Search Results
Results for: 'red blood cells'
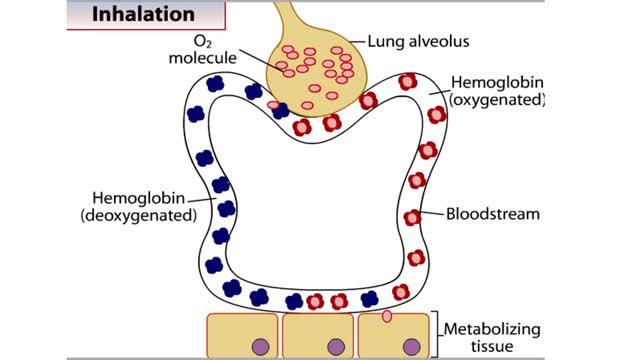
How Hemoglobin Picks Up and Delivers Oxygen
By: HWC, Views: 10310
All of the cells in our bodies require oxygen (02) for survival and must release carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste product. The respiratory and circulatory systems work together as delivery systems for these gases. The lungs exchange these gases between the environment and the bloodstream. The bloo...
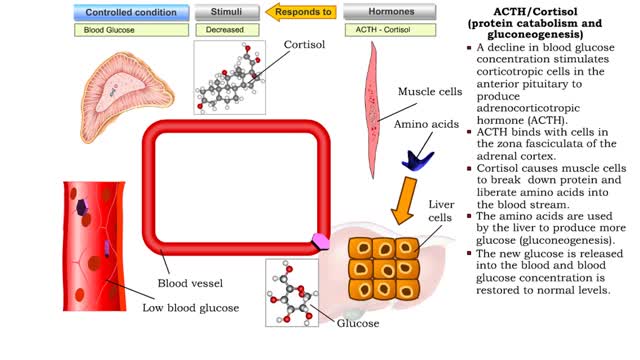
ACTH/Cortisol (glycogenolysis, protein catabolism, lipolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 10808
• A decline in blood glucose concentration stimulates corticotropic cells in the anterior pituitary to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). • ACTH binds with cells in the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex. • Increased ACTH promotes the production of cortisol, the major gluco...
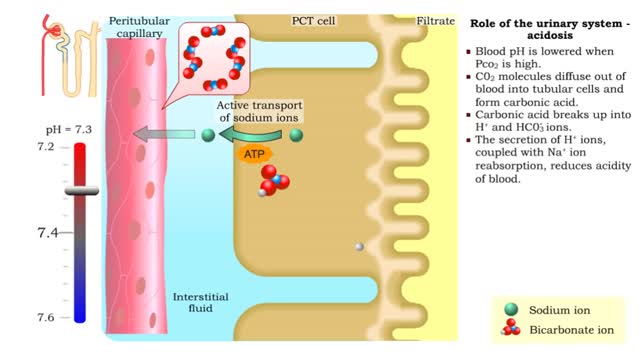
Role of the urinary system - acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11068
• Tubular cells of the proximal convoluted tubule and collecting tubules can alter filtrate pH and therefore blood pH. • These cells can affect blood pH with two coupled mechanisms: • Reabsorption of bicarbonate ions. • Secretion of hydrogen ions. • The reabsorption of bicarbonate...
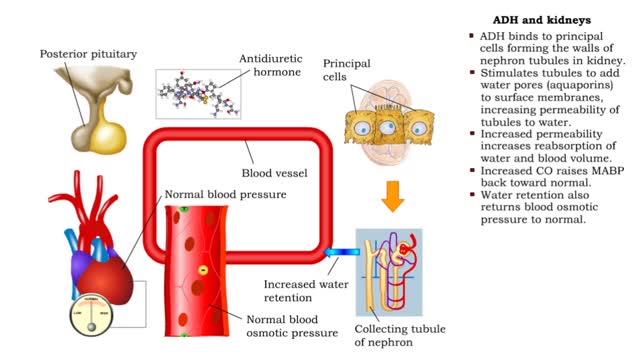
ADH and the arterioles, kidneys, sweat glands and the Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
By: HWC, Views: 11014
• ADH is also known as vasopressin. • Produced by hypothalmus and secreted by neurosecretory cells in posterior pituitary gland. • Responds to high blood osmotic pressure representing low amounts of water in the blood. • Binds to smooth muscle cells in walls of arterioles, stimulate...
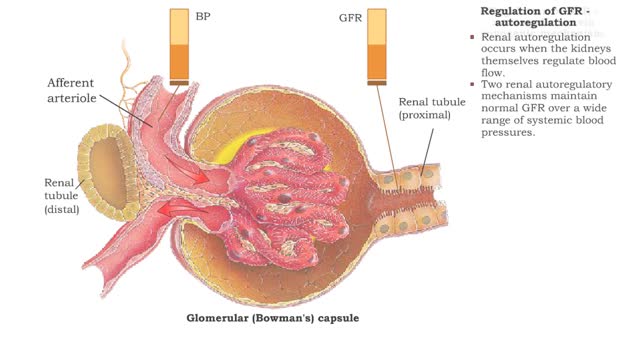
Regulation of GFR: three methods, autoregulation & autoregulation via myogenic mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 11452
• GFR can be regulated by adjusting: • Blood flow in and out of the glomerular capillaries. • Surface area of glomerular capillaries. • There are three main ways to make these adjustments: • Renal autoregulation. • Nervous regulation. • Hormonal regulation. • Ren...
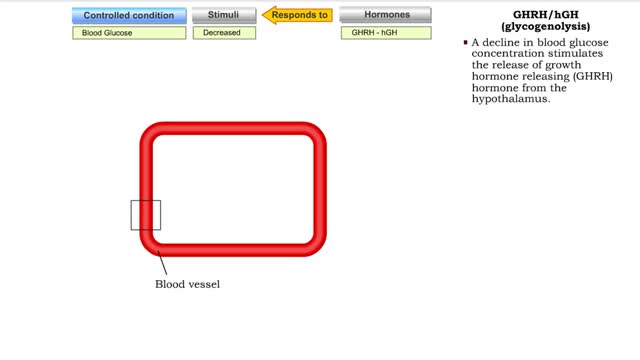
Hormonal feedback loop components & Glucagon (glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 10740
The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: • Stimulus - a change in a body condition. • Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone after ...
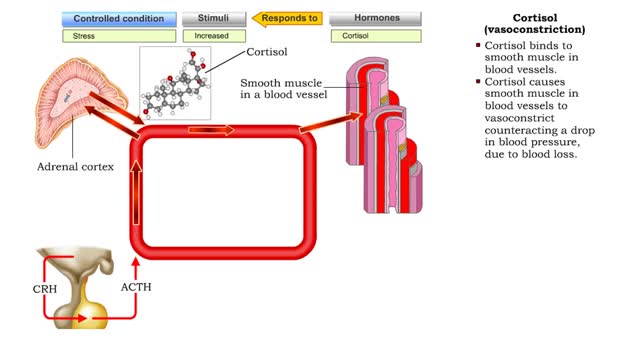
Cortisol (protein catabolism, gluconeogenesis, vasoconstriction & anti-inflammation)
By: HWC, Views: 10661
• Stressors stimulate production of hypothalamic releasing hormones, corticotropin releasing hormone, hormone (CRH) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) stimulate. • These hormones promote increased production of 1 cortisol from the zona fasciculata cells of the adrenal cortex. • Cort...
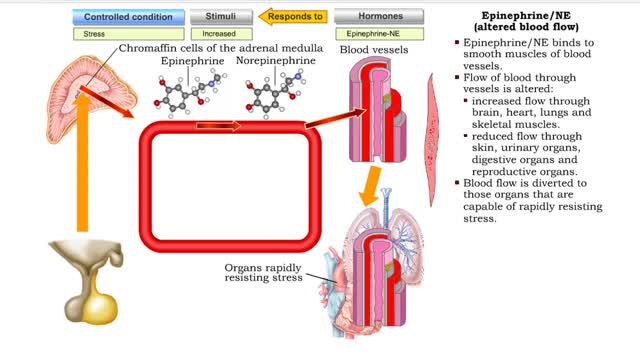
Epinephrine/NE (heart rate, altered blood flow, glycogenolysis & bronchodilation)
By: HWC, Views: 10795
• Stressors trigger increased sympathetic stimulation from the hypothalamus to the chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla. • This causes the immediate release of epinephrine and norepinephrine (NE). • Epinephrine/NE binds to the cardiac muscles of the heart. • Cardiac muscle cells ...
Apicomplexan life cycle Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5313
Malaria is caused by the sporozoan, Plasmodium. It is transferred to humans by mosquitoes. When an infected mosquito feeds, infective sporozoites move from her salivary glands into the human body. The bloodstream carries the sporozoites to the liver. Here, they reproduce asexually and...
Advertisement