Search Results
Results for: 'ED'
Isovolumetric VC, Ventricular ejection, Isovolumetric & Passive ventricular filling
By: HWC, Views: 10834
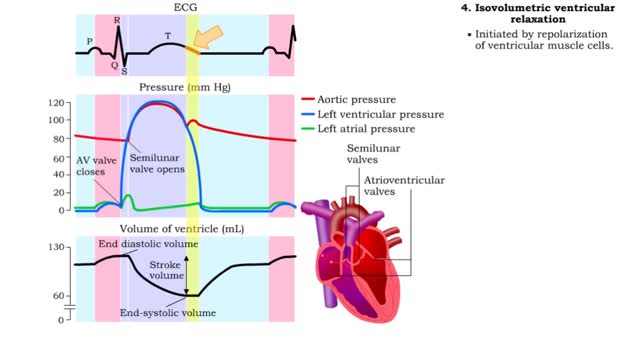
• Isovolumetric means that blood volume does not change. • Ventricular blood volume and cell length remain constant. • With valves closed and contraction continuing, ventricular pressure continues to rise. • Ventricular pressure rises above arterial pressure. • Increased ventr...
By: HWC, Views: 10912
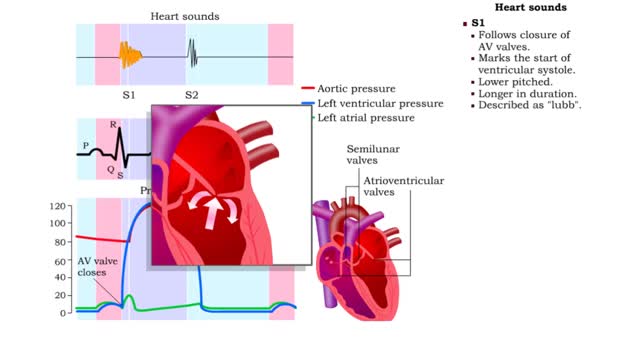
During a normal, healthy heartbeat, or what we call a cardiac cycle, the top two chambers of the heart, called the atria, contract simultaneously. Then, as they relax, the bottom two chambers, called the ventricles, contract. This explains what happens during a cardiac cycle, but what it doesn't ...
Exercise and cardiac output & Definition of stroke volume
By: HWC, Views: 10910
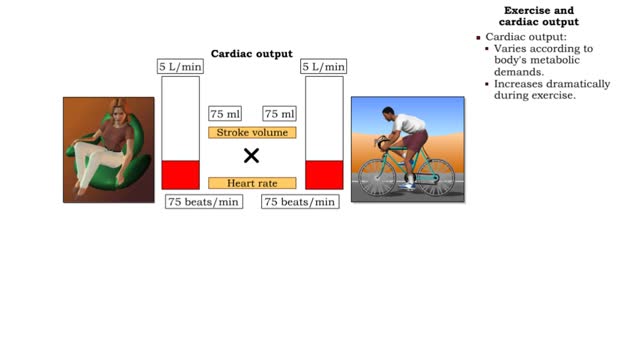
▪ Cardiac output: • Maintains blood flow throughout the body. • Measure of blood volume ejected from the heart over a given time. • Determined by multiplying heart rate by stroke volume (CO = SV x HR). • Heart rate: Number of beats/min. • Stroke volume: Amount of blood eject...
By: HWC, Views: 10888
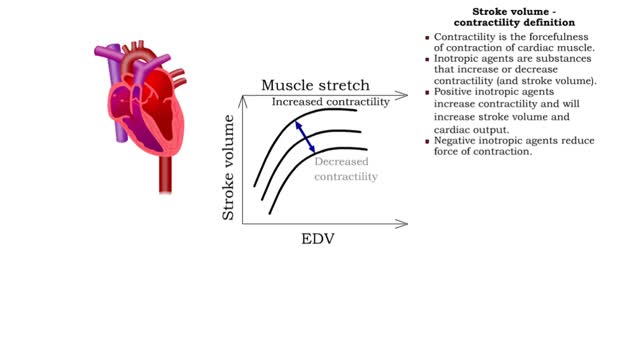
Preload definition • Preload is the degree of stretch of cardiac muscles cells prior to contraction. • The amount of stretch is related to the end-diastolic volume[EDV]. • Increased return blood flow from the veins increases end-diastolic volume. Cardiac muscle sarcomeres stretch and ...
By: HWC, Views: 11061
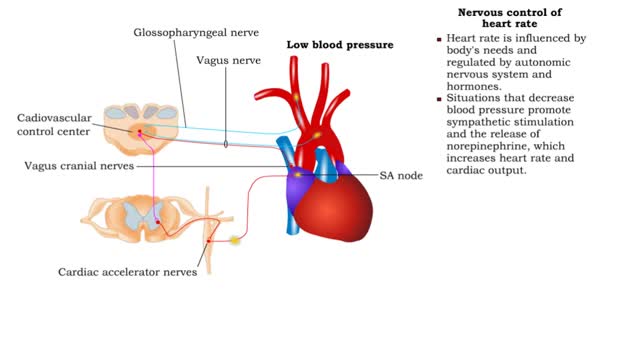
• Heart rate is determined by the rate of depolarizations of the sinoatrial (SA) node. • Cardiac output is directly proportional to heart rate, the greater the heart rate the greater the cardiac output. • Changes in heart rate are associated with exercise, stress or injury. Nervous ...
By: HWC, Views: 11005
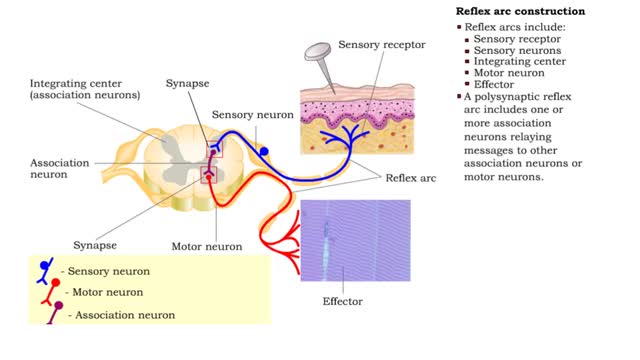
• Somatic reflexes are the rapid, predictable, and automatic responses of skeletal muscle to changes in stimuli. • A reflex arc is the pathway followed by the nerve impulse producing the reflex. • Reflex arcs include: • Sensory receptor • Sensory neurons • Integrating c...
By: HWC, Views: 11027
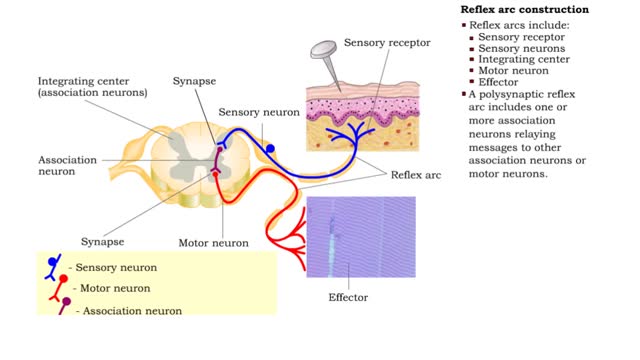
• Somatic reflexes are the rapid, predictable, and automatic responses of skeletal muscle to changes in stimuli. • A reflex arc is the pathway followed by the nerve impulse producing the reflex. • Reflex arcs include: • Sensory receptor • Sensory neurons • Integrating cen...
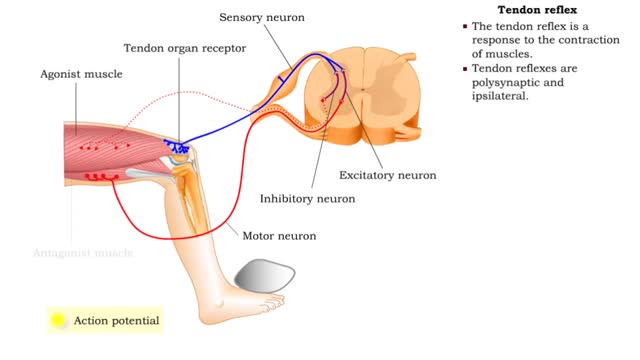
Stretch reflex & Tendon reflex
By: HWC, Views: 10759
• The stretch reflex is a response to the stretching of muscles. It is monosynaptic and ipsilateral. • Stretching stimulates receptors in the muscle spindle of the agonist (stretched) muscle. • One or more action potentials are generated by the receptors and propagate along the axon of ...
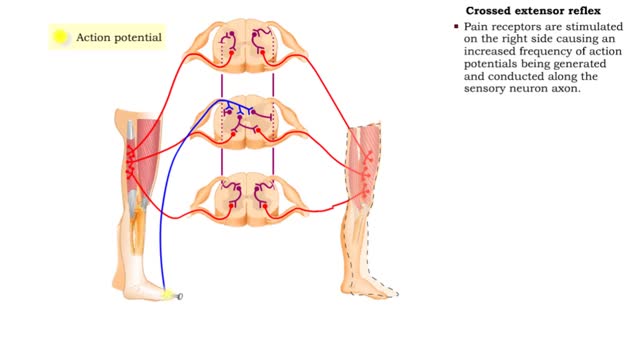
Flexor reflex & Crossed extensor reflex
By: HWC, Views: 10868
• The flexor reflex is a response to pain. This reflex is polysynaptic, ipsilateral, and intersegmental. • Pain receptors are stimulated causing increased frequency of action potentials to be generated and conducted along the sensory neuron axon. • The sensory impulses excite several ass...
Advertisement