Search Results
Results for: 'plasma cells'
Endocytosis - pinocytosis, receptor mediated and Transcytosis
By: HWC, Views: 11585
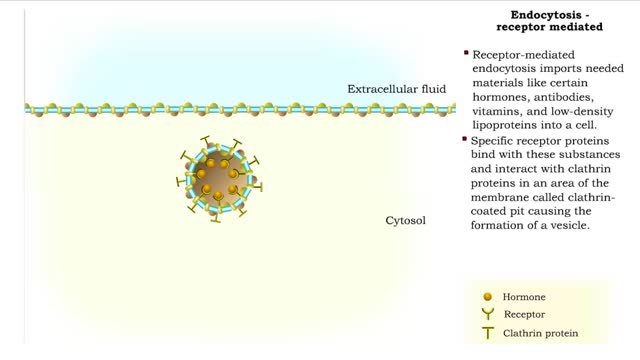
Pinocytosis is the process in which a cell "drinks" a tiny droplet Of extracellular fluid, including its solutes. Pinocytosis (Cell Drinking) is the process by which the cell takes in fluids (as well as any small molecules dissolved in those fluids). • The plasma membrane folds inward to...
By: HWC, Views: 9767
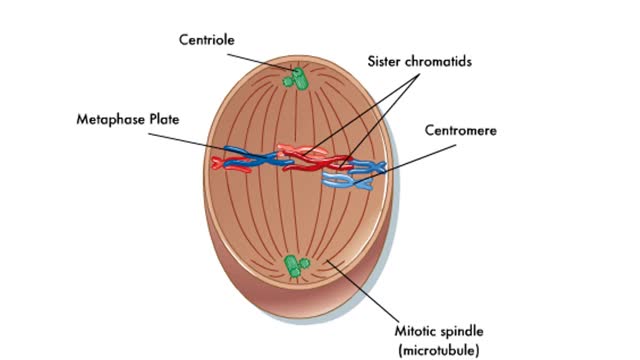
Prophase is the first step in the mitotic process. During prophase, the chromosomes condense. The centrosomes begin to form a spindle and move into position on opposite sides of the cell. Sister chromatids are held together by a protein called cohesin at the centromere. Prometaphase is the sec...
By: HWC, Views: 11897
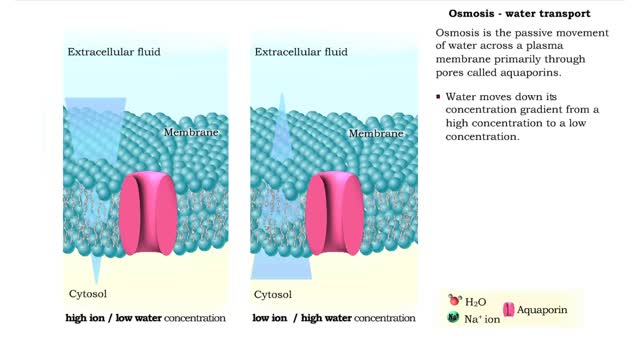
Osmosis is the flow of water down its concentration gradient, across a semi-permeable membrane. Osmosis is an example of diffusion, which is when molecules tend to distribute themselves evenly in a space. what is a semi-permeable membrane? It is a membrane or barrier that allows some molec...
Cellular Respiration & Glucose Mobilization (Glucose transport & Phosphorylation of Glucose)
By: HWC, Views: 11445
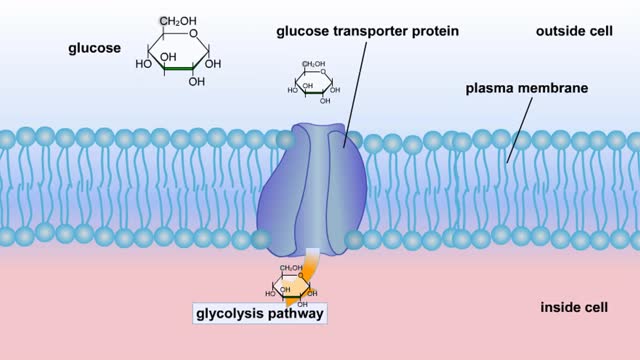
Glucose is completely broken down into CO2 and H2O during the process of cellular respiration, which includes 3 stages: 1) glycolysis; 2) the Krebs Cycle; and 3) the electron transport chain. Glucose enters this energy yielding pathway of cellular respiration in the first stage known as...
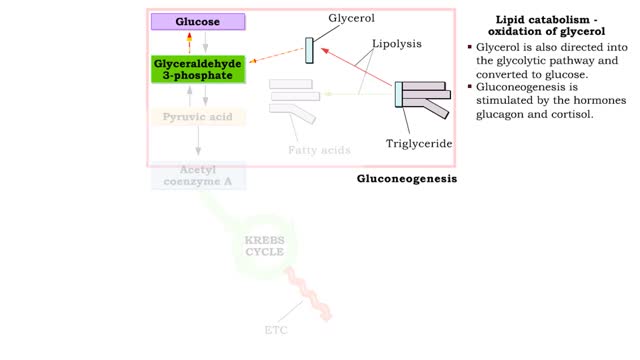
Lipid catabolism ( ketogenesis and oxidation of glycerol) and Lipid anabolism (lipogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 12067
• During excessive beta oxidation, the two-carbon fatty acid fragments are converted into acidic ketone bodies. • Ketosis, the overproduction of ketone bodies, can lead to acidosis (ketoacidosis) of the blood. • After lipolysis, glycerol is converted to pyruvic acid. • Pyruvic aci...
By: HWC, Views: 11235
■ Secreted by kidney cells when blood oxygen is low. ■ Targets cells in red bone marrow that will become red blood cells. ■ Promotes increased numbers of mature red blood cells. ■ More mature red blood cells carry more oxygen so blood oxygen level is restored to normal.
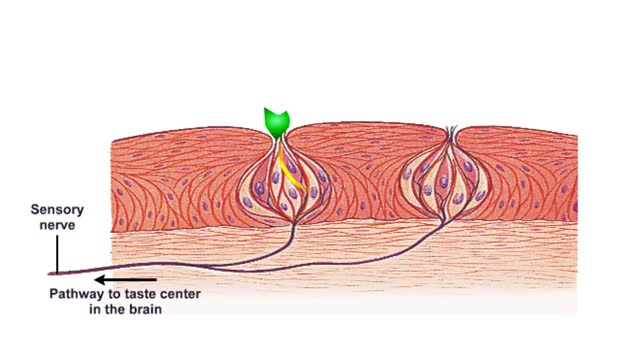
What are Taste Receptors? How Does it Work? Animation
By: HWC, Views: 8600
Do you ever wonder how you can taste the foods you eat? It all starts with taste receptors in your muscular tongue. Taste receptor neurons are found in your taste buds but you are not looking at the taste buds. The raised bumps on the surface of the tongue that you see are specialized epith...
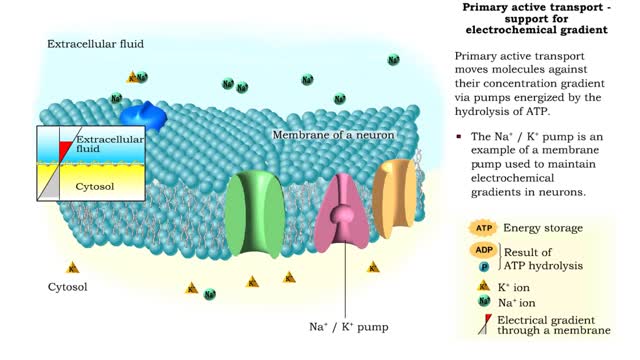
Primary Active Transport - electrochemical gradient and ion transport / water movement
By: HWC, Views: 11933
Energy derived from ATP changes the shape of a transporter protein which pumps a substance across a plasma membrane against its concentration gradient An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consis...
By: HWC, Views: 11343
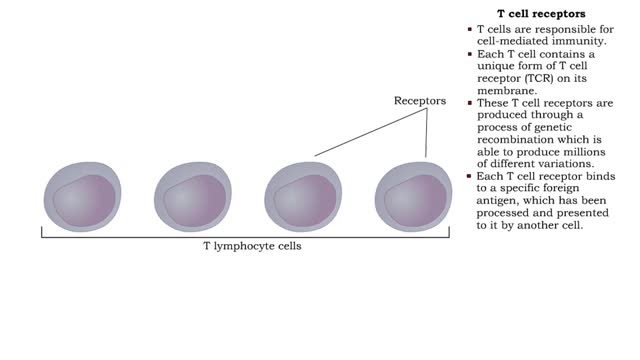
• T cells are responsible for cell-mediated immunity. • Each T cell contains a unique form of T cell receptor (TCR) on its membrane. • These T cell receptors are produced through a process of genetic recombination which is able to produce millions of different variations. • Each T ce...
Advertisement