Search Results
Results for: 'brain'
By: HWC, Views: 11338
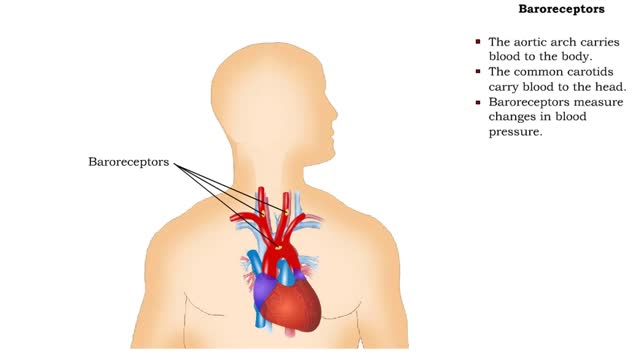
A baroreceptor is a specialized nerve ending that allows your brain to sense blood flow and blood pressure in the major blood vessels of your circulatory system. • The aortic arch carries blood to the body. • The common carotids carry blood to the head. • Baroreceptors measure chang...
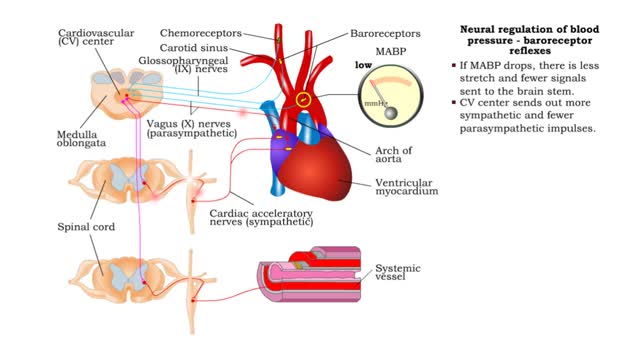
Neural regulation of blood pressure - baroreceptor and chemoreceptor reflexes
By: HWC, Views: 11995
• The nervous system regulates blood pressure with two reflex arcs: baroreceptor and chemoreceptor. ■ Baroreceptors (pressure) and chemoreceptors (chemical) are located in the carotid sinus and aortic arch. • Carotid sinus reflex helps maintain normal blood pressure in brain. • Ba...
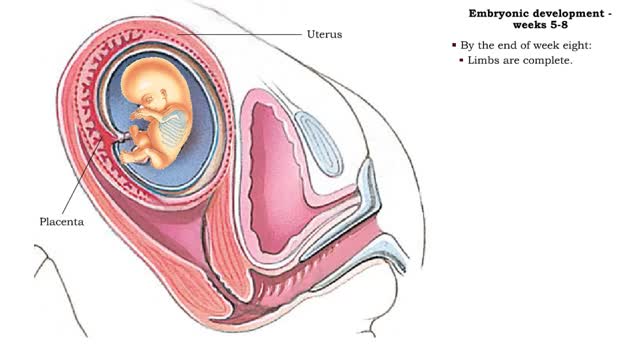
Embryonic development - Weeks 5 to 8
By: HWC, Views: 11750
• The second month of development is characterized by rapid development of the head and limbs as well as continued organogenesis. • During the fifth and sixth weeks growth of the brain, and therefore head, is rapid. • Hands and feets begin to form. • During week seven, even more deve...
By: Administrator, Views: 14870
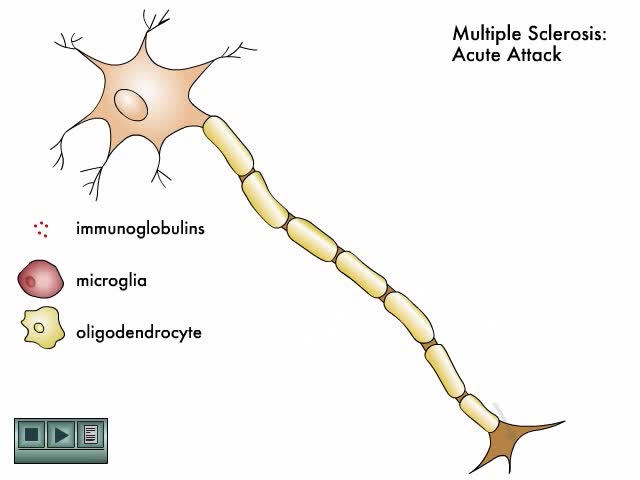
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a demyelinating disease in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This damage disrupts the ability of parts of the nervous system to communicate, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, mental, and so...
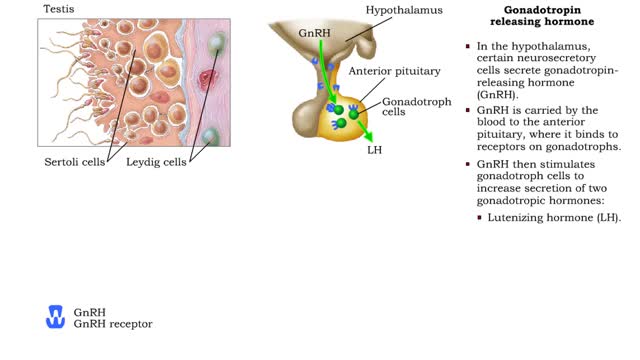
Male Reproductive System - The gonadotropin releasing hormone
By: HWC, Views: 12369
• Hormonal mechanisms that influence male reproductive function involve endocrine tissues contained in the: • Hypothalamus of the brain. • Anterior pituitary. • Testes. • In the hypothalamus, certain neurosecretory cells secrete gonadotropin- releasing hormone (GnRH). • GnRH ...
By: Administrator, Views: 14673
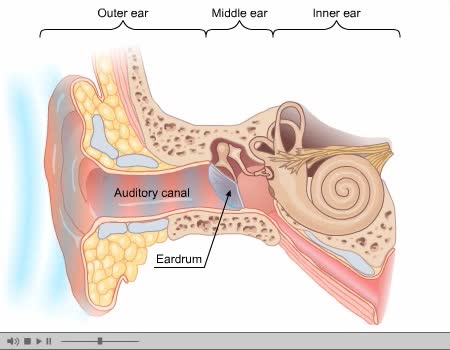
The ear is the organ of hearing and, in mammals, balance. In mammals, the ear is usually described as having three parts—the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear consists of the pinna and the ear canal. Since the outer ear is the only visible portion of the ear in most ani...
By: Administrator, Views: 14900
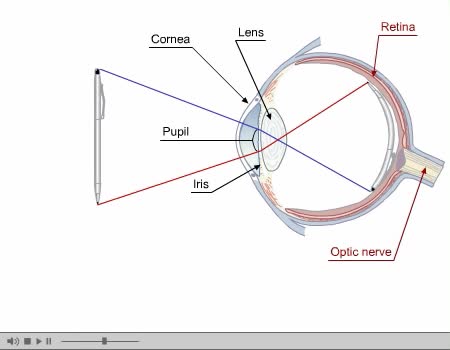
Eye Composed of special anatomical structures that work together to facilitate sight: Cornea Pupil Lens Vitreous body Light stimulates sensory receptors (rods and cones) in the retina or innermost layer of the eye. Vision is made possible through the coordinated actions of nerves that co...
By: Administrator, Views: 14949
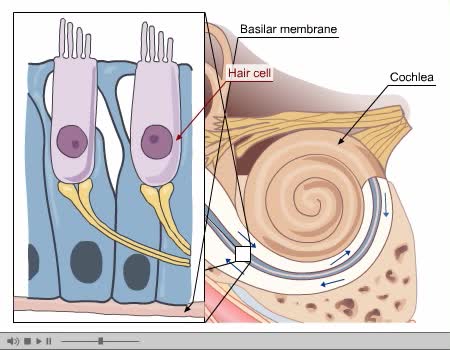
Process of Hearing Sound waves are directed to the eardrum, causing it to vibrate. These vibrations move the three small bones of the middle ear (malleus, incus, and stapes). Movement of stapes at oval window sets up pressure waves in the perilymph and endolymph. Process of Hearing The wav...
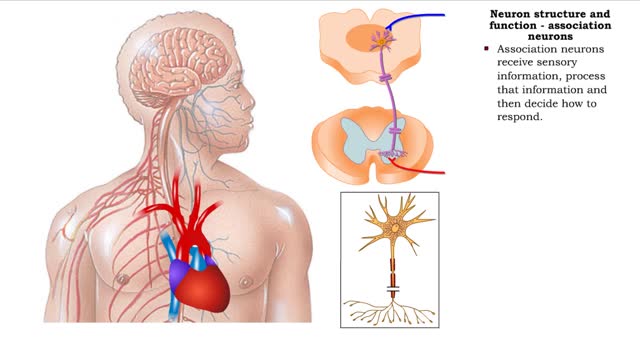
Neuron structure and function - sensory neurons, association neurons & motor neurons
By: HWC, Views: 11572
• The primary function of the nervous system is to provide rapid communication within the body to maintain homeostasis. • This function underlies behaviors, thinking and control of organ functions. • The basic functions of the nervous system are provided by: • Sensory neurons • ...
Advertisement