Search Results
Results for: 'hydrogen group'
Types of Transport - Uniport, Antiport and Symport (Glucose and Na+K+ Transporters)
By: HWC, Views: 11427
Some transport proteins bind and transport molecules very selectively. Uniport is the transport of one solute molecule. Symport is the transports of two solute molecules in the same direction. Antiport is the transports of two solute molecules in opposite directions. 1. Glucose bin...
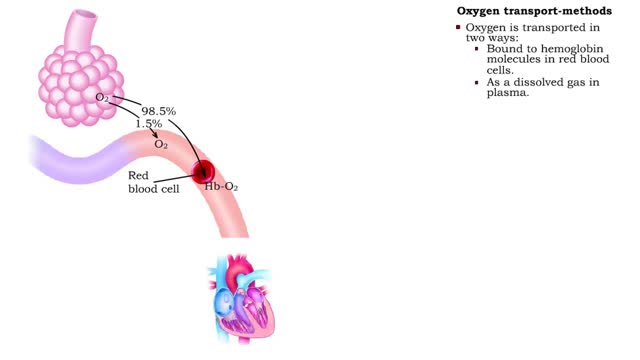
Oxygen transport - methods and oxyhemoglobin
By: HWC, Views: 11606
• The blood is the medium used for gas transport throughout the body. • Oxygen is only available in the lungs. Because the partial pressure of oxygen is higher in the alveoli than in the blood, oxygen diffuses into the blood and is transported to systemic cells. • At the tissues the par...
By: HWC, Views: 10763
Living things must accomplish a great number of tasks just to get through a day, and these tasks are accomplished by a diverse range of biological molecules. In the range of tasks that molecules accomplish, however, proteins reign supreme. Almost every chemical reaction that takes place in living...
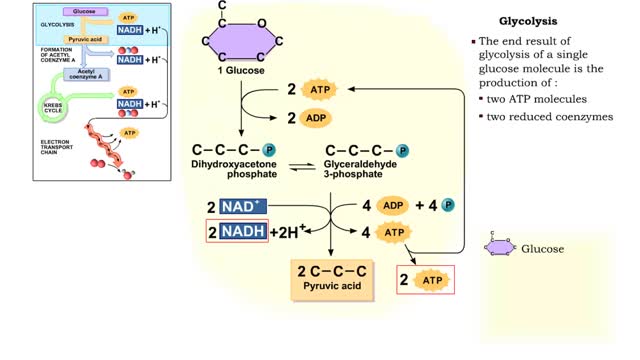
By: HWC, Views: 12017
The first reactions involve a single 6-carbon glucose sugar undergoing phosphorylation using two ATP molecules and resulting in two 3-carbon compounds. • The rest of this pathway involves an oxidation reduction reaction, forming two reduced coenzymes, and generation of four ATP molecules. ...
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
By: Administrator, Views: 14821
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body in both health and disease. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the or...
What are Strong & Weak Acids and How they're different?
By: HWC, Views: 10493
Let's consider the changes that take place when hydrogen chloride, HCI, is added to water. You will need to recognize space-filling models of HCI molecules, hydronium ions (H30+), chloride ions (C11, and water molecules (H20). They are shown at the right. When HC1 molecules dissolve in water, ...
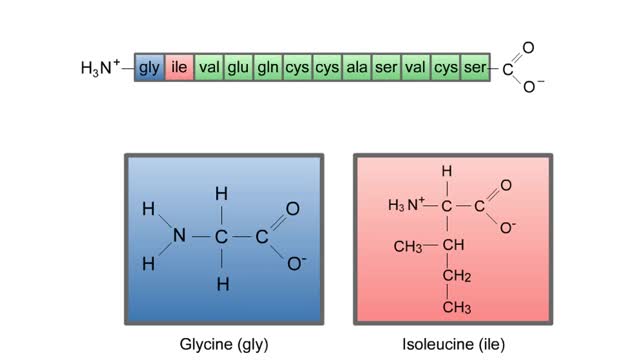
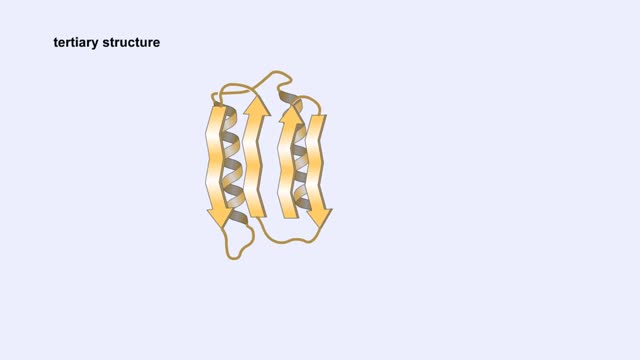
Protein Structure - Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary
By: HWC, Views: 11606
A protein's first order structure, or primary structure, begins with the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain. The 20 different amino acids can be arranged in an infinite number of sequences. For example, the hormone insulin, which regulates the uptake of glucose from the blood into ce...
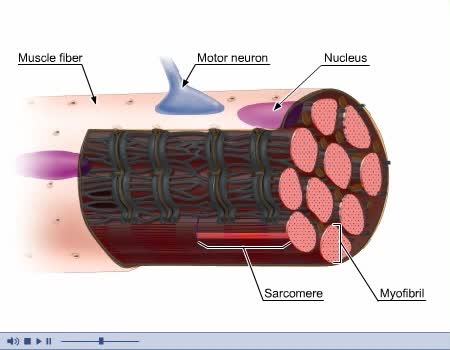
By: Administrator, Views: 14575
Three basic types of muscles: - Skeletal - Smooth - Cardiac Composed of striated or smooth muscle tissue and classified according to their functions and appearance. Skeletal Muscle: - Also known as voluntary or striated muscle. - Controlled by the conscious part of the brain and attach...
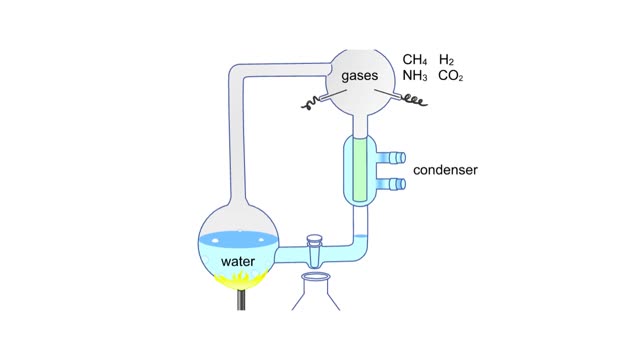
Miller's reaction chamber experiment Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5473
A simple diagram of Stanley Miller and Harold Urey's experimental apparatus. The lower portion of the apparatus was filled with water. The upper portion was filled with a mixture of gases that simulated the earth's early atmosphere. Examples are methane, ammonia, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. ...
Advertisement