Search Results
Results for: 'hydronium ions'
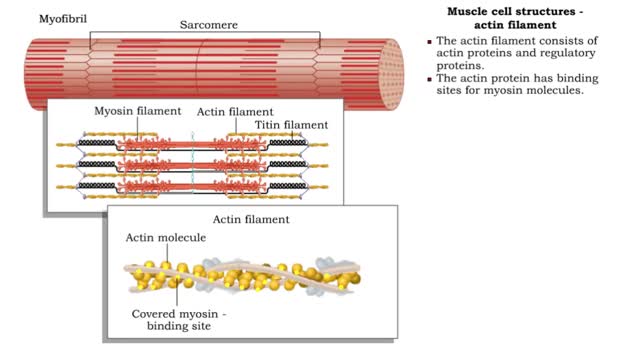
Muscle cell structures - actin, myosin and titin filaments
By: HWC, Views: 9841
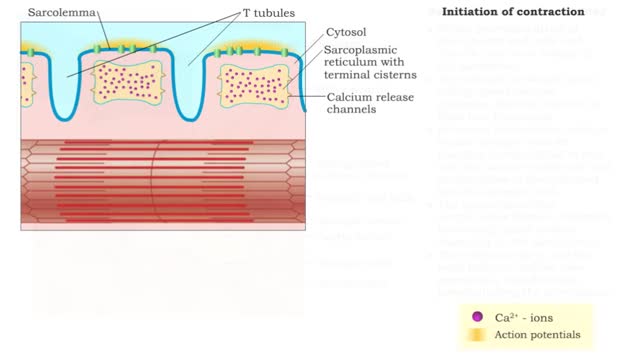
Once the muscle cell has been excited it will contract. • A muscle action potential will trigger the release Of Ca2+ ions into the sarcoplasm. • The Ca2+ ions bind to the regulatory proteins and trigger contraction. • Within skeletal muscle cells are structures that provide the ability...
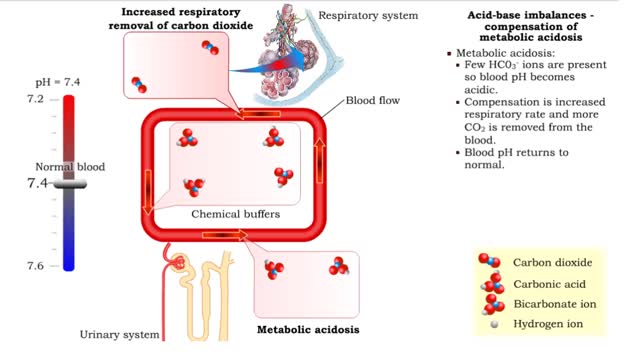
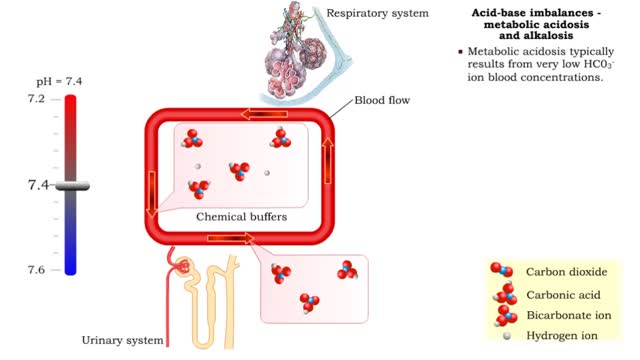
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 9879
1. Metabolic acidosis: • Few HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased respiratory rate and more CO2 is removed from the blood. • Blood pH returns to normal. 2. Metabolic alkalosis: • Many HC03- ions are present so blood pH becomes alkaline...
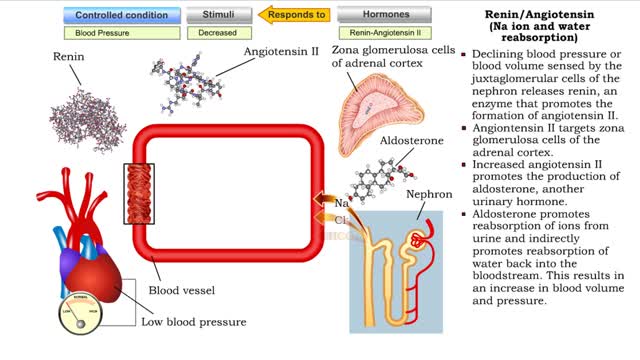
Renin/Angiotensin (water gain from urine & Na ion and water reabsorption)
By: HWC, Views: 9580
• Sensing declining blood pressure or blood volume, juxtaglomerular cells of the nephron release renin, an enzyme that promotes the formation of angiotensin II. • Angiotensin II targets smooth muscle cells in blood vessels that provide blood to the nephron. • Angiotensin II causes thes...
Nervous pathway to the Neuromuscular (NMJ)
By: HWC, Views: 10171
• A nervous impulse, also called an action potential, starts from the brain or spinal cord to signal skeletal muscle cell contraction. Action potentials continue along a motor neuron to the muscle cell. • The signal to contract must cross a synapse - the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) - betwe...
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 9836
• When one pH balancing system is affected then the other balancing system attempts to correct, or compensate for, the pH imbalance. - Respiratory acidosis: • Excessive CO2 is present so blood pH becomes acidic. • Compensation is increased secretion of H+ into urine and reabsorption ...
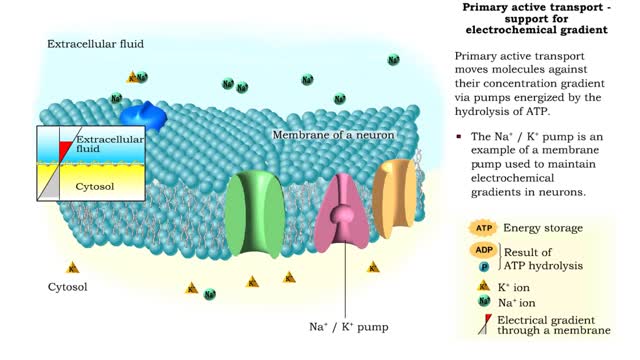
Primary Active Transport - electrochemical gradient and ion transport / water movement
By: HWC, Views: 9829
Energy derived from ATP changes the shape of a transporter protein which pumps a substance across a plasma membrane against its concentration gradient An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consis...
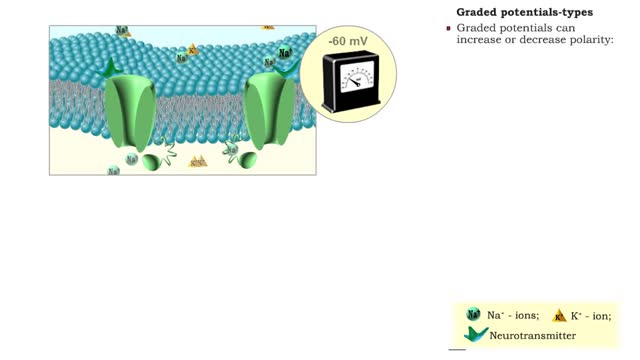
Graded potentials - electrical characteristics and types
By: HWC, Views: 9904
• A graded potential occurs when a gated channel is opened or closed, altering ion flow through the membrane. • Changes in ion and charge distributions cause voltage changes to the resting membrane potential. • The strength of the stimulus determines the number of gated channels affect...
By: HWC, Views: 9811
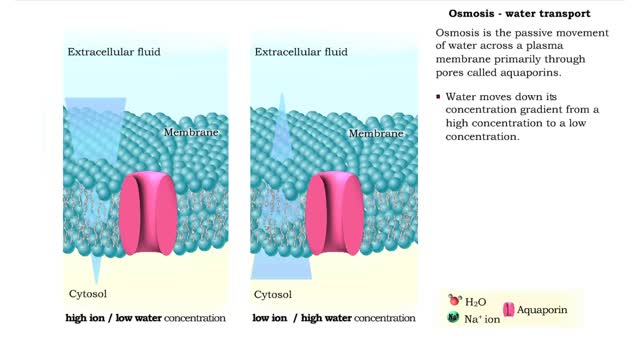
Osmosis is the flow of water down its concentration gradient, across a semi-permeable membrane. Osmosis is an example of diffusion, which is when molecules tend to distribute themselves evenly in a space. what is a semi-permeable membrane? It is a membrane or barrier that allows some molec...
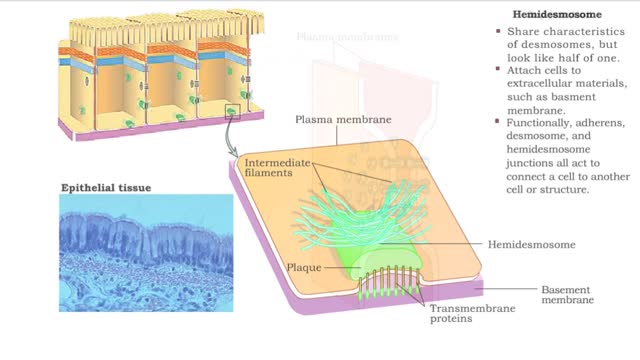
Type of Cell Junctions - Desmosome, Hemidesmosomes and Gap Junctions
By: HWC, Views: 10015
Cell Junctions: Cell junctions are found in some multi-cellular organisms. They exist of complexes and are found between cells and between cells and other structures. The junctions provide a way for cells to connect and exchange signals. What are tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions...
Advertisement