Search Results
Results for: 'Cellular Defects'
By: Administrator, Views: 15492
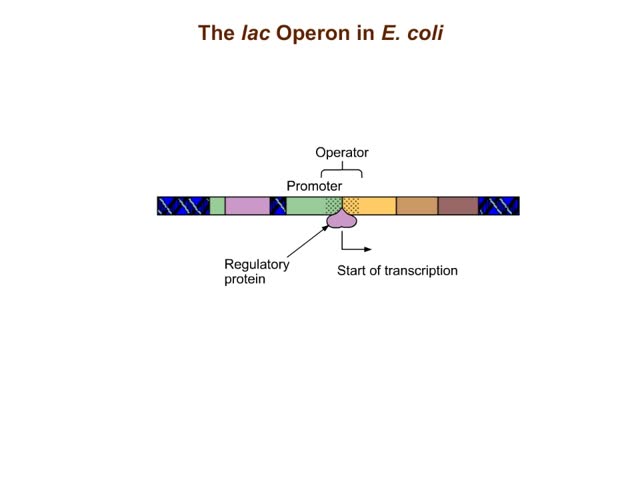
The lac operon (lactose operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is no...
Type of Cell Junctions - Desmosome, Hemidesmosomes and Gap Junctions
By: HWC, Views: 11689
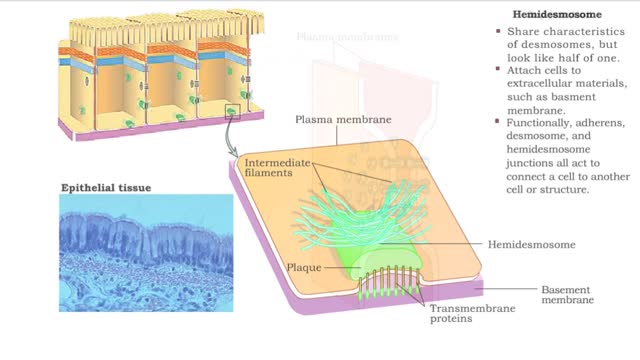
Cell Junctions: Cell junctions are found in some multi-cellular organisms. They exist of complexes and are found between cells and between cells and other structures. The junctions provide a way for cells to connect and exchange signals. What are tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions...
Hierarchical Sequencing Method - Sequence Tagged Sites
By: HWC, Views: 10640
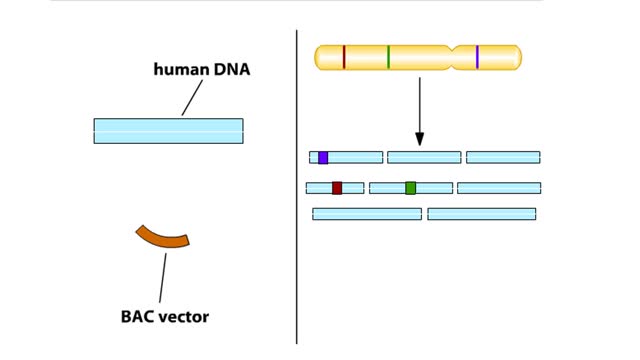
In the hierarchical sequencing method, researchers begin by collecting cells. In humans, each cell contains 23 pairs of chromo-somes. Here we specifically track the DNA from just one of the 23 pairs. Chromosomes have a series of unique DNA sequences, called sequence-tagged sites (STSs), that a...
Structure of Amino Acid, Peptide Bonds & Polypeptides
By: HWC, Views: 10935
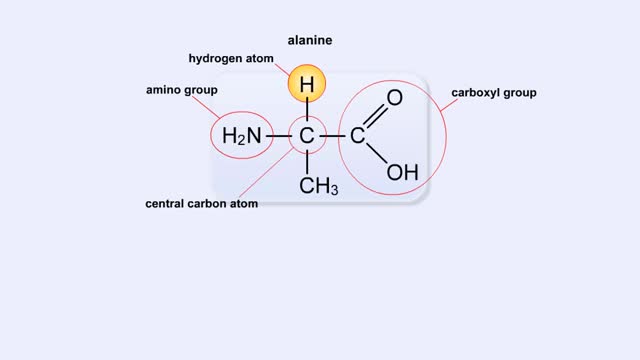
Here are the molecular formulas of three different amino acids. All amino acids share this backbone. The main difference between every amino acid is the side groups seen here, and these side groups give each of the amino acids their different characteristics. But before we get into that, let's ...
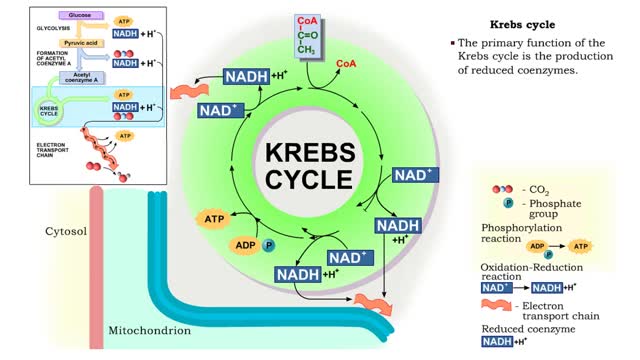
Krebs cycle : Formation of acetyl coenzyme A and Electron transport chain
By: HWC, Views: 11576
The oxidation of glucose to produce ATP is cellular respiration. Four sets of reactions are involved: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Krebs cycle reactions Electron transport chain reactions • The second pathway of glucose catabolism, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, is a transi...
Advertisement