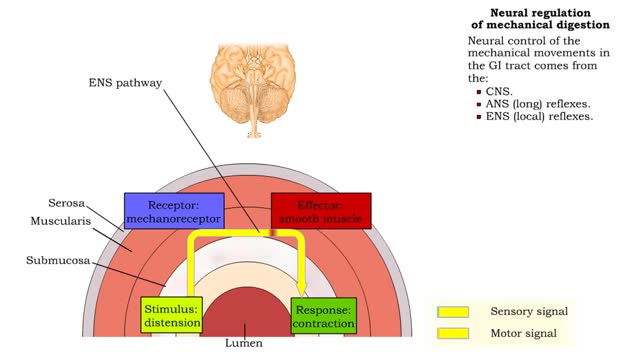
Neural regulation of mechanical digestion- CNS voluntary, ANS & ENS controlled involuntary movements
By: HWC, Views: 10812
• The gastrointestinal [GI] tract is basically a muscular tube that contains and processes food as it moves from the mouth to the anus. • Mechanical digestive functions consist of both voluntary and involuntary muscle contractions and relaxation including: • Chewing and swallowing food....
By: Administrator, Views: 15005
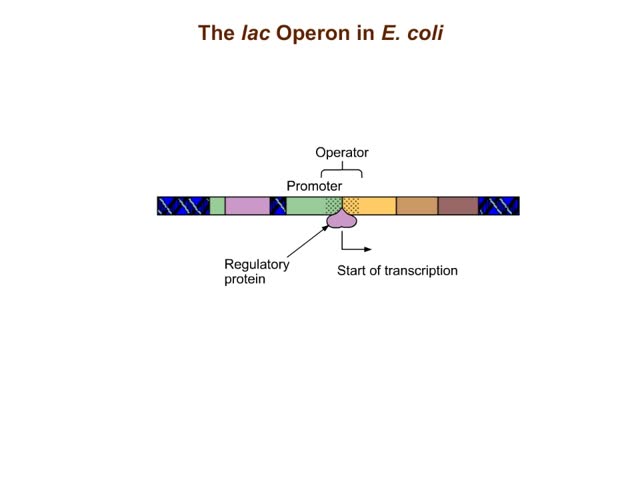
The lac operon (lactose operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is no...
Brain Anatomy Animation (Part 2 of 2)
By: Administrator, Views: 15209
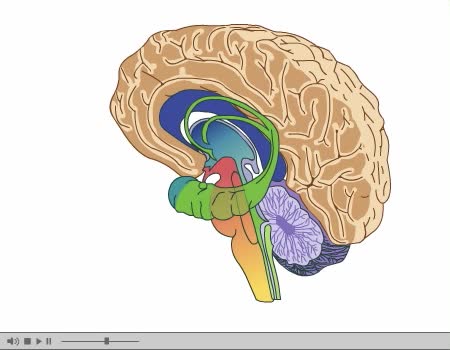
Its nervous tissue consists of millions of nerve cells and fibers. It is the largest mass of nervous tissue in the body. The brain is enclosed by three membranes known collectively as the meninges: dura mater arachnoid pia mater The major structures are the: cerebrum cerebellum dienc...
Advertisement