Search Results
Results for: 'Energy inputs and release in glycolysis Animation'
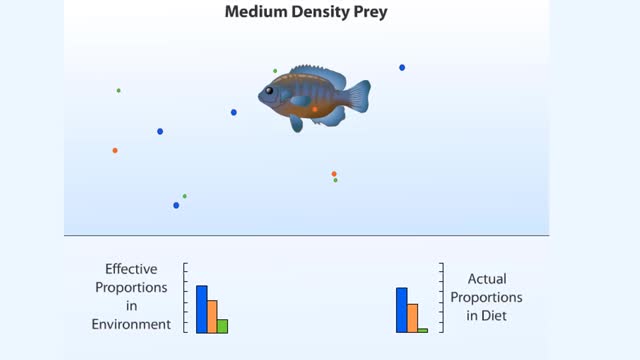
How does an animal choose what food to eat?
By: HWC, Views: 10358
One might assume that natural selection has influenced the foraging behaviors of animals, and that most animals forage efficiently, spending the least energy to gain the most nutrients. This is the underlying assumption of optimality modeling, a scientific approach to studying foraging behavior. ...
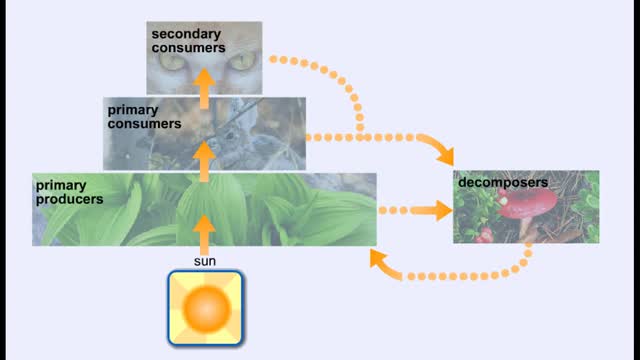
Energy Flow - Trophic Levels and Food
By: HWC, Views: 10517
All of these relationships between different species are founded on one thing: energy. Organisms get food in order to get energy, which is used by the organism for growth, maintaining health, and reproduction. We can classify the members of a community according to how they obtain food. Produc...
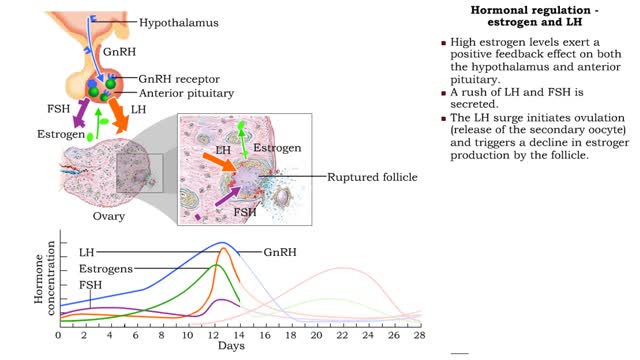
Phases of the Female Reproductive Cycle - Hormonal regulation
By: HWC, Views: 11368
FSH, LH and estrogen • FSH travels through the bloodstream from the anterior pituitary to the ovaries. • FSH promotes follicular growth. Increased follicular growth promotes estrogen production. • Small increases in blood estrogen levels inhibit the release of FSH and LH into the bl...
By: Administrator, Views: 13755
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), poor nourishment, poor circulation, loss of hormonal support, loss of nerve supply to the target organ, excessive amount of apoptosis of c...
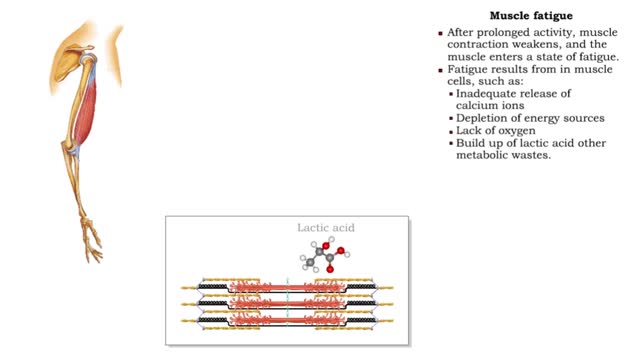
By: HWC, Views: 10625
• After prolonged activity, muscle contraction weakens, and the muscle enters a state of fatigue. • Fatigue results from in muscle cells, such as: • Inadequate release of calcium ions • Depletion of energy sources • Lack of oxygen • Build up of lactic acid other metabolic w...
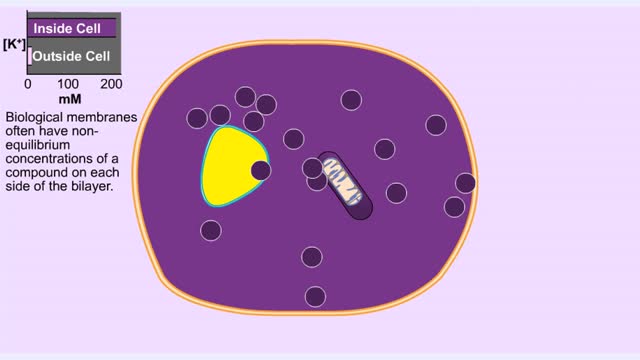
Membrane Protein and Facilitated Transport (Passive Vs Active)
By: HWC, Views: 10502
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins span the membrane, with hydrophobic amino acids interacting with the lipid bilayer and hy...
What are the Parts of a Plant Cell?
By: HWC, Views: 9909
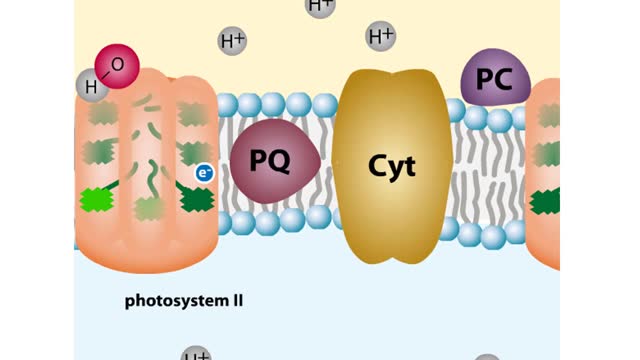
Every chloroplast in a plant cell is packed with stacks of flattened sacs called thylakoids. The thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll, as well as most of the other components required for the light reactions of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll-containing structures within the membranes are c...
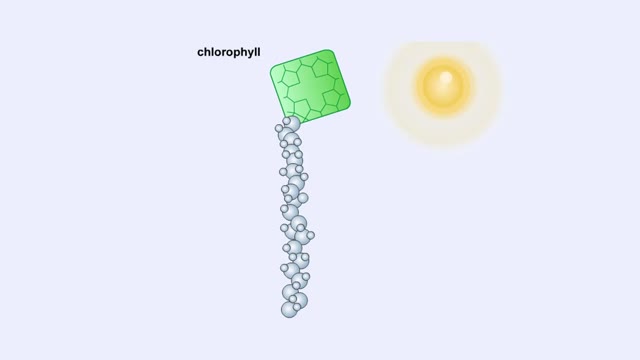
Electromagnetic Spectrum, Chlorophyll and Pigment & Light
By: HWC, Views: 10682
The sun gives off radiation that is called the electromagnetic spectrum. This is energy that travels as wavelengths and includes radio waves, X-rays and ultraviolet light. A portion of this radiation is known as visible light, and is the type of radiation that plants use to manufacture sugars. ...
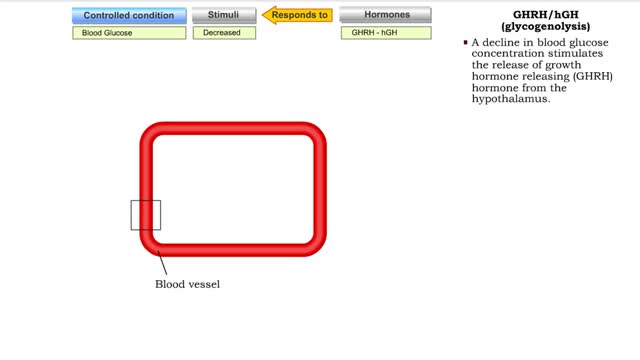
Hormonal feedback loop components & Glucagon (glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 10715
The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: • Stimulus - a change in a body condition. • Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone after ...
Advertisement