Search Results
Results for: 'Energy inputs and release in glycolysis Animation'
Mitochondrial Structure & ETC Protein Complexes (Protein Complexes and Electron Transport)
By: HWC, Views: 10643
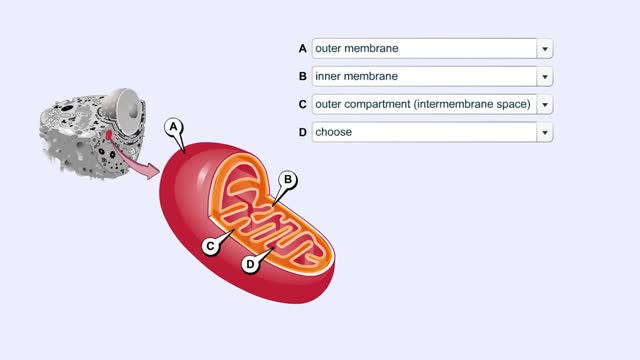
The energy carrying molecules, NADH and FADH2, that were generated in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, now are processed in the mitochondria where their high energy electrons are deposited in an electron chain complex located in the inner mitochondrial membranes. These high-energy electrons now dr...
By: HWC, Views: 11364
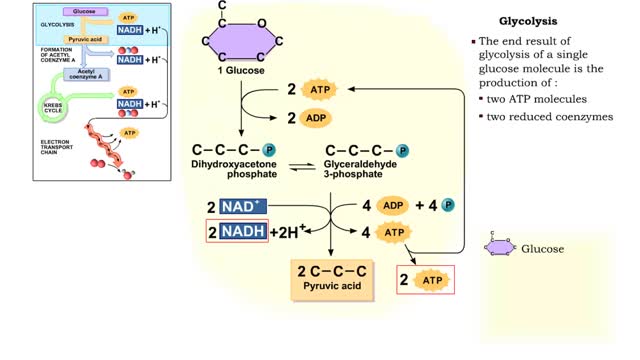
The first reactions involve a single 6-carbon glucose sugar undergoing phosphorylation using two ATP molecules and resulting in two 3-carbon compounds. • The rest of this pathway involves an oxidation reduction reaction, forming two reduced coenzymes, and generation of four ATP molecules. ...
By: HWC, Views: 11256
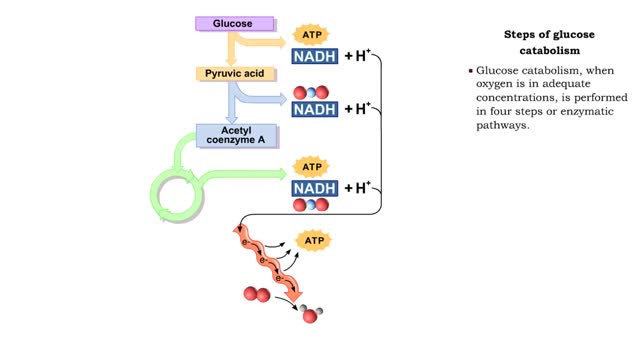
• During digestion, complex carbohydrates are hydrolyzed into monosaccharides, primarily glucose. • The catabolism of glucose is the primary source of energy for cellular production of ATP. • The anabolism of glucose is important in regulating blood glucose levels. • Glucose cat...
By: HWC, Views: 10842
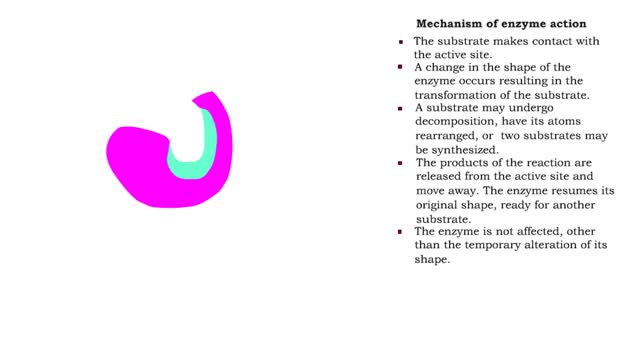
■ The substrate makes contact with the active site. ■ A change in the shape of the enzyme occurs resulting in the transformation of the substrate. ■ A substrate may undergo decomposition, have its atoms rearranged, or two substrates may be synthesized. ■ The products of the reaction...
Activation Energy - Valence Electrons
By: HWC, Views: 10457
■ Shared electrons in the outermost orbital form bonds. These electrons are called valence electrons. ■ Valence electrons are disrupted and can be rearranged into a new bond. ■ The energy necessary to start a reaction and break bonds is called the activation energy. ■ Reactants have...
By: HWC, Views: 11229
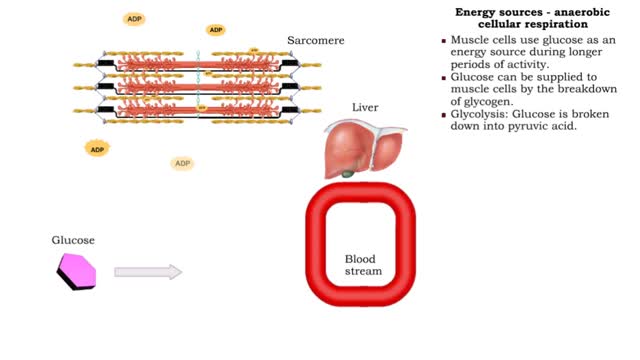
• The amount of ATP stored in a skeletal muscle cell can only provide muscular activity for two to three seconds. • Muscle cells must be able to generate additional molecules of ATP to continue contracting. • Muscle cells can generate ATP from several processes: • Phosphogen syste...
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Carbohydrates
By: HWC, Views: 10611
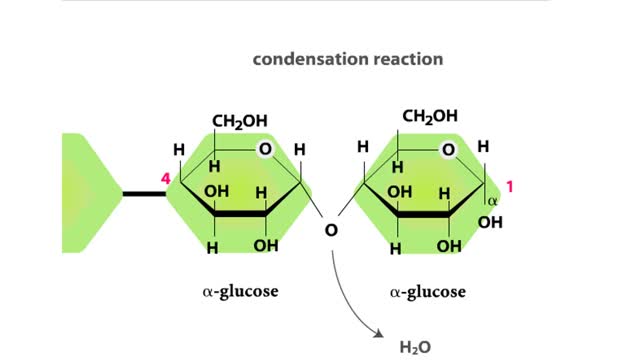
Carbohydrates include simple sugars (monosaccharides) as well as large polymers (polysaccharides). Glucose is a hexose, a sugar composed of six carbon atoms, usually found in ring form. A starch macromolecule is a polysaccharide composed of thousands of glucose units. Glucose molecules can be ...
By: HWC, Views: 11312
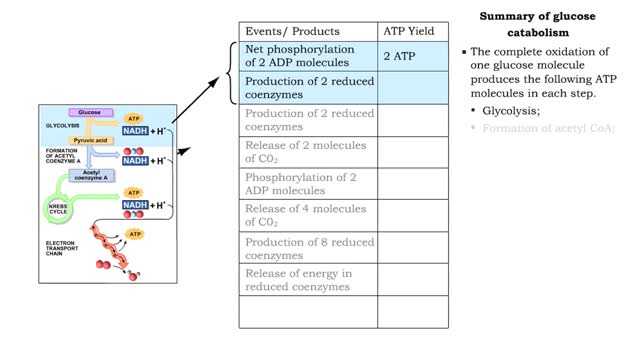
■ The complete oxidation of one glucose molecule produces the following ATP molecules in each step. • Glycolysis; • Formation of acetyl CoA; • Krebs cycle; • Electron transport chain. ■ In addition, glucose catabolism produces six CO2 molecules and water.
Protein catabolism (Krebs cycle) and Protein anabolism (protein synthesis)
By: HWC, Views: 11600
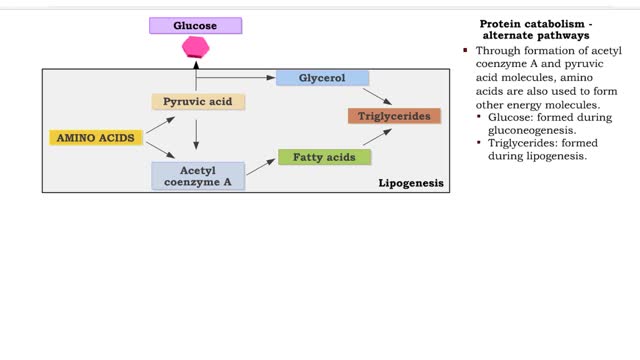
• Deaminated acids are brought into the Krebs cycle to be oxidized to CO2 and H2O. • Before entering the Krebs cycle, the deaminated acids are converted into intermediate products (pyruvic acid, acetyl coenzyme A, carbonic acids). • In the Krebs cycle, amino acids are oxidized to form r...
Advertisement